Videos
Browse videos by topic
All Videos
Showing 1129-1152 of 1435 videos

NNIT Webinar: IDMP enforcement in Europe in 2021
NNIT | We make a mark
/@NNITvideo
Jan 25, 2021
This video provides a critical update on the European Medicines Agency's (EMA) Identification of Medicinal Products (IDMP) initiative, focusing on its enforcement timelines and the latest developments in the implementation guide. The speakers, regulatory affairs experts from NNIT, detail the expected publication of IDMP Implementation Guide Version 2 on February 22, 2021, which sets the mandatory go-live date for PMS (Product Management System) Iteration 1 fields for the industry by February 22, 2023. The discussion highlights the significant impact on regulatory affairs, the need for comprehensive data management and quality, and the ongoing evolution of EMA's approach to IDMP, including an agile documentation strategy and updates on substance data management. Key Takeaways: * **Imminent IDMP Enforcement:** The EMA has set a concrete timeline for IDMP enforcement, with PMS Iteration 1 becoming mandatory for industry by February 22, 2023, following the publication of Implementation Guide Version 2. This signals a definitive move towards compliance after years of delays. * **"One Side IDMP, Always IDMP" Mandate:** An unofficially confirmed but critical rule states that once a company submits IDMP information for one product, all other products in its portfolio must subsequently follow suit. This eliminates the possibility of small-scale pilots and necessitates a comprehensive, portfolio-wide IDMP strategy from the outset. * **Holistic Data & Process Transformation:** IDMP compliance extends beyond IT systems, requiring significant organizational effort in locating and ensuring the quality of required data, as well as fundamental changes to business processes across regulatory, commercial, and potentially clinical operations. * **Evolving Substance Data Management:** The EMA is actively cleansing and synchronizing substance data through its EU SRS and SMS projects, with a focus on aligning with the FDA's GSRS. This indicates a push towards greater international harmonization in substance identification and management. * **Limitations of Standard RIM Systems:** While many Regulatory Information Management (RIM) system providers are incorporating IDMP roadmaps, their solutions primarily address data model expansion and basic functionality. They often do not cover critical aspects like comprehensive data quality monitoring, integration with other enterprise systems, or the necessary adjustments to overall submission processes, highlighting the need for broader data engineering and process re-design efforts. * **Strategic Industry Preparation is Crucial:** Companies must proactively prepare by staying updated on regulatory changes, mapping substances and referentials, and raising internal awareness. It's essential to plan for all product types (centralized, mutual recognition, decentralized, and national procedures) from the beginning, rather than focusing solely on centralized products.

Arriello Modernizes Pharmacovigilance with Veeva Vault Safety
Veeva Systems Inc
/@VeevaSystems
Jan 25, 2021
This video provides an overview of how Arriello, a leading provider of pharmacovigilance (PV) and regulatory affairs services since 2008, successfully implemented and utilized Veeva Vault Safety to modernize its operations. Ivan Mihalic, the Pharmacovigilance Safety System Manager at Arriello, shares his 12 years of experience in the IT industry and details the strategic advantages the platform offers to a service provider operating within the highly regulated life sciences sector. The core purpose of the implementation was to leverage a comprehensive, modern system that could support high-volume PV activities, manage regulatory connectivity, and facilitate rapid client expansion. The adoption of Veeva Vault Safety yielded several critical operational benefits for Arriello. Foremost among these is the ability to utilize powerful reporting capabilities directly integrated within the safety database, streamlining the process of data analysis and insight generation. Furthermore, the system provides a crucial gateway connection, enabling seamless communication and data exchange with regulatory authorities and various partners. This regulatory connectivity is essential for maintaining compliance and timely submission of safety data. For a service provider like Arriello, the platform’s capacity to efficiently onboard new clients is a significant competitive advantage, supported by powerful features that enhance daily PV activities. Mihalic characterizes Veeva Vault Safety as a modular web solution, highlighting its dual strengths: robust functionality combined with high flexibility regarding customization possibilities. This balance allows Arriello to tailor the system to specific client needs while relying on a standardized, powerful core. A notable achievement mentioned was the short implementation timeline, demonstrating the platform's readiness for rapid deployment. Crucially, the speaker emphasizes the value of Veeva’s structured release management process. This process provides detailed guidance before each new software update, which simplifies the application of new features for clients like Arriello and, most importantly, helps ensure the system remains in a "valid" state—a critical requirement for GxP and regulatory compliance in pharmacovigilance. Key Takeaways: • **Integrated Reporting Capabilities:** Veeva Vault Safety provides direct access to powerful reporting features within the safety database itself, eliminating the need for complex external data extraction and integration for routine PV analysis and submissions. • **Streamlined Regulatory Connectivity:** The platform includes a built-in gateway connection designed to facilitate efficient and compliant data exchange with regulatory authorities (e.g., FDA, EMA) and external partners, ensuring timely safety reporting. • **Competitive Advantage in Client Onboarding:** For CROs and service providers like Arriello, the system's powerful features and architecture support the rapid and efficient onboarding of new clients, allowing for scalable growth and faster time-to-service delivery. • **Balance of Power and Flexibility:** Vault Safety is described as a modular web solution that offers robust, powerful functionalities while retaining significant flexibility for customization, allowing organizations to adapt the system to unique operational or client requirements. • **Accelerated Implementation Timeline:** Arriello experienced a "really short" implementation timeline, suggesting that the standardized nature of the Vault platform can significantly reduce deployment time compared to traditional, highly customized legacy safety systems. • **Maintaining System Validity (Compliance Focus):** The structured Veeva release management process is vital for regulatory compliance, providing detailed guidance that helps clients apply new software updates while ensuring the system maintains its validated state (critical for 21 CFR Part 11 and GxP environments). • **Strategic Value for PV Service Providers:** The system’s capabilities—especially in reporting, regulatory connectivity, and quick client onboarding—make it an ideal foundational technology for companies specializing in outsourced pharmacovigilance and regulatory affairs services. • **Focus on Daily Activity Support:** The platform is designed to offer powerful features that directly support and optimize the daily operational activities of pharmacovigilance teams, leading to increased efficiency and accuracy in case processing. Tools/Resources Mentioned: * **Veeva Vault Safety:** The core pharmacovigilance safety database and management platform discussed. * **Veeva Release Management:** The structured process provided by Veeva for guiding clients through software updates to ensure system validity and compliance. Key Concepts: * **Pharmacovigilance (PV):** The science and activities relating to the detection, assessment, understanding, and prevention of adverse effects or any other drug-related problem. * **Regulatory Affairs:** The function responsible for ensuring that a company’s products comply with the regulations and laws of the regions where they are marketed. * **System Validity:** In the context of regulated life sciences software (GxP), this refers to the state where a computerized system is documented, tested, and maintained to ensure it performs consistently and reliably according to its intended specifications and regulatory requirements.

Webinar Preview: Bring Your Own Content (BYOC) - Life Sciences Training Reimagined
Veeva Systems Inc
/@VeevaSystems
Jan 22, 2021
This webinar preview outlines a strategic shift in how life sciences companies manage mandatory employee training and regulatory compliance: the "Bring Your Own Content" (BYOC) approach. The core premise is that the traditional model—where companies purchase a Learning Management System (LMS) bundled with content libraries from a single vendor—is outdated, inefficient, and hinders compliance efforts. This legacy approach often results in companies feeling "stuck" with stand-alone LMS systems, leading to costly integrations and fragmented data management. The BYOC methodology advocates for the separation of the training delivery solution (the LMS technology) from the selection of content libraries. This allows organizations to select "best-in-breed" solutions for both components, maximizing value and flexibility. The primary benefit highlighted is the ability to unify and connect training activities directly with quality documents and quality events within a single system, such as Veeva Vault Training. This unification is crucial for the pharmaceutical sector, as it automates training assignments based on changes to standard operating procedures (SOPs) or quality incidents, thereby dramatically improving regulatory compliance and audit readiness. The discussion, led by Kent Malmuro of Veeva Systems and John Constantine of Orchestral, aims to provide practical guidance on implementing BYOC. It addresses how companies can determine their priorities when making this separation and details best practices for ensuring the seamless deployment of a new LMS alongside third-party content libraries. The underlying technical enablers for this separation are established eLearning standards like SCORM and AICC, which ensure content portability across different learning management systems. Ultimately, the BYOC approach is presented as a necessary evolution to ensure that employees are consistently qualified and prepared for their roles in a rapidly changing business environment, moving beyond mere convenience toward efficiency and effectiveness in compliance training. Key Takeaways: * **The BYOC Mandate:** The Bring Your Own Content (BYOC) approach is necessary for modern life sciences companies to move away from legacy, bundled LMS systems that lead to high integration costs and compliance bottlenecks. * **Decoupling Technology and Content:** The core strategy involves separating the selection of the LMS (the training delivery solution) from the selection of third-party content libraries, allowing companies to choose best-in-breed options for each. * **Compliance Automation through Unification:** A major benefit of adopting a modern, unified system (like Veeva Vault Training) is the ability to connect training records directly with quality documents and quality events, automating training assignments when SOPs change or incidents occur. * **Improving Audit Readiness:** Automating training assignment and tracking based on quality system changes ensures that employees are always qualified and prepared, significantly improving GxP compliance and streamlining regulatory audits. * **Leveraging Portability Standards:** The BYOC approach is technically feasible due to established eLearning standards, specifically SCORM and AICC, which ensure that training content can be easily moved and deployed across different learning management platforms. * **Strategic Prioritization:** Companies must determine whether their priority lies in selecting the most robust training delivery technology (LMS) or the most comprehensive content libraries, recognizing that the BYOC model allows for excellence in both. * **Targeting Quality and Compliance Leaders:** The insights are specifically tailored for Directors and VPs of Quality Training, Compliance, QA/QC, and Clinical Operations, addressing their pain points regarding system integration and training effectiveness. * **Efficiency Over Convenience:** While buying an LMS and content from a single vendor was traditionally convenient, the current regulatory and business environment demands an approach focused on efficiency, effectiveness, and regulatory adherence, which BYOC facilitates. * **Seamless Deployment Practices:** The webinar promises to cover best practices for deploying a new LMS and integrating external content libraries to ensure a smooth transition and rapid time-to-value without disrupting ongoing operations. Tools/Resources Mentioned: * **Veeva Systems:** Specifically Veeva Vault Training, positioned as a best-in-breed LMS technology solution for the life sciences industry. * **SCORM (Sharable Content Object Reference Model):** An established set of technical standards for eLearning software that allows content to be portable across different LMS platforms. * **AICC (Aviation Industry CBT Committee):** Another set of standards ensuring content portability between learning management systems. Key Concepts: * **Bring Your Own Content (BYOC):** A strategic framework suggesting that organizations should select their LMS technology independently of their content library provider to achieve maximum flexibility, integration, and compliance effectiveness. * **Unifying Training and Quality:** The concept of integrating the training management system directly with the quality management system (QMS) to automate mandatory training assignments based on updates to quality documents (e.g., SOPs) or the occurrence of quality events.
Technologies that improve site, sponsor and CRO execution of studies by Veeva Systems
SCDM - Society for Clinical Data Management
/@SCDMchannel
Jan 20, 2021
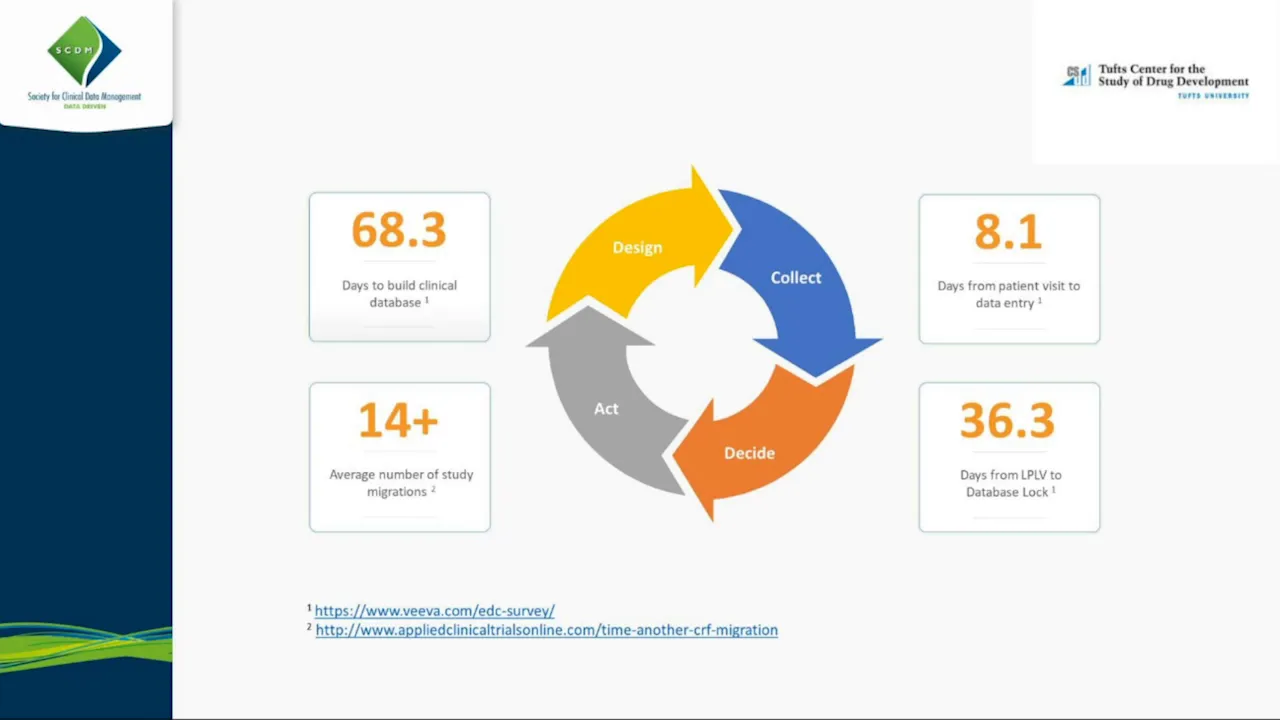
This presentation, delivered by Veeva Systems representatives, explores the critical role of technology and philosophical shifts in optimizing the execution of clinical trials for sites, sponsors, and CROs, with a strong emphasis on adapting to increasing trial complexity and the accelerated virtualization driven by the COVID-19 pandemic. The core message is that technology must evolve from being a limiting factor to providing flexible, future-proof foundations that support adaptive trials and decentralized models. The speakers highlight that the average database build time (nearly 70 working days) and the resulting delays in data entry and database lock are unacceptable, especially given that studies not ready before First Patient First Visit (FPFV) experience significantly worse outcomes. To address these inefficiencies, Veeva advocates for five principles of agile design: standards and reuse, fusing design and specification, configuration over custom programming, collaborative User Acceptance Testing (UAT), and simplified amendments. The goal is to reduce database build times to four to six weeks, or even days for urgent needs like COVID-19 trials. The methodology involves moving away from traditional waterfall processes, where specifications are written offline and then programmed, toward a visual, self-documenting build environment (Veeva Studio). This allows study teams to build and review the system iteratively, eliminating the lengthy "ping-pong" cycle of testing and fixing, and enabling real-time, collaborative UAT. The presentation provides concrete examples of simplification, such as using reusable event groups and a powerful, configurable rules engine to manage complex protocols. For instance, an oncology trial with 32 cycles was reduced to two reusable groups by using dynamics to conditionally add forms and events based on patient criteria, minimizing programming effort. Furthermore, the speakers discuss the importance of the "Diff Report," a tool that compares study versions or standards, enabling teams to adopt a risk-based approach to UAT by focusing testing efforts only on the elements that have changed. This focus on architectural flexibility also allowed Veeva to rapidly deploy configurable objects, such as a "COVID-19 reason" field, across existing studies to document missed procedures without requiring system downtime or custom code migration. Key Takeaways: * **Prioritize Database Readiness for FPFV:** Studies where the database is not ready before FPFV experience significantly longer data entry times (doubling) and database lock times (increasing by 60%), underscoring the necessity of reducing average build times from 70 days to four to six weeks. * **Adopt Configuration for Complexity:** Utilize a robust rules engine to handle complex study logic (e.g., dynamic form display, conditional event addition) through configuration rather than custom programming (C# or Java), which introduces rigidity, delays, and risk during subsequent protocol amendments. * **Simplify Protocol Amendments:** Technology must support simplified amendments that do not require full database migrations or system downtime. Changes should be applied prospectively (for new patients) or retrospectively (for existing patients) by simply appending the new design version to the existing data structure, eliminating data loss risk. * **Implement Risk-Based UAT:** Leverage automated differential reporting tools to compare study designs against standards or prior versions. This allows UAT efforts to be focused solely on the components that have changed, drastically accelerating the testing and approval cycle. * **Leverage Standards for Speed:** Aggressively utilize reusable components (forms, items, event groups) and industry-standard templates (e.g., those based on FDA guidance for COVID-19) to accelerate study builds, enabling rapid deployment in days rather than weeks. * **Foundational Architecture Enables Agility:** Ensure the underlying technology architecture is flexible and extendable, allowing for the swift introduction of new features (like COVID-19 data fields or decentralized trial capabilities) as configurable objects without requiring extensive custom development or system downtime. * **Empower Sites with Dedicated Technology:** Provide sites with free, purpose-built tools, such as an e-reg binder (SiteVault), to improve site engagement, standardize document management, and facilitate remote Source Data Verification (SDV), a critical need during decentralized operations. * **Fuse Design and Specification:** Move the specification process into the visual build environment (Studio) so that documentation is self-generated as the system is built. This eliminates the lengthy, sequential waterfall process of writing, programming, and then testing specifications. * **Ensure Data and Document Connectivity:** The foundational architecture must support seamless Clinical Data Exchange, ensuring real-time visibility and sharing of both data (EDC) and documents (eTMF, e-reg binder) across sponsors, CROs, and sites. #### Tools/Resources Mentioned * **Veeva Vault EDC/CDMS:** The core clinical data management system. * **Veeva Vault Studio:** The visual, self-documenting build environment for EDC design. * **Veeva Vault SiteVault:** A free e-reg binder and document management solution for clinical sites. * **Diff Report (Differences Report):** A tool used to compare study versions or standards to identify changes for focused UAT. #### Key Concepts * **Agile Design Principles:** A methodology for EDC build emphasizing iterative development, collaboration, configuration, and continuous review. * **Self-Documenting Specification:** The process where building the study design in the system automatically generates the necessary specification documentation. * **Clinical Data Exchange:** An architectural concept promoting seamless sharing of data and documents across all stakeholders in a clinical trial.

Veeva Systems CEO on powering Covid-19 treatments, pharma partnerships
CNBC Television
/@CNBCtelevision
Jan 14, 2021
This video features Peter Gassner, CEO and founder of Veeva Systems, discussing his company's pivotal role in supporting the life sciences industry, particularly in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic. The interview, conducted by CNBC's "Squawk on the Street" team, delves into how Veeva's technology bridges operational gaps and enhances efficiency for pharmaceutical companies, from drug development to manufacturing and distribution. Gassner provides a comprehensive overview of Veeva's contributions to accelerating the delivery of critical treatments and vaccines, highlighting the industry's rapid response and the underlying technological infrastructure. Gassner elaborates on the specific ways Veeva's technology empowers life sciences companies. He explains that Veeva provides solutions for designing and operating clinical trials, collecting and analyzing patient data, and monitoring manufacturing controls. This includes ensuring that production processes are compliant and safe, which is paramount in the highly regulated pharmaceutical sector. The CEO emphasizes that their technology is instrumental in helping companies become more efficient and effective, ultimately speeding up the process of bringing essential medicines and therapeutics to market. The discussion frequently circles back to the unprecedented speed at which the life sciences industry developed COVID-19 vaccines, attributing part of this success to cloud technology and the dedication of their customers. A significant portion of the conversation is dedicated to the broader impact of Veeva's work on productivity, efficiency, and cost reduction within the pharmaceutical industry. Gassner underscores that cloud technology enables companies to streamline operations, reduce costs, and accelerate timelines, which was particularly critical during the pandemic. He expresses immense pride in the life sciences industry's performance, giving it an "A" grade for its rapid innovation and deployment of vaccines, noting that such speed was previously unimaginable. He also points out that long-term investments in technologies like RNA, made years ago, are now paying off dramatically. The interview concludes with a discussion of Veeva's recent conversion to a Public Benefit Corporation (PBC), a move that legally obligates the company to consider the interests of its customers, employees, and society alongside shareholders, signaling a shift towards a more inclusive form of capitalism. Key Takeaways: * Veeva Systems' core mission is to serve the life sciences industry by providing technology that significantly enhances efficiency and effectiveness in the development and distribution of medicines and therapeutics. * The company's technology supports critical stages of drug development, including the design and operation of clinical trials, the collection and analysis of patient data, and the rigorous monitoring of manufacturing controls. * A key focus of Veeva's solutions is ensuring regulatory compliance and safety throughout the entire manufacturing process, which is vital for pharmaceutical and biotech companies. * Cloud technology is highlighted as a fundamental enabler for achieving greater efficiency and speed, particularly in accelerating the development and market entry of new treatments like COVID-19 vaccines. * The life sciences industry demonstrated an unprecedented level of speed and productivity during the pandemic, a success partially attributed to the availability of advanced technology and significant prior investments in areas such as RNA technology. * Veeva Systems recently made history by becoming the first public company to convert to a Public Benefit Corporation (PBC), following an overwhelming shareholder vote of over 99% in favor. * This PBC conversion legally expands Veeva's corporate responsibility beyond just financial returns for shareholders to include a broader commitment to customers, employees, and society in general. * The move to a PBC signifies a strategic shift towards a new model of capitalism that integrates social and environmental considerations alongside traditional financial objectives, aligning with the growing trend of ESG investing. * The CEO expresses strong confidence and pride in the life sciences industry's ability to innovate rapidly and deliver critical solutions under immense pressure, despite the inherent challenges in vaccine distribution. * The discussion underscores the ongoing and accelerating digitization of the pharmaceutical sector, where technology plays an increasingly crucial role in bridging operational gaps, optimizing processes, and improving overall outcomes. Key Concepts: * **Public Benefit Corporation (PBC):** A type of for-profit corporate entity, authorized in many U.S. states, that includes positive impact on society and the environment in addition to profit as its legally defined goals. * **ESG Investing:** Environmental, Social, and Governance investing, a framework used to evaluate corporate performance and ethical impact beyond traditional financial metrics. * **Digitization of Life Sciences:** The ongoing transformation of pharmaceutical and biotech operations through the adoption of digital technologies to improve efficiency, data management, and regulatory compliance. * **Clinical Trials:** Research studies conducted on human volunteers to evaluate the safety and efficacy of new drugs, medical devices, or treatments. * **Manufacturing Controls:** Systems and procedures implemented in pharmaceutical manufacturing to ensure product quality, consistency, and compliance with regulatory standards. Examples/Case Studies: * **COVID-19 Vaccine and Treatment Development:** The video frequently references the rapid development and distribution of COVID-19 vaccines and treatments as a prime example of the life sciences industry's efficiency and the role of technology. * **RNA Technology Investment:** Peter Gassner specifically mentions the significant investments made in RNA technology six to ten years prior, which proved crucial in enabling the rapid development of mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccines.

2021-01-11 TMF Reference Model General Meeting
TMF Reference Model
/@TMFReferenceModel
Jan 12, 2021
This video provides an in-depth exploration of the TMF Reference Model, detailing its history, current status, and future initiatives as presented during its first general meeting of 2021. The session, led by Karen Roy, co-chair of the reference model and chair of the steering committee, aimed to refresh attendees on the model's purpose and evolution, while also soliciting community feedback on potential improvements and new directions. Key discussions revolved around standardizing Trial Master File (TMF) content, structure, naming conventions, and metadata to enhance collaboration, streamline regulatory inspections, and improve overall operational efficiency within clinical trials. The presentation delved into the foundational aspects of the TMF Reference Model, which originated in 2009 from a DIA EDM reference model initiative to standardize TMF structures across the industry. It highlighted the significant growth of the model, now managed by a formal Charter, a 14-member Steering Committee, and a Change Control Board responsible for version control and incorporating community feedback. The benefits of adopting a standardized TMF structure were emphasized, particularly for sponsors and Contract Research Organizations (CROs) working together, as well as for regulatory inspectors who are increasingly familiar with the model. The discussion also touched upon the practicalities of implementing the model, including strategies for transitioning from company-specific structures and the role of vendors in supporting different versions. A significant portion of the meeting was dedicated to reviewing existing deliverables and proposing areas for refresh and new initiatives. Current deliverables include guidance on email communication, a real-world study document index, and a TMF plan template. Three key documents identified for potential revision were TMF Quality Control, Inspection Readiness (including RACI and FAQs), and TMF Metrics, with a strong emphasis on updating them to reflect advancements like ICH GCP R2/R3, the rise of virtual inspections, and the integration of artificial intelligence into TMF systems. The active initiative on the TMF Exchange Mechanism was also presented, outlining its role as a technical standard using APIs, the TMF Reference Model coding, and XML to facilitate efficient, quality-preserving transfer of TMF information between collaborators. Future initiatives, driven by community surveys, included developing a formal training course, expanding coverage to all study types, bridging clinical and regulatory documentation, and establishing a definitive set of minimal metadata per artifact. Key Takeaways: * **Standardization is Crucial for TMF Management:** The TMF Reference Model's primary purpose is to standardize TMF content, structure, naming, and minimal metadata, which is essential for consistent documentation across the pharmaceutical and life sciences industries. * **Enhanced Collaboration and Regulatory Compliance:** Adopting the TMF Reference Model significantly improves collaboration between sponsors and CROs by providing a common framework. It also aids regulatory inspections, as inspectors are increasingly familiar with the standardized structure, reducing queries and streamlining audits. * **Structured Governance and Continuous Improvement:** The TMF Reference Model is managed by a formal Charter, a diverse Steering Committee, and a Change Control Board, ensuring its ongoing relevance, controlled version releases (maintenance, minor, major), and responsiveness to industry feedback. * **Strategic Implementation of TMF Model Updates:** Organizations should take a risk-based approach when updating their TMF systems from one minor version to another (e.g., 3.1 to 3.2), considering the relevance of changes to their operations. Major releases (e.g., to 4.0) may warrant a more comprehensive re-evaluation. * **Vendor Support for TMF Versions:** The industry sees a mixed approach from vendors regarding support for multiple TMF Reference Model versions, with some systems accommodating different versions for different studies, while others facilitate migration. * **Key Deliverables and Their Refresh Needs:** Existing deliverables like Email Communication Guidance, Real World Study Document Index, and TMF Plan Template are valuable. However, documents on TMF Quality Control, Inspection Readiness, and TMF Metrics require updates to incorporate ICH GCP R2/R3, new technologies, virtual inspection protocols, and the impact of AI. * **The TMF Exchange Mechanism for Data Integrity:** This technical standard facilitates the efficient and quality-preserving transfer of TMF information between collaborators (sponsors, CROs, sites, labs). It leverages APIs, the TMF Reference Model's common language (coding), and XML as a shared protocol to ensure "quality by design" and reduce re-checking efforts. * **Impact of AI on TMF Operations:** The integration of artificial intelligence into TMF systems is a growing area, with implications for TMF metrics (e.g., measuring AI effectiveness/accuracy) and the need to adapt SOPs for AI coding, which will interact with inspection readiness and QC standards. * **Community-Driven Future Initiatives:** The TMF Reference Model actively seeks community input for future initiatives. Top priorities identified include developing a formal TMF Reference Model training course and exploring comprehensive coverage for all study types, including early phase and digital solutions/wearable devices. * **Bridging Clinical and Regulatory Documentation:** A recognized need exists to better integrate clinical and regulatory documentation, specifically addressing the overlap between TMF content and CTA (Clinical Trial Application) submission documents, especially with evolving European regulations. * **Importance of Metadata Standardization:** There is a recognized need to establish a more definitive set of minimal metadata per artifact within the TMF Reference Model to enhance data consistency and utility. * **Effective Communication and Engagement:** The TMF Reference Model encourages participation through its website (tmfr model.com), mailing list, forums for questions and feedback, and a LinkedIn group, emphasizing the importance of whitelisting their email for updates. **Tools/Resources Mentioned:** * **TMF Reference Model Website:** www.tmfr model.com (for resources, forums, joining mailing list, downloading documents) * **TMF Exchange Mechanism:** An XML-based technical standard for TMF data transfer, utilizing APIs and TMF Reference Model coding. * **LinkedIn Group:** A platform for community engagement and updates. **Key Concepts:** * **TMF (Trial Master File):** A collection of essential documents that individually and collectively permit the evaluation of the conduct of a clinical trial and the quality of the data produced. * **TMF Reference Model:** A standardized, hierarchical model for organizing TMF documents, providing a common structure, naming conventions, and minimal metadata. * **eTMF (Electronic Trial Master File):** A TMF managed electronically, often through specialized software systems. * **ICH GCP (International Conference on Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use – Good Clinical Practice):** An international ethical and scientific quality standard for designing, conducting, recording, and reporting trials that involve the participation of human subjects. R2 and R3 refer to different revisions of these guidelines. * **Inspection Readiness:** The state of being prepared for regulatory inspections, ensuring all TMF documents are complete, accurate, and readily accessible. * **TMF Quality Control (QC):** Processes and procedures implemented to ensure the quality, completeness, and accuracy of TMF documents. * **TMF Metrics:** Quantitative measures used to assess the performance, completeness, and efficiency of TMF management processes. * **TMF Exchange Mechanism:** A technical standard designed to facilitate the secure and efficient transfer of TMF documents and associated metadata between different systems and organizations, preserving data quality. * **Sponsor:** The individual, company, institution, or organization that takes responsibility for the initiation, management, and/or financing of a clinical trial. * **CRO (Contract Research Organization):** An organization that provides support to the pharmaceutical, biotechnology, and medical device industries in the form of research services outsourced on a contract basis. * **Investigator Site File (ISF):** The collection of essential documents maintained by the investigator at the clinical trial site. * **Metadata:** Data that provides information about other data; in the TMF context, it describes characteristics of TMF documents (e.g., date, author, version). * **AI in TMF:** The application of artificial intelligence technologies to automate, optimize, and enhance various aspects of TMF management, such as document classification, quality control, and data analysis.

GSK: Preparing Business for Study Start-up Change - Overview
Veeva Systems Inc
@VeevaSystems
Jan 12, 2021
This video provides an in-depth overview of GSK’s comprehensive "unified technology journey," specifically detailing their transformation efforts within Clinical Operations using the Veeva Clinical Vault program. The primary goal of this initiative was to consolidate disparate clinical operations and technology solutions under a single umbrella to maximize value, drive efficiency, and achieve industry-leading study start-up (SSU) timelines. GSK structured this major business change around three core pillars: People, Process, and Technology, emphasizing that success requires balancing all three, rather than favoring one over the others. The presentation highlights the critical need for this transformation, noting that GSK was previously trailing industry benchmarks in study start-up timelines due to siloed systems and reliance on manual processes, such as Excel trackers. The transformation strategy focused heavily on improving the user experience for clinical operations staff. From a "People" perspective, the initiative aimed to build staff capabilities and ensure talented employees spent time on high-value activities instead of navigating non-integrated systems. This was supported by the introduction of a global study start-up team tasked with challenging conventional decisions, leveraging data, and enabling the necessary cultural shift toward metrics-driven performance. On the "Process" front, the Clinical Vault implementation served as a catalyst to standardize ways of working across different business units and study phases. By starting with a "blank sheet of paper," GSK aligned processes based on regulatory requirements rather than historic, siloed practices, simplifying workflows to work seamlessly with the new technology. Technologically, the shift involved creating a unified clinical ecosystem with a single entry point for workflows, providing staff with a complete view of operations. This unified approach not only improved the user experience but also enabled integrated reporting, which was crucial for improving data quality and driving data-driven decisions—a key ambition for the organization. Specifically within Veeva SSU, the integration of systems and simplification of processes allowed GSK to achieve industry-leading timelines for some priority studies, significantly accelerating the journey from Final Protocol Approval (FPA) to First Subject First Visit (FSFV). The presentation concludes by emphasizing the strategic necessity of a cross-Vault mindset, moving away from managing singular applications toward viewing the entire Veeva ecosystem as interconnected. Furthermore, the success of the transformation hinged on robust change management, requiring dedicated time and resources to address changes in systems, culture, and mindset. This involved engaging end-users early, identifying change champions, and building a system that inherently suits user needs to maximize adoption upon go-live. ### Key Takeaways * **Balanced Transformation Framework:** Major business change, such as optimizing study start-up, must be driven by a balanced focus on People, Process, and Technology; favoring one pillar over the others will undermine the effectiveness of the transformation. * **User Experience is Paramount:** Improving the user experience for clinical operations staff is critical for efficiency gains. The goal is to ensure talented staff spend time on activities that truly matter, eliminating the need to revert to manual tools like Excel trackers due to poor system integration. * **Technology as a Catalyst for Process Change:** The implementation of a unified technology platform (Veeva Clinical Vault) should be used as a catalyst to challenge and standardize historic ways of working, aligning processes across business units based on current regulatory requirements rather than past practices. * **Shift to Data-Driven Decision Making:** The unified clinical ecosystem enables integrated reporting and improved data quality, which is essential for moving toward much more data-driven decisions in clinical operations and SSU. * **Organizational Enablement is Required:** GSK introduced a global study start-up team to sit on central teams, helping to drive alignment, challenge decisions based on metrics, and enable the cultural shift required to move from "safe timelines" to ambitious, industry-leading performance goals. * **Focus on Regulatory Requirements:** When simplifying processes, organizations should start with a blank sheet of paper and focus on what regulators actually require, rather than replicating complex, historic, and often siloed business unit-specific workflows. * **Cross-Vault Strategy is Essential:** Organizations must adopt a cross-Vault mindset, understanding how decisions made in one application (e.g., SSU) impact and require buy-in from other applications within the larger Veeva ecosystem. * **Agile Decision-Making Structure:** The transformation team needs to be structured to drive alignment while remaining lean and agile, enabling quick decisions regarding system configuration and business change enablement. * **Measure FPA to FSFV:** A key metric for success in SSU is the speed of turnaround between Final Protocol Approval (FPA) and First Subject First Visit (FSFV); GSK is now seeing industry-leading timelines for priority studies through this combination of factors. * **Prioritize Change Management:** Dedicating sufficient time and resources to change management is non-negotiable for success. This includes involving end-users and change champions from the start to build a system that meets their needs and increases adoption rates immediately upon go-live. ### Tools/Resources Mentioned * Veeva Clinical Vault * Veeva SSU (Study Start-Up) ### Key Concepts * **Unified Technology Journey:** A strategic initiative to bring together multiple clinical operations and technology solutions under a single, integrated platform (like Clinical Vault) to maximize value and efficiency. * **Study Start-Up (SSU):** The critical phase in clinical trials encompassing activities between final protocol approval and the first subject being enrolled (First Subject First Visit - FSFV). * **Cross-Vault Mindset:** A strategic approach to managing the Veeva ecosystem where changes and decisions are considered across all integrated Vault applications, rather than treating each application in isolation.

Nutrien's Commitment to Safety | ETQ
ETQ Reliance: Leading Quality Management System
/@ETQReliance
Jan 7, 2021
This video details Nutrien's strategic implementation of ETQ Reliance as its core platform for safety, health, and environment (SHE) management, following the company's formation in 2008 from the merger of Agrium and Potash Corp. The speaker, whose role was to evaluate all existing SHE software, describes the objective of identifying the "best of both companies" to establish a unified and robust safety culture. Nutrien's safety ethos is deeply rooted in a commitment to ensuring every worker gets "home safe every day," a principle they strive to tie back to their customers and overall company purpose. The evaluation process involved a thorough market analysis alongside leveraging prior knowledge of ETQ Reliance from one of the legacy companies. The platform was ultimately chosen for its proven capabilities and inherent flexibility, which were deemed critical for adapting to Nutrien's diverse and constantly growing global operations. The company successfully rolled out the platform across its North American legacy organization within a year, followed by global implementation in the subsequent year. This rapid deployment underscored the platform's adaptability to various business units and regulatory environments, a key factor in its success. The speaker emphasizes the inspiring nature of playing a part in such a critical initiative, highlighting the personal satisfaction derived from contributing to a culture where employee safety is paramount. The video effectively showcases how a large, complex organization can centralize and standardize its safety and environmental management processes through a flexible enterprise software solution. It illustrates the journey from a post-merger integration challenge to establishing a cohesive, scalable system that supports a fundamental corporate value: the well-being of its employees. Key Takeaways: * **Strategic Post-Merger Software Evaluation:** Following a significant merger, it is critical to conduct a comprehensive evaluation of existing software solutions across all operational areas, particularly for critical functions like safety, health, and environment (SHE), to identify the best-in-class tools and consolidate efforts. * **Culture-Driven Technology Adoption:** Nutrien's decision to implement ETQ Reliance was heavily influenced by its deeply ingrained safety culture, centered on the principle of "home safe every day." Aligning technology solutions with core company values can drive higher adoption and more effective outcomes. * **Importance of Platform Flexibility and Scalability:** The selection of ETQ Reliance was based on its known capabilities and flexibility, which proved essential for a global company with diverse business units and continuous growth. Enterprise software must be adaptable to evolving organizational structures and operational needs. * **Centralized SHE Management:** Implementing a single, core platform for "all things safety health and environment" provides a unified approach to managing critical risks, ensuring consistency in processes, and streamlining compliance across a large, distributed organization. * **Rapid Global Deployment Strategy:** Nutrien successfully deployed the platform across its North American operations in one year and globally in the next, demonstrating that rapid, phased rollouts are achievable with a flexible system and strong project management. * **Leveraging Prior Knowledge and Market Analysis:** The decision-making process combined internal knowledge of ETQ Reliance from a legacy company with external market analysis, ensuring both a proven track record and a best-fit solution were considered. * **Employee Engagement through Safety Initiatives:** The speaker's personal inspiration from contributing to employee safety highlights how robust safety programs, supported by effective technology, can foster a positive and committed work environment. * **Continuous Adaptation for Growth:** The world and the company are constantly growing, necessitating a SHE platform that can continuously adjust to new businesses, regulations, and operational complexities without slowing down critical safety processes. * **Integration for Comprehensive Compliance:** While not explicitly detailed in the transcript, the description of ETQ Reliance as a "Quality, EHS, Food Safety and Compliance management software" implies its role in integrating various compliance aspects, crucial for regulated industries. * **Proactive Risk Mitigation:** The use of a leading quality management system for identifying, mitigating, and preventing high-risk events through integration, automation, and collaboration is a best practice for maintaining operational excellence and regulatory adherence. Tools/Resources Mentioned: * **ETQ Reliance:** A leading Quality Management System (QMS) and EHS (Environmental, Health, and Safety) management software used by Nutrien as its core platform for safety, health, and environment. Key Concepts: * **Safety Culture:** The shared attitudes, beliefs, perceptions, and values that employees share in relation to safety. Nutrien's culture is based on "commitment" and the goal of "home safe every day." * **SHE (Safety, Health, and Environment) Management:** A systematic approach to managing risks related to occupational safety, employee health, and environmental protection within an organization. * **Quality Management System (QMS):** A formalized system that documents processes, procedures, and responsibilities for achieving quality policies and objectives. In this context, it extends to safety and compliance. * **Enterprise Application Integration (EAI):** The process of connecting disparate applications within an organization to allow them to share data and business processes, crucial for a comprehensive platform like ETQ Reliance. Examples/Case Studies: * **Nutrien's ETQ Reliance Implementation:** A real-world example of a global agriculture company (formed from the merger of Agrium and Potash Corp. in 2008, with over 22,000 employees) successfully deploying a comprehensive SHE management system across its worldwide operations within two years.

Cloud-provider Veeva Systems CEO on supporting vaccine, drug development processes
CNBC Television
/@CNBCtelevision
Dec 22, 2020
This video provides an in-depth exploration of how Veeva Systems, an "industry cloud for life sciences," is driving the digitization of pharmaceutical and biotech companies, particularly in the context of vaccine and drug development. Peter Gassner, CEO of Veeva Systems, discusses with Jim Cramer the critical role of cloud software in accelerating the entire lifecycle of medicines, from clinical trials to commercialization and regulatory adherence. The conversation highlights the ongoing shift from traditional paper-based processes to digital solutions, emphasizing efficiency, compliance, and the long-term growth trajectory of the life sciences sector. Gassner elaborates on Veeva's comprehensive platform, which includes over 30 applications designed to support various stages of drug development and delivery. He cites prominent customers like Moderna, Pfizer, and Glaxo, underscoring Veeva's direct contribution to speeding up the end of the pandemic through its technology. A key theme is the significant, yet still early, transition from manual, paper-heavy operations, especially in large-scale clinical trials. Gassner projects a substantial reduction in paper usage in clinical development within a few years, reinforcing the idea that digitization is a future-proof trend for the two-trillion-dollar life sciences industry, independent of the immediate pandemic-driven demand. The discussion also delves into the evolving landscape of commercial operations and regulatory compliance within the pharmaceutical industry. Gassner acknowledges a potential shrinkage in sales forces (around 10%) due to increased efficiency driven by digital tools. He positions Veeva as a technology and data provider that enables this shift, supporting remote engagement with doctors through specialized, compliant software for activities like virtual meetings and digital sample signing. Furthermore, the interview touches on critical aspects such as cybersecurity vigilance against state-sponsored threats and the company's readiness to partner with administrations to navigate evolving regulatory environments, aiming to make healthcare more efficient and potentially less expensive through digitization. Key Takeaways: * **Veeva as the Industry Cloud:** Veeva Systems positions itself as the specialized "industry cloud for life sciences," offering a comprehensive platform with over 30 applications that support the entire drug lifecycle, from development and clinical trials to regulatory submissions and commercialization. * **Accelerating Drug Development:** Veeva's cloud software plays a crucial role in accelerating the development and delivery of medicines, including vaccines, by digitizing critical processes for major pharmaceutical companies like Moderna, Pfizer, and Glaxo. * **Digitization of Clinical Trials:** While significant progress has been made in commercialization, clinical trial management still heavily relies on paper-based processes. Veeva is actively working to digitize this area, with the CEO projecting a 50% reduction in paper usage within two to three years. * **Long-Term Industry Stability:** The life sciences industry is a massive, two-trillion-dollar sector critical for human health and happiness. Its growth and importance are long-term trends that predate COVID-19 and will continue long after the pandemic, dispelling concerns about post-pandemic decline. * **Impact on Commercial Operations:** Digitization is leading to increased efficiency in pharmaceutical commercial operations, potentially resulting in a 10% reduction in sales forces. This shift is beneficial for technology providers like Veeva, as companies adopt more digital tools to drive efficiency. * **Enabling Remote Engagement:** Veeva provides specialized software to facilitate remote interactions between pharmaceutical companies and healthcare professionals, such as compliant virtual meetings and digital signing for drug samples, adapting to the rise of telemedicine and remote work. * **Cybersecurity Vigilance:** Given the sensitive nature of pharmaceutical data and the high value of drug development, robust cybersecurity is paramount. Companies must assume constant threats and maintain vigilant defenses against attempts to access their systems. * **Regulatory Compliance Support:** Veeva's technology aids pharmaceutical companies in adhering to complex industry regulations. The company anticipates partnering with administrations worldwide to provide technology that supports better and more efficient healthcare, even with potentially stricter regulatory environments. * **Efficiency Drives Cost Reduction:** By digitizing and streamlining processes, Veeva contributes to making the overall value proposition of healthcare better and more efficient. This efficiency can ultimately lead to less expensive healthcare, though the distribution of these savings depends on administrative and policy decisions. * **Full Spectrum Support:** Veeva's applications cover the full spectrum of pharmaceutical operations, including manufacturing, clinical development, regulatory submissions, and patient outreach, demonstrating its integrated approach to industry challenges. **Tools/Resources Mentioned:** * **Veeva Systems Platform:** The core cloud-based software suite for life sciences. * **Veeva's 30+ Applications:** A suite of specialized software tools supporting various aspects of drug development, clinical trials, regulatory compliance, and commercial operations. **Key Concepts:** * **Industry Cloud:** A specialized cloud computing platform tailored to the unique needs and regulatory requirements of a specific industry, in this case, life sciences. * **Digitization of Life Sciences:** The ongoing process of converting information and processes from analog (e.g., paper) to digital formats and leveraging technology to improve efficiency, data management, and compliance across the pharmaceutical and biotech sectors. * **Remote Engagement:** The use of digital tools and platforms to facilitate interactions between pharmaceutical companies and healthcare professionals, replacing traditional in-person meetings.

Preview Increasing Speed & Accuracy of Remote Audits with Modern Cloud QMS
Veeva Systems Inc
/@VeevaSystems
Dec 17, 2020
This video provides an in-depth exploration of the challenges and best practices for conducting remote audits in the life sciences industry, particularly in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic and the shift to virtual working environments. Featuring insights from quality experts at Merck & Co. and GlaxoSmithKline, alongside Veeva Systems, the discussion centers on how modern cloud solutions and adapted methodologies can enhance the speed and accuracy of virtual audits. The speakers delve into the practical difficulties encountered during remote audits and share lessons learned from their organizations' experiences. Ralph Mazenko, Executive Director of Clinical Quality Assurance at Merck, highlights several key challenges. He emphasizes the loss of non-verbal communication, specifically body language, as a significant impediment in virtual settings. Technical difficulties, or "snafus," such as struggling with mute buttons or inadvertently talking over others on platforms like MS Teams or Zoom, are also cited as common issues. Furthermore, scheduling complexities, especially across different time zones, contribute to the overall difficulty. Mazenko notes that remote audits often require more time than in-person audits because it's harder to cover the same number of topics, leading to auditors working longer hours even without travel. Marcus Massingham, Senior Director of Quality Systems at GlaxoSmithKline, expands on the technological and logistical hurdles. He points out the stark difference in documentation access between physical and virtual audits; in a physical setting, documents are readily available in a control room, whereas virtual audits necessitate an extra step for transmission, consuming valuable time. Massingham also addresses the challenges of connectivity and technology infrastructure within manufacturing or laboratory areas, which can impede attempts to conduct visual inspections or gather real-time information remotely. Both speakers underscore the need for organizations to adapt their audit plans and embrace new strategies to navigate these virtual complexities effectively. The discussion culminates in practical recommendations for improving the remote audit experience. Key lessons learned include the importance of scheduling fewer topics per audit with more allocated time for each, incorporating regular breaks to allow participants to gather requested information, and critically, providing opportunities for teams to practice using the technology without stress before a live audit. The overarching theme is that successful remote auditing requires not just technology adoption, but also a fundamental rethinking of processes, a focus on preparation, and an understanding of the unique human and technical dynamics of virtual interactions. Key Takeaways: * **Loss of Non-Verbal Cues:** Remote audits significantly suffer from the absence of body language and other non-verbal cues, making it challenging for auditors to fully understand context and nuances, which can impact the depth and accuracy of the assessment. * **Prevalence of Technology Snafus:** Basic technical difficulties, such as managing mute functions, avoiding speaking over others, or navigating virtual meeting platforms, are common and can disrupt the flow and efficiency of remote audit proceedings. * **Increased Time Allocation Required:** Virtual audits inherently demand more time per topic compared to in-person audits, as information exchange, clarification, and document review processes are often slower in a remote setting. * **Auditor Workload Intensification:** Despite eliminating travel, auditors frequently experience longer working days during remote audits due to the unique demands of virtual collaboration and the extended time required to complete tasks. * **Strategic Scheduling for Remote Audits:** To optimize efficiency and reduce fatigue, it is advisable to schedule fewer audit topics, allocate more time for each, and incorporate regular breaks to allow participants to gather information offline or rest. * **Mandatory Technology Practice:** Prior to a live remote audit, all participants should engage in stress-free practice sessions to familiarize themselves with the chosen virtual meeting platform and ensure seamless interaction and system access. * **Documentation Access and Transmission Challenges:** Unlike physical audits with centralized control rooms, virtual audits introduce an additional, time-consuming step for transmitting requested documentation, which requires robust digital processes. * **Connectivity and Infrastructure Limitations:** Conducting virtual inspections or gathering real-time data from manufacturing or laboratory facilities can be severely hampered by inadequate internet connectivity or insufficient technology infrastructure in those physical locations. * **Adaptation, Not Replication:** Organizations must recognize that remote audit processes cannot simply mirror traditional in-person methods; they require a fundamental re-evaluation and adaptation of methodologies, scheduling, and technological support. * **Continuous Learning and Improvement:** The life sciences industry is still in a learning phase regarding remote audits, emphasizing the need for ongoing evaluation, lessons learned sessions, and continuous improvement of virtual audit strategies.

Intellect QMS and Netsuite ERP Integration
Intellect
/@IntellectQMS
Dec 11, 2020
This video provides an in-depth demonstration and overview of Intellect QMS 4.0, a Quality Management System built on a no-code platform designed to standardize processes and ensure the delivery of quality products and services, particularly within highly regulated industries like medical devices and pharmaceuticals. The presentation, led by the CMO/VP of Business Development and the QMS Product Manager, emphasizes the benefits of moving away from manual, paper-based systems to increase productivity, lower operational costs, and improve data accessibility and communication. A core focus is placed on the system's "extreme configurability," allowing users to modify out-of-the-box applications or build entirely new business applications without coding expertise. The central part of the demonstration focuses on the seamless, integrated workflow between three critical quality applications: Complaints Management, Non-Conformance (NC), and Corrective and Preventive Actions (CAPA). Using the relatable example of a "leaking IV bag" complaint received by a medical device company, the presenters illustrate how a complaint (Complaint 59) is documented, reviewed for validity and reportability (e.g., 30-day FDA reporting window), and investigated through defined steps like Device History Record (DHR) review and sample evaluation. If the complaint trend warrants further action, the system allows for escalation, automatically copying all relevant data from the complaint record into a new or existing Non-Conformance record (NC 170), thus ensuring data integrity and traceability. The progression continues as the NC investigation, which involves a thorough root cause analysis using tools like 5 Whys or 6M, leads to the definition of immediate containment actions and, if necessary, further escalation to a CAPA (CAR 60). The CAPA module is structured around the 8D methodology (Disciplines 1 through 8), defining a formal corrective action plan, implementing those actions, and crucially, verifying their effectiveness over time (e.g., 30, 60, or 90 days). The system maintains a closed-loop process, where a failed effectiveness check automatically triggers the creation of a new CAPA, ensuring continuous improvement and regulatory adherence. Beyond the core trio, the platform integrates other essential quality applications, including Document Control, Employee Training, Calibration, Validation, and Supplier Management, all linked to the Non-Conformance module to maintain a comprehensive, interconnected quality ecosystem. The final segment highlights the platform’s no-code design, showing how quickly a non-programmer can design templates, define workflows using drag-and-drop functionality, and deploy new applications, underscoring the flexibility required to meet rapidly changing business and regulatory requirements. Key Takeaways: • **Closed-Loop Quality Management:** Intellect QMS 4.0 provides a seamless, integrated workflow connecting Complaints Management, Non-Conformance (NC), and CAPA, ensuring full traceability and automatic data transfer between records to prevent double data entry and maintain regulatory compliance. • **Regulatory Compliance Features:** The system is designed with regulated industries in mind, featuring 21 CFR Part 11 compliant e-signatures for approvals and built-in tracking for regulatory reporting deadlines (e.g., the 30-day window for reporting serious complaints to regulatory agencies like the FDA). • **Structured Investigation Methodologies:** The platform supports industry-standard quality methodologies; the CAPA module is explicitly structured around the 8D methodology, and the investigation phase allows for the use of root cause analysis tools such as 5 Whys and 6M (Man, Machine, Method, Material, Measurement, Mother Nature/Environment). • **Extreme Configurability via No-Code:** The QMS is built on a no-code platform, allowing quality managers and non-programmers to easily modify existing applications, change workflows, update fields, and build entirely new business applications (e.g., contract management, inventory tracking) to meet unique business requirements. • **Dynamic Workflow Management:** Workflows are visually designed using drag-and-drop tools, allowing for complex logic, including infinite loops (e.g., if an action is rejected, it returns to the "Take Action" step) and conditional field visibility based on previous selections. • **Comprehensive Quality Ecosystem:** In addition to core compliance apps (Complaints, NC, CAPA), the system integrates applications for Document Control, Employee Training (linked to document changes), Supplier Management, Calibration, and Audit Management, all feeding into the NC process for holistic quality tracking. • **Effectiveness Verification:** The CAPA process includes a mandatory Effectiveness Verification step (D8), which can be scheduled for 30, 60, or 90 days post-closure; if the corrective action is found to be ineffective, the system automatically triggers a new CAPA, enforcing a continuous improvement cycle. • **Automated Notifications and Traceability:** The system features full-blown automated email notifications for every activity, including overdue tasks, and provides full visibility and traceability across all linked records, which is crucial for internal audits and regulatory inspections. • **Mobile Capabilities:** The platform supports mobile deployment, allowing users to access QMS applications via a container app on the App Store or Google Play, with the option for custom-branded container apps for enhanced user experience. Tools/Resources Mentioned: * Intellect QMS 4.0 (Quality Management System) * Intellect No-Code Platform * NetSuite ERP (mentioned in the title/description as an integration point) * Google Play Store / App Store (for mobile container apps) Key Concepts: * **QMS (Quality Management System):** Software designed to standardize processes, ensure product quality, and manage compliance within an organization. * **CAPA (Corrective and Preventive Action):** A process that investigates and corrects causes of non-conforming product or quality issues and takes action to prevent recurrence. * **Non-Conformance (NC):** A deviation from a specification, standard, or procedure. In the demo, NCs are often escalated from customer complaints. * **21 CFR Part 11:** FDA regulation governing electronic records and electronic signatures, which the system supports with e-signature compliance. * **8D Methodology:** A disciplined, eight-step problem-solving approach used in quality management, particularly for CAPA, focusing on defining, containing, investigating, and verifying solutions. * **5 Whys / 6M:** Root cause analysis techniques used during the investigation phase of NC and CAPA records. 6M refers to Man, Machine, Method, Material, Measurement, and Mother Nature (Environment). Examples/Case Studies: * **Leaking IV Bag Complaint:** A medical device company receives a complaint about a leaking IV bag. This complaint is documented, investigated (including DHR and sample evaluation), and escalated to a Non-Conformance (NC 170) due to the frequency of the issue, which is then further escalated to a CAPA (CAR 60) to define a long-term preventive action plan. * **Custom Application Development:** Examples of applications built by customers on the no-code platform include contract management, invoice and capex automation, mobile field services, safety observations, accident reporting, inventory management, and asset tracking.

Habit Action Veeva Oxford - New HQ Design & Build
Habit Action
/@habitaction2523
Dec 10, 2020
This video provides an in-depth look at the design and build of Veeva's new headquarters in Oxford, UK, as narrated by Sean Lorimer, the Facilities Manager for Veeva Oxford. The primary purpose of the video is to showcase the successful collaboration between Veeva and Habit Action, the design and build firm, in creating a modern, functional, and employee-centric workspace. The narrative highlights Veeva's corporate values, particularly its focus on employee well-being and fostering a positive work environment, which heavily influenced the office design. The project was executed during the challenging period of the COVID-19 pandemic, demonstrating effective remote collaboration and project management. The video details the process from the initial decision to move from their old buildings to the final completion of the new HQ. Sean Lorimer explains that Veeva sought a building that was "very corporate but fun, slightly individual," while still adhering to a global corporate image. Habit Action's approach involved a "Workplace Strategy process," which included extensive consultation with Veeva's team leads and key stakeholders to understand the unique operational needs of various departments. This meticulous understanding of user requirements, combined with a smooth design and build process, even amidst lockdown restrictions, resulted in a space that perfectly encapsulates Veeva's identity as a global software company in the pharmaceutical and tech sector. Key themes explored include the importance of a user-friendly and modern workspace, reflecting Veeva's tech-company identity while prioritizing employee comfort and collaboration. The office features a variety of spaces, including open-plan areas, comfortable huddle spaces, small meeting rooms with screens, and dedicated zones for different teams (e.g., global help desk and engineers separated from visitor areas). The design also incorporates elements like games in the kitchen and spaces for team-building events, reinforcing Veeva's people-focused culture. The seamless execution, constant communication via Zoom during lockdown, and the high quality of the final build, including specific details like lighting and "zoom rooms," are repeatedly praised by the client, underscoring the success of the project. Key Takeaways: * **Veeva's Corporate Culture and Values:** Veeva is portrayed as a "global software company" and "tech company" that is "very people focused" and "looks after their employees extremely well." This emphasis on employee well-being and a positive workspace environment is a core aspect of their brand and operational strategy. * **Strategic Workspace Design:** The new HQ was designed to be "very corporate but fun, slightly individual," balancing global corporate image with local autonomy. This approach ensures that physical spaces reflect and reinforce the company's brand identity and values. * **Importance of User Requirements:** Habit Action's success stemmed from taking the time to "fully understand Veeva's ways of working" by speaking to all team leads and key stakeholders. This deep dive into diverse team needs is crucial for creating truly functional and appreciated workspaces. * **Adaptability in Project Management:** The project was managed effectively despite the challenges of the COVID-19 pandemic, with constant meetings held via Zoom. This highlights the importance of flexible communication strategies and robust project management in adverse conditions. * **Seamless Collaboration:** The video emphasizes the "very smooth process" and "constant engagement" between the design firm and Veeva's teams, including stakeholders located internationally (e.g., Angel in Barcelona). Effective client-vendor collaboration is key to project success. * **Employee-Centric Design:** The office features a variety of spaces tailored for different activities and team needs, such as comfortable huddle spaces, open-plan areas, and dedicated quiet zones. This multi-functional design supports diverse work styles and promotes productivity and collaboration. * **Technology Integration in Workspace:** The design incorporates modern technology, including screens in all meeting rooms and "zoom rooms," reflecting Veeva's identity as a tech company and facilitating seamless communication and collaboration. * **Brand Reinforcement through Environment:** Veeva is "incredibly proud of their offices," viewing each as individual and a "perfect example of the thought that has gone into the design." Physical office spaces are seen as critical tools for attracting and retaining talent and reinforcing corporate pride. * **Strategic Zoning:** The layout strategically separates different functions, such as client waiting areas and training rooms from general working spaces and noisy global help desk/engineer teams. This ensures operational efficiency and minimizes distractions. * **Positive Client Testimonial Power:** Sean Lorimer's enthusiastic recommendation of Habit Action ("absolutely I would recommend Habit Action and have done so to quite a few companies already") underscores the value of delivering exceptional service and building strong client relationships. Tools/Resources Mentioned: * **Zoom:** Utilized extensively for meetings and collaboration during the COVID-19 lockdown. * **Veeva CRM (Implicit):** As Veeva is a "global software company" and a leader in the pharmaceutical and tech sector, their primary product, Veeva CRM, is implicitly central to their operations and identity. Key Concepts: * **Workplace Strategy Process:** A methodology used by Habit Action to thoroughly understand a client's operational needs, culture, and future growth plans before designing a workspace. * **Employee-Centric Design:** An approach to office design that prioritizes the comfort, well-being, and productivity of employees by offering diverse spaces and amenities. * **Corporate Image & Autonomy:** Balancing a consistent global corporate identity with the ability for individual country offices to have some unique design elements.

Title: Generation Veeva | Meet Celine: CDP: What I've Learned
Generation Veeva
/@GenerationVeeva
Dec 7, 2020
This video provides an insider's perspective on the Veeva Consultant Development Program (CDP), as shared by Celine, a former participant. The main purpose of the video is to showcase the value and structure of the CDP, positioning it as an ideal launchpad for young professionals seeking a fast-paced career in the specialized field of life sciences technology consulting. The program is explicitly designed to integrate new talent into Veeva's culture, emphasizing a "fast-growing, very young, very cool environment" that fosters rapid professional growth and community building. A central theme of the CDP, according to Celine, is the creation of a supportive and communal environment. She highlights the benefit of starting the program alongside peers who are in similar situations—such as relocating to a new city like Barcelona—which immediately establishes a strong internal network. This community structure, combined with supportive managers and colleagues, is crucial for the program's success. The CDP is specifically tailored to help participants identify and work on both their professional weaknesses and strengths in a comfortable setting, suggesting a high emphasis on continuous feedback and psychological safety, which are foundational for effective consulting development. The most significant aspect of the CDP highlighted is the accelerated assumption of responsibility. Unlike traditional programs where associates might spend significant time in preparatory roles, the Veeva CDP immediately places participants onto active projects. This hands-on methodology ensures that consultants quickly learn the intricacies of project management, client interaction, and execution. Celine notes that she quickly transitioned from feeling like an "associate" to a full "consultant," gaining the necessary confidence and practical knowledge early on. This rapid deployment model culminates in the opportunity for participants to take on leadership roles; Celine shared that she was able to lead her own projects, including complex global initiatives, even before completing the typical two-year duration of the program. This demonstrates Veeva’s commitment to empowering young talent with significant ownership early in their careers, provided they leverage the robust support system available. The overall progression of the video emphasizes the transformative nature of the program. It not only provides technical and project management skills but also focuses on "rounding" the individual as a professional. The experience is framed as foundational, providing lasting skills and beautiful memories, underscoring the value of starting a career in a high-support, high-challenge environment focused on regulated enterprise software consulting within the life sciences sector. Key Takeaways: • **Accelerated Project Ownership:** The Veeva CDP model emphasizes immediate placement onto active client projects, allowing new consultants to rapidly acquire practical knowledge of project mechanics and leadership skills, rather than relying solely on theoretical training. • **High-Challenge, High-Support Model:** The program is structured to push young professionals into roles with significant responsibility, such as leading global projects early in their tenure, while mitigating risk through a strong, accessible support network of managers and peers. • **Focus on Professional Rounding:** The training aims to develop well-rounded professionals by focusing equally on identifying and improving both professional weaknesses and strengths, ensuring consultants are versatile in client management, technical execution, and leadership. • **Community as a Critical Success Factor:** The program intentionally fosters a strong sense of community among participants, which is vital for providing mutual support, facilitating knowledge transfer, and easing the transition for consultants who may be relocating or new to the industry. • **Rapid Transition to Consultant Identity:** The CDP is designed to quickly instill a "consultant" mindset, encouraging participants to take ownership and act as full consultants rather than remaining in an "associate" capacity, thereby boosting confidence and client-facing effectiveness. • **Importance of Accessible Mentorship:** The supportive environment ensures that consultants feel comfortable approaching managers and experienced colleagues with questions, which is essential when tackling complex, challenging assignments in the regulated life sciences technology space. • **Talent Pipeline Insight:** For consulting firms specializing in Veeva, this video highlights that Veeva’s internal talent pipeline is trained to assume leadership roles quickly and is accustomed to working within a collaborative, fast-paced, and high-stakes environment. • **Methodology for Skill Acquisition:** The core methodology involves learning by doing, where project experience is the primary driver of skill acquisition, supplemented by structured feedback and peer learning within the CDP framework. Key Concepts: * **Consultant Development Program (CDP):** A structured, fast-track training and mentorship program for new consultants at Veeva, designed for rapid skill acquisition, project leadership, and integration into the company culture. * **Professional Rounding:** The comprehensive development process that ensures consultants acquire a broad range of skills—including technical expertise, soft skills, project management, and leadership—to become versatile and effective professionals in the regulated life sciences sector.

Generation Veeva | Meet Abigail: At Home with Veeva
Generation Veeva
/@GenerationVeeva
Dec 7, 2020
This video provides an intimate look into the daily professional life of a Veeva Associate Consultant, Tammy Armstrong, detailing her work-from-home routine and responsibilities focused on client configuration and internal development within the Veeva ecosystem. The content serves as a practical illustration of the implementation and consulting processes that underpin successful deployments of Veeva solutions in the life sciences sector. The speaker structures her day around proactive planning, collaborative technical execution, and managing clients through the critical final stages of system deployment. The consultant’s day is highly structured, beginning with detailed action planning at 8:00 AM, emphasizing the need for early engagement and prioritization in a consulting role. Her schedule is a dynamic mix of internal commitments, such as workshops with the Consultant Development Program (CDP) group—highlighting Veeva’s commitment to continuous training—and external client deliverables. The core technical work revolves around "configuration for some clients," which involves customizing the Veeva platform (likely Veeva CRM or related modules) to meet specific pharmaceutical business requirements. A unique methodology highlighted is the use of collaborative "working sessions" conducted via Zoom. In these sessions, the consultant and a peer (Alyssa) work silently alongside each other on their respective tasks, maintaining an open line of communication to quickly address technical roadblocks or configuration questions as they arise. This collaborative approach ensures efficiency and rapid knowledge transfer, which is crucial when dealing with complex, regulated enterprise software like Veeva. The day culminates with focused efforts on a specific client project nearing completion: finalizing configuration steps for a client about to go live with **Veeva Engaged Meetings**. This involves meticulous quality assurance, incorporating final client feedback, and preparing the official go-live communication, demonstrating the critical project management and regulatory compliance focus required at the end of an implementation cycle. The insights provided into the consultant's workflow—from internal training and collaborative configuration to managing the final steps of a major module deployment—are highly valuable for firms like IntuitionLabs.ai that specialize in Veeva CRM consulting. The video confirms the operational realities of Veeva deployment, emphasizing the importance of technical configuration skills, structured project management, and the ability to manage multiple client deliverables simultaneously, all while ensuring readiness for specific commercial modules like Engaged Meetings. Key Takeaways: * **Veeva Consultant Workflow:** The daily life of a Veeva implementation specialist involves a necessary balance between internal professional development (CDP workshops) and hands-on client configuration and project management. * **Proactive Planning for Configuration:** Successful consulting requires rigorous time management, demonstrated by the consultant's practice of creating a detailed action plan early in the morning (8:00 AM) to prioritize configuration tasks and client meetings. * **Collaborative Configuration Methodology:** The use of Zoom "working sessions" for silent, parallel work with immediate access to peer support is an effective strategy for accelerating complex configuration tasks and resolving technical issues quickly, minimizing project delays. * **Focus on Veeva Engaged Meetings Deployment:** The specific mention of a client preparing for go-live with Engaged Meetings indicates a current and critical area of deployment activity within the pharmaceutical commercial operations space, requiring specialized configuration expertise. * **Go-Live Readiness Protocol:** The final stages of a Veeva implementation are characterized by meticulous quality checks, incorporating last-minute client feedback, and preparing formal go-live communications, underscoring the need for detailed project closure processes in regulated environments. * **Importance of Internal Training (CDP):** The frequent participation in Consultant Development Program (CDP) workshops suggests that Veeva relies on structured, ongoing training to ensure a high level of technical competency and consistent methodology among its implementation workforce. * **Remote Efficiency in Regulated Software:** The video confirms that complex, client-facing Veeva configuration and project management can be executed efficiently and effectively in a remote work environment, relying heavily on digital collaboration tools like Zoom. * **Multi-Client Management:** The consultant manages configuration tasks for multiple clients concurrently, highlighting the necessity for robust organizational skills and the ability to context-switch between different project requirements and technical specifications. Tools/Resources Mentioned: * Zoom (Used for collaborative working sessions and internal meetings) * Veeva Engaged Meetings (A specific Veeva module being configured and deployed for a client) Key Concepts: * **Configuration:** The process of setting up and customizing the Veeva platform (e.g., CRM) according to specific client business rules, workflows, and regulatory requirements. * **CDP (Consultant Development Program):** Veeva's internal program designed to train, mentor, and standardize the skills of new consultants entering the implementation field. * **Veeva Engaged Meetings:** A Veeva solution designed to facilitate compliant, remote, and digital interactions between pharmaceutical sales representatives and healthcare professionals (HCPs), a critical component of modern commercial operations. * **Go-Live:** The final phase of a software implementation project where the configured system is officially launched and adopted by the client's end-users.

Generation Veeva | Meet Abby: CDP: What I've Learned
Generation Veeva
/@GenerationVeeva
Dec 7, 2020
This video provides an intimate look into the experience of a consultant, Abby, participating in the Research & Development (R&D) Consultant Development Program (CDP) at Veeva Systems. The primary purpose of the content is to showcase the internal culture, training philosophy, and community support within Veeva, particularly highlighting how consultants adapted to the challenges of the global pandemic and the shift to entirely virtual work. Abby emphasizes that the CDP structure, which focuses on communication and connection, proved invaluable in maintaining professional momentum and personal well-being during a time when traditional client travel ceased. The core theme revolves around the structure and unique value proposition of the Veeva CDP. Abby describes the program as fostering strong peer connections, noting that the community aspect—including regular Friday meetings and workshops focused on both technical topics and soft skills—is crucial for success. These workshops are presented as collaborative forums where peers discuss topics that one of them chooses to present, ensuring continuous learning and skill development. A significant portion of the discussion is dedicated to the importance of work-life balance, which Abby actively manages by taking breaks for activities like walking, demonstrating a focus on consultant well-being within the program’s framework. A key differentiator highlighted by Abby is the CDP’s philosophy of empowering consultants to "find your own path" or even "create your own path" within the organization. Unlike traditional development programs that might offer rigid career tracks, the Veeva CDP is portrayed as supportive of entrepreneurial initiative. If a current opportunity or established path does not exist, the program actively assists the consultant in creating one. This emphasis on self-direction and customized career growth is presented as the defining feature that sets the Veeva CDP apart from other industry programs, suggesting a highly flexible and talent-retention-focused approach to developing expertise in the regulated life sciences technology space. The narrative progression moves from the immediate context of remote work and peer connection to the long-term impact of the program on career development. Abby stresses the importance of the initial connections made during the first job, suggesting that the relationships forged within the CDP—specifically mentioning her cohort of women who started in August 2019—are expected to be lifelong professional and personal connections. Ultimately, the video serves as a testimonial to the strength of Veeva’s internal community and its commitment to developing highly adaptable, well-rounded consultants capable of navigating the complex R&D and life sciences landscape. Key Takeaways: • **Veeva’s Consultant Development Program (CDP) Structure:** The program utilizes regular, mandatory peer connection meetings (e.g., Friday sessions) to ensure continuous communication and community building, which proved critical for maintaining morale and productivity during the transition to fully remote work. • **Focus on Soft Skills and Technical Topics:** The CDP workshops are designed to cover a balanced curriculum, addressing both technical topics relevant to the R&D practice and essential soft skills, indicating a holistic approach to consultant readiness. • **Importance of Peer-Led Learning:** The workshops often involve peers presenting on topics they select, suggesting a decentralized, knowledge-sharing model that encourages ownership and deep dives into specific areas of interest within the Veeva ecosystem. • **Emphasis on Work-Life Balance:** The video explicitly highlights the program’s recognition of the importance of work-life balance, particularly in a virtual environment, suggesting that consultant well-being is integrated into the operational philosophy of the R&D practice. • **Unique Career Pathing Philosophy:** The Veeva CDP differentiates itself by encouraging consultants to define or even invent their own career trajectories, providing support to create opportunities where none currently exist, which fosters internal innovation and retention of high-potential talent. • **Strength of Cohort Connections:** The program is structured to build deep, lasting professional relationships among cohort members, recognizing that these initial connections are vital for long-term career support and networking within the specialized life sciences consulting field. • **Adaptability in Regulated Consulting:** The experience shared demonstrates the successful transition of complex, client-facing consulting work (typically requiring travel) to a fully virtual model, highlighting the adaptability of Veeva’s internal communication and project management processes. • **Competitive Intelligence on Talent Development:** Understanding how Veeva trains its R&D consultants provides valuable insight for competing consulting firms, revealing the high standard of communication, community, and self-directed growth expected from professionals entering the Veeva ecosystem. Key Concepts: * **Veeva R&D CDP (Consultant Development Program):** A structured internal program designed to train and integrate new consultants into Veeva’s Research & Development practice, focusing on both technical expertise and essential professional skills. * **Work-Life Balance in Consulting:** The recognition and active management of the demands of a consulting career, particularly when working remotely, emphasizing the need for intentional breaks and personal connection. * **Customized Career Pathing:** A development philosophy where the organization supports the individual consultant in defining or creating their own unique role and progression within the company, rather than adhering to rigid, pre-defined ladders.

Generation Veeva | Meet Erica: CDP: What I've Learned
Generation Veeva
/@GenerationVeeva
Dec 7, 2020
This video features Erica Tang, an alumna of the Generation Veeva program and its Consultant Development Program (CDP), reflecting on her four years at Veeva Systems and the profound impact the development track had on her career trajectory. The primary focus is not on technical product details but on the holistic personal and professional growth fostered by the program, positioning Generation Veeva as a transformative experience rather than just a training course. Erica emphasizes that the CDP provided foundational life lessons alongside professional skills, citing examples of being pushed to try new things and develop confidence in her abilities. A central theme of the reflection is the necessity of proactive engagement and self-trust in accelerating one’s career within the fast-paced life sciences technology sector. Erica highlights the difficulty of summarizing four years of intense development but distills the most crucial lesson: the power of staying open to new opportunities and actively pursuing them. She notes that often, the only difference between those who achieve significant milestones and those who do not is the willingness to simply "ask" for what they want or to chase a desired role or project. This perspective underscores the high-initiative culture expected of consultants working on complex Veeva implementations for pharmaceutical clients. Furthermore, the speaker stresses the importance of community and reciprocal support within a consulting environment. Recognizing that success is never achieved in isolation, Erica advocates for the necessity of "giving back" as soon as one is able and actively creating opportunities for others to grow. This commitment to mentorship and collaborative advancement is presented as essential for achieving the best collective work. The video ultimately serves as a motivational testimonial, demonstrating how Veeva’s structured development programs aim to build not just technically proficient consultants, but confident, proactive, and socially responsible leaders ready to tackle the challenges of the life sciences industry. Key Takeaways: • **Holistic Consultant Development:** The Generation Veeva program is designed to be more than a technical training track; it focuses heavily on personal development, confidence building, and pushing participants beyond their comfort zones, which is crucial for consultants handling high-stakes pharmaceutical client projects. • **The Imperative of Proactivity:** A core lesson imparted to new consultants is the necessity of actively seeking and "chasing" new opportunities, rather than waiting for them to be assigned. This proactive mindset is vital for success in the dynamic environment of Veeva CRM implementation and customization. • **Value of Self-Trust:** The program aims to instill a deep sense of self-trust and capability in its participants, enabling them to take on greater responsibility and complex challenges, such as integrating AI solutions or managing large-scale data engineering projects. • **Ask for What You Want:** Consultants are encouraged to practice self-advocacy, recognizing that simply asking for desired roles, projects, or resources can often be the deciding factor in career advancement within the consulting structure. • **Mentorship and Reciprocity:** Success in the Veeva ecosystem is viewed as a collective effort. Consultants are advised to prioritize finding ways to "give back" and create growth opportunities for colleagues as soon as they are in a position to do so, fostering a strong, supportive team environment. • **Culture of Continuous Growth:** The emphasis on trying new things and taking on more responsibility suggests that Veeva cultivates a culture of continuous professional evolution, which is necessary for consultants who must stay current with evolving regulatory requirements and technology (like LLMs). • **Resilience through Challenge:** The speaker’s reflection on being "pushed to try new things" highlights that the program uses challenges and new experiences to build resilience, a necessary trait for managing the complexities and pressures of pharmaceutical commercial operations consulting. • **Teamwork for Optimal Results:** The final takeaway reinforces that the best work is achieved when team members actively support each other and remember to "bring other people with us as we move forward," ensuring knowledge transfer and sustained organizational success. Tools/Resources Mentioned: * **Generation Veeva Program:** A talent development initiative at Veeva Systems. * **Consultant Development Program (CDP):** A specific track within Generation Veeva focused on training new consultants. Key Concepts: * **Veeva Systems:** The foundational technology platform for pharmaceutical and life sciences commercial operations, central to the speaker's career context. * **Consultant Development Program (CDP):** A structured training and mentorship program designed to rapidly onboard and develop high-potential employees into client-facing consultants.

Generation Veeva | Meet Annalisa: At Home with Veeva
Generation Veeva
/@GenerationVeeva
Dec 7, 2020
This video provides a personal account from Annalisa, an Associate Consultant in the Veeva Consultant Development Program (CDP) in Europe, detailing her experience transitioning from an office-based role in Barcelona to a fully remote working environment in Italy due to the COVID-19 pandemic. The video serves as a testimonial highlighting Veeva's corporate culture, resilience, and commitment to maintaining team cohesion and professional development despite significant operational disruption. It frames the initial challenge of losing the dynamic, open office environment—which fostered spontaneous idea exchange, product knowledge sharing, and social activities like weekly team lunches—against the successful adaptation to remote operations. The core narrative focuses on how Veeva managed to replicate essential aspects of its collaborative culture virtually. Annalisa emphasizes that while the physical setting changed, the frequency and quality of interaction did not significantly diminish. Key activities like team meetings transitioned seamlessly to Zoom, and the company actively organized virtual social events, including remote lunches, coffee breaks, cooking classes, and welcome drinks for new joiners. This adaptation ensured that consultants, particularly those new to the program like Annalisa, continued to feel supported and integrated into the "big orange family." A significant theme is the resilience of the Veeva consulting model and the benefits derived from the shift to remote work. Annalisa describes the remote environment not as a limitation, but as a "huge opportunity." It forced consultants to adapt to new routines, learn how to better manage work-life balance, and take on increased responsibilities, suggesting a rapid acceleration of professional maturity within the CDP cohort. The ease of organizing quick support calls with colleagues underscored the strong internal relationships and accessible support structure, which are critical components for consultants working on complex pharmaceutical and life sciences projects. Ultimately, the video portrays Veeva’s ability to maintain a strong sense of community and effective professional development, even when its workforce is distributed across different locations. Key Takeaways: • **Veeva Consultant Development Program (CDP) Structure:** The video confirms that the European CDP is typically an office-based program (specifically mentioning the Barcelona office), emphasizing the value Veeva places on in-person collaboration for rapid knowledge transfer and cultural integration among new consultants. • **Operational Resilience in Consulting:** Veeva successfully transitioned its high-touch consulting operations to a fully remote model, demonstrating strong infrastructure and organizational flexibility necessary to support complex client engagements in the regulated life sciences sector without interruption. • **Maintaining Virtual Team Cohesion:** The company prioritized replicating social and collaborative office functions virtually, utilizing tools like Zoom for both formal meetings and informal interactions (lunches, coffee breaks, welcome drinks), which is crucial for retaining talent and maintaining morale in high-pressure consulting roles. • **Accelerated Professional Development:** The shift to remote work acted as a catalyst for professional growth, forcing new consultants to develop stronger self-management skills, adapt to new routines, and take on greater individual responsibility for managing their work-life balance and project deliverables. • **Importance of Accessible Support Systems:** Annalisa highlighted the ease and speed with which she could organize "quick calls" with any colleague for support, indicating a culture of open communication and readily available mentorship, which is essential for consultants navigating complex Veeva implementations. • **Cultural Integration via Remote Means:** Despite physical distance, Veeva effectively maintained its "big orange family" culture, successfully integrating new joiners through organized remote activities, proving that strong corporate culture can be sustained and transmitted digitally. • **Strategic Value of Work-Life Balance:** The remote environment provided consultants with an opportunity to "better manage the work life balance," suggesting that flexible work arrangements are viewed internally as a valuable benefit that contributes to consultant satisfaction and long-term retention. • **Focus on Knowledge Exchange:** The initial description of the Barcelona office emphasized the "exchange ideas, opinions, experiences and also product knowledge," underscoring that continuous, dynamic learning is a foundational element of the Veeva consulting methodology that needed to be consciously preserved in the remote setting. Tools/Resources Mentioned: * **Zoom:** Used as the primary platform for switching formal meetings and informal social gatherings (lunches, coffee breaks) to a remote format. * **Veeva Consultant Development Program (CDP):** The structured entry program for new consultants in Europe, which is typically office-based but successfully adapted to remote work. Key Concepts: * **Veeva CDP:** A talent pipeline designed to train and integrate new consultants into Veeva’s specialized consulting services, focusing on deep product knowledge and industry expertise within the life sciences sector. * **Remote Consulting Adaptation:** The successful organizational and cultural shift required to deliver high-quality, complex consulting services (such as Veeva CRM implementation and optimization) while operating in a distributed, remote environment, emphasizing the need for robust virtual collaboration tools and strong internal support networks.

Embracing a New Way of Engaging with HCPs at Unprecedented Speed
Veeva Systems Inc
@VeevaSystems
Dec 4, 2020
This video provides an in-depth case study of how the pharmaceutical company Grünenthal rapidly transitioned its global customer engagement strategy to a digital-first model in response to the initial COVID-19 lockdowns. Florent Edouard, SVP, Global Head of Commercial Excellence at Grünenthal, details the immediate realization that medical representatives and medical science liaisons (MSLs) would lose the ability to engage physicians face-to-face, necessitating a broad and immediate deployment of digital tools across all continental geographies in Europe and the Americas. The central achievement highlighted is the incredibly fast launch of Veeva Engage Meeting, moving from a limited pilot to a comprehensive global deployment in less than one month. This initiative was driven by a decisive organizational commitment to maintain connectivity with Healthcare Professionals (HCPs) and patients worldwide. The progression of the discussion centers on the successful execution and the resulting impact of this rapid digital pivot. Edouard notes that in some countries, the company achieved up to 80% of pre-COVID interaction levels, now delivered entirely through Veeva Engage Meetings. This success was attributed to a combination of three critical factors: looking eastward and realizing the necessity of an early, broad move; organizational empowerment to "just decide, let's go, let's do it everywhere"; and a robust partnership with Veeva that allowed Grünenthal to challenge conventional timelines and scale a pilot program globally in a matter of weeks. This shift demonstrated that digital engagement was not merely a temporary solution or a "buzzword," but a fundamental change that needed to be integrated into the core fabric of the organization's commercial operations. Furthermore, the speaker emphasizes that this transformation was welcomed by the target audience, noting very good feedback from both the HCPs and the field force. The physicians, in particular, are seeking a change in how pharmaceutical companies engage with them, demanding more focused, high-quality content delivered when and how they want it. This initiative has taught Grünenthal a valuable lesson in innovation: the ability to go live very quickly with a Minimum Viable Product (MVP), test it, and iterate. This approach is set to deeply impact the company's future commercialization strategy, ensuring that innovation is brought to market faster and that digital tools provide mutual benefits—allowing the company to operate efficiently while providing HCPs with tailored, dedicated digital engagement sessions. Key Takeaways: • **Achieving Near-Total Interaction Recovery:** In some geographies, Grünenthal successfully recovered up to 80% of its pre-COVID customer interactions by rapidly transitioning engagement to digital channels, demonstrating the effectiveness of the new model. • **The Power of Decisive, Global Action:** The success hinged on the leadership's early realization of the impending crisis and the immediate decision to deploy the solution globally, rather than attempting phased rollouts or extensive internal debates. • **Three Pillars of Success for Rapid Deployment:** The speaker identifies the core success factors as: 1) Early realization and commitment to a broad move; 2) Organizational empowerment allowing for rapid, decisive action; and 3) A strong, collaborative partnership with the technology provider (Veeva). • **Leveraging Technology Partnerships for Speed:** The relationship with Veeva was crucial, enabling Grünenthal to move from a single-country pilot deployment of Veeva Engage Meeting to a global launch across multiple continents in less than one month. • **Digital is Foundational, Not Temporary:** The experience solidified the organizational realization that digital engagement is not a temporary fix but a permanent fixture that must be built into the core "fabric of things" and the standard way of working for the benefit of patients and HCPs. • **HCP Demand for Focused Digital Engagement:** Physicians are actively seeking a change in engagement, preferring dedicated, high-quality digital sessions that allow them to focus on content when and where they choose, confirming the long-term viability of the digital model. • **Adopting an MVP Approach to Innovation:** The project demonstrated the effectiveness of launching a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) quickly, testing it in the field, and iterating based on real-world feedback, accelerating the pace of commercial innovation. • **Deep Impact on Commercialization Strategy:** The success of this rapid deployment is expected to fundamentally change Grünenthal’s commercialization approach, shifting the focus toward faster innovation cycles and deeply integrated digital processes. • **Mutual Benefits of Digital Transformation:** The digital shift is framed as a win-win scenario, benefiting the company through operational efficiency and benefiting HCPs by providing them with high-quality, on-demand content and dedicated engagement time. Tools/Resources Mentioned: * **Veeva Engage Meeting:** The specific digital platform used by Grünenthal to facilitate remote interactions between their field force (Medical Representatives and MSLs) and Healthcare Professionals (HCPs). Key Concepts: * **Commercial Excellence:** Refers to the optimization of commercial operations, including sales, marketing, and customer engagement, to achieve superior business results and efficiency within the pharmaceutical sector. * **Minimum Viable Product (MVP):** A product launched with just enough features to satisfy early adopters and provide feedback for future product development. In this context, it refers to the strategy of quickly deploying the core functionality of the digital engagement tool globally before perfecting every feature. * **Digital Customer Engagement:** The strategy of interacting with customers (HCPs) through digital channels (e.g., virtual meetings, email, portals) rather than traditional face-to-face interactions.

LEO Pharma: Accelerating Content Creation through Integrated Platforms
Veeva Systems Inc
/@VeevaSystems
Dec 3, 2020
This video provides an in-depth exploration of LEO Pharma’s successful strategy for accelerating digital content creation and delivery by integrating key enterprise platforms. Prompted by the pandemic, which necessitated a rapid shift to digital channels, LEO Pharma focused on creating a unified, global platform architecture where Veeva systems serve as a critical cornerstone alongside their web platform and Salesforce Marketing Cloud. The core objective was to move beyond siloed content creation to enable rapid repurposing of high-value assets across various engagement channels, thereby maximizing content investment and enhancing the customer experience for healthcare professionals (HCPs). The presentation highlights the rapid implementation of Veeva Engage, which was accelerated and completed across the company in a matter of weeks, demonstrating organizational agility in response to market demands. This technical acceleration was paired with a strategic effort to repurpose existing face-to-face content for digital engagement formats, including Veeva CRM Approved Emails. This integrated approach led to a significant "uptick" in platform utilization across all components—Marketing Cloud, corporate websites, and Veeva Approved Email—validating the strategy of providing seamless, compliant digital pathways for commercial and medical teams. A central theme is the vision for digital asset management (DAM), leveraging Veeva Vault PromoMats to its full capacity. LEO Pharma aims to treat costly content pieces as reusable assets that can be easily pulled down and deployed across any channel—whether email, web, face-to-face interactions, or engaged meetings. This standardization of content usage yields a secondary, crucial benefit: the ability to track individual content pieces and compare performance across disparate channels. This cross-channel tracking is essential for harvesting richer data, allowing marketeers and medical affairs teams to understand consumption patterns, performance across geographies and segments, and ultimately, utilize this data for a closed-loop feedback mechanism. The long-term goal of this integrated platform strategy is twofold: to drastically improve the customer experience by serving HCPs with content tailored to their needs, and to significantly reduce operational costs. By maximizing the reuse and repurposing of compliant content through Vault PromoMats, the company reduces the need for redundant content creation. The savings and efficiency gains are then reinvested, allowing the organization to allocate budget toward creating even higher-quality, impactful content pieces in the future, ensuring a continuous cycle of improvement driven by performance data. Key Takeaways: • **Pandemic-Driven Acceleration:** The necessity imposed by the pandemic served as a catalyst for LEO Pharma to rapidly accelerate planned digital initiatives, including the quick, company-wide implementation of Veeva Engage within weeks. • **Integrated Global Platform Architecture:** The strategic foundation for digital success rests on a tripartite platform integration, positioning Veeva (specifically Approved Emails and Engage) as one cornerstone, complemented by the web platform and Salesforce Marketing Cloud for marketing automation. • **Content Repurposing as a Core Strategy:** The vision for digital asset management (DAM) is centered on the ability to take high-cost content pieces originally designed for one channel (e.g., face-to-face) and easily repurpose them across all digital channels (email, web, engaged meetings). • **Maximizing Vault PromoMats Utilization:** LEO Pharma aims to utilize Vault PromoMats' full capacity to manage and compare content performance, enabling teams to understand which assets are performing well and how they are consumed across different segments and geographies. • **Enabling Cross-Channel Tracking and Comparison:** Standardizing and reusing content across the integrated platform allows for robust tracking of individual content pieces, facilitating comparison of performance metrics across email, web, and face-to-face channels. • **Closed-Loop Data Utilization:** The ultimate goal is to establish a closed-loop system where data harvested from content performance tracking informs the marketeers and medical affairs teams, enabling them to iteratively create better, more effective content and customer experiences. • **Cost Reduction Through Reuse:** A significant operational benefit of the strategy is cost reduction; the more content that can be reused and repurposed compliant assets, the less budget is needed for redundant creation, freeing up resources for higher-quality future content. • **Focus on Customer Needs:** The entire content strategy is driven by the desire to better understand customer needs (HCPs) through data, ensuring that future content creation is highly targeted and relevant, thereby improving engagement and satisfaction. • **Operational Insight for Medical Affairs:** The integration ensures that medical affairs teams receive crucial feedback on how their content is being consumed and performing in the field, allowing them to refine their educational and informational strategies. Tools/Resources Mentioned: * **Veeva Engage:** Used for accelerating digital engagement initiatives. * **Veeva CRM Approved Emails:** Utilized for compliant, personalized email communication with HCPs. * **Veeva Vault PromoMats:** The designated digital asset management (DAM) platform used for content storage, compliance, and cross-channel repurposing. * **Salesforce Marketing Cloud:** Used alongside Veeva for marketing automation and broader digital campaign execution. Key Concepts: * **Digital Asset Management (DAM):** The strategic process of organizing, storing, and retrieving rich media assets, with the specific goal here being the compliant reuse and repurposing of pharmaceutical content across multiple channels. * **Closed-Loop Marketing (CLM):** A process where data gathered from customer interactions (e.g., email opens, web views) is fed back to the content creators and commercial teams to continuously refine and improve future marketing and medical communications efforts.

qmsWrapper - Live Demo Part 4: Document Management
qmsWrapper
/@qmswrapper4150
Dec 2, 2020
This video provides an in-depth look at the critical role of the Document Management module within a compliant Quality Management System (QMS) software, specifically using qmsWrapper as an example. The presentation establishes that meeting regulatory requirements—such as those mandated by ISO 9001, ISO 13485 (for medical devices), and 21 CFR 820—necessitates a robust, integrated system for managing documentation and records. The core premise is that a QMS is only as effective as its ability to control and prove the integrity of its documentation, reinforcing the industry adage: "if it isn't documented, it didn't happen." The system is architected around secured, centralized, cloud-hosted storage, utilizing reliable infrastructure like Amazon services for backup and data security. This architecture ensures that files are accessible from any supported device, anywhere, anytime, providing the necessary flexibility for modern, distributed life sciences operations. A major focus is placed on the necessity of a proper system for structuring documents. As pharmaceutical and biotech companies grow, the volume of controlled documentation rapidly increases, making an intuitive and scalable organizational structure crucial for maintaining QMS integrity and operational efficiency. The value proposition of the electronic document management system centers on its capacity to "track, store, and control documents to prove compliance." The software achieves this through a suite of essential regulatory features designed to automate and secure the document lifecycle. These functionalities include stringent versioning control, formal electronic approvals, systematic tagging for categorization, comprehensive audit trails (essential for 21 CFR Part 11 adherence), formal change control mechanisms, security protocols, file locking, and granular permissions management. These features are designed to simplify compliance burdens, allowing the system to manage the regulatory complexity rather than forcing users into cumbersome manual processes. Ultimately, the implementation of such a system is presented as a strategic move to reduce operational risks, simplify the overall compliance posture, and significantly accelerate audit readiness. By transitioning to electronic records and automated signature workflows, organizations eliminate the time and inefficiency associated with chasing physical signatures, ensuring that all required documentation is immediately available and verifiable, thereby streamlining both internal and external regulatory reviews. Key Takeaways: • **Regulatory Necessity of Integrated Document Control:** QMS software must include a dedicated, integrated module for managing records and documentation to satisfy fundamental regulatory requirements, particularly those governing quality systems in the life sciences sector (e.g., 21 CFR 820). • **Centralized and Secured Cloud Infrastructure:** Utilizing centralized, cloud-hosted storage (such as Amazon services) provides essential data security, reliable backup, and ubiquitous accessibility, allowing global teams to access controlled documents from any supported device while maintaining data integrity. • **Scalable Document Structure is Crucial:** As the number of documents grows with business expansion, the underlying system for structuring and organizing documentation becomes a critical factor in maintaining an efficient and well-established QMS. • **Mandatory Compliance Features:** A compliant electronic document management system must include features such as robust versioning, formalized electronic approvals, comprehensive audit trails, and strict change control to ensure document integrity and traceability throughout its lifecycle. • **Audit Trail for 21 CFR Part 11 Compliance:** The comprehensive audit trail feature is vital for tracking every action taken on a document (creation, modification, access, approval), providing the necessary evidence for electronic records compliance required by regulatory bodies. • **Streamlining Approvals with Electronic Records:** Implementing electronic records and signatures eliminates the time wasted on manual signature collection, directly speeding up compliance workflows and ensuring that documents are formally approved in a timely, auditable manner. • **Risk Mitigation through Control:** Features like file locking and granular permissions are essential security measures that prevent unauthorized changes, restrict access to sensitive controlled documents, and maintain the overall integrity of the quality system documentation, thereby reducing regulatory risk. • **Efficiency in Audits:** The use of electronic records significantly simplifies and speeds up both internal and external audits by providing immediate, verifiable proof of compliance and adherence to established quality processes. • **Managing Through Quality (MTQ) Philosophy:** The integrated approach combines quality management processes with project management, ensuring that operational projects are inherently driven by quality requirements, leading to more efficient and compliant execution. Tools/Resources Mentioned: * qmsWrapper (Quality Management System Software) * Amazon Services (Used for cloud hosting and backup) Key Concepts: * **Document Management System (DMS):** A system designed to manage the lifecycle of documents, including creation, review, approval, distribution, and archival, ensuring compliance and control. * **Audit Trail:** An electronic record that chronologically logs all events and actions related to a document or record, providing an immutable history necessary for regulatory compliance (e.g., 21 CFR Part 11). * **Change Control:** A formal process used to manage modifications to controlled documents, ensuring that changes are reviewed, approved, and documented before implementation to maintain QMS integrity. * **Versioning:** The process of assigning unique identifiers to successive iterations of a document, ensuring that only the current, approved version is in use while maintaining access to historical records. * **Electronic Records:** Digital documentation and data that must be managed according to strict regulatory standards to ensure authenticity, integrity, and confidentiality.

Webinar Preview: Building a Business Case for Quality Management Transformation in Life Sciences
Veeva Systems Inc
/@VeevaSystems
Dec 1, 2020
This webinar preview outlines a strategic framework for justifying large-scale Quality Management (QM) transformations within the life sciences sector. The core objective is to equip quality professionals with the tools and language necessary to elevate the QM function from a necessary cost center to a recognized source of business value. The presentation emphasizes that successful transformation requires moving beyond traditional justifications—which often focus solely on achieving compliance—to demonstrating tangible financial and operational benefits that resonate with executive leadership. The central theme revolves around fundamentally changing the conversation surrounding quality. Instead of focusing on the "cost of quality," organizations must measure and articulate the "value of quality." This value must be quantified from dual perspectives: the patient perspective (e.g., improved safety, reduced risk) and the business perspective (e.g., revenue generation, cost savings). The speakers stress that executives—specifically the CEO and COO—do not understand the technical language of quality but respond directly to the language of business, which includes metrics like revenue, total cost of ownership (TCO), and brand image improvement. To illustrate the potential financial impact, the presentation provides a compelling example based on a hypothetical $10 billion company. A mere one percent increase in revenue attributed to improved quality could translate into $100 million. Furthermore, a 25% reduction in the cost of quality—a typical benchmark for organizations—could yield savings between $75 million and $125 million. These substantial figures underscore the necessity of framing the business case around key financial levers: revenue enhancement, cost reduction, inventory optimization, and, critically, the reduction of regulatory risk profile. For the quality organization to be "up-leveled" and demonstrate its worth, it must adopt this business-centric communication strategy, focusing on outcomes like improving brand image for the CEO and reducing TCO for quality systems. Key Takeaways: • **Shift from Cost to Value:** Quality organizations must transition their narrative from being a "cost of doing business" to a "value-added and respected partner" by quantifying the financial benefits derived from robust quality systems and processes. • **Executive Communication Strategy:** When presenting to executives, quality professionals must abandon technical quality jargon and adopt the language of business, focusing on metrics such as revenue growth, total cost of ownership (TCO) reduction, and brand image improvement. • **Quantifiable Financial Justification:** A successful business case must demonstrate anticipated benefits using hard numbers, such as the potential for a 1% revenue increase (equating to $100 million for a $10B company) or a 25% reduction in the cost of quality (yielding $75M–$125M in savings). • **Dual Value Measurement:** The value of quality must be measured and described from two critical angles: the patient perspective (e.g., safety, efficacy) and the business perspective (e.g., market advantage, operational efficiency). • **Key Business Levers:** The core components of a quality transformation business case should include projections for increased revenue, reduced operational costs, optimized inventory levels, and a significantly improved regulatory risk profile. • **TCO Reduction as a COO Focus:** When engaging the Chief Operations Officer (COO), the focus should be on reducing the total cost of ownership (TCO) for quality systems, demonstrating long-term operational efficiency and resource savings. • **Brand Image and CEO Alignment:** Discussions with the Chief Executive Officer (CEO) should center on how quality transformation improves the overall brand image and market trust, which directly impacts long-term shareholder value and market position. • **Transformation Requires Justification Experience:** Many organizations lack the internal experience needed to develop robust, financially-driven business cases required to justify large, disruptive projects, necessitating the adoption of structured frameworks for justification. • **Beyond Compliance:** While compliance is foundational, the transformative project must look well beyond merely achieving regulatory adherence, focusing instead on creating sustainable value and continuous improvement enabled by modern, cloud-based systems (as noted in the description). Key Concepts: * **Cost of Quality:** Traditional view of quality management expenses, often seen as overhead or a necessary regulatory burden. * **Value of Quality:** The measurable benefits derived from effective quality management, including financial savings, revenue generation, risk mitigation, and brand enhancement. * **Business Case Framework:** A structured methodology for calculating and presenting the anticipated benefits, costs, and risks associated with a major transformation project to gain executive approval. * **Pharma 4.0:** (Mentioned in description) The application of advanced technologies (like AI, IoT, and cloud systems) to optimize pharmaceutical manufacturing and quality processes, driving efficiency and compliance.

GSK: Tips for Fast and Coordinated Content Distribution
Veeva Systems Inc
@VeevaSystems
Nov 23, 2020
This video provides an in-depth exploration of how a major pharmaceutical company, GSK, ensures fast and coordinated content distribution by creating a seamless connection between content approval and field execution, leveraging the Veeva ecosystem. The central challenge addressed is bridging the gap between a material being approved in Veeva PromoMats and its actual execution in the field, followed by the subsequent capture of performance data for actionable insights. The speaker emphasizes that achieving this unique level of tracking and coordination hinges entirely on establishing and enforcing rigorous data standards. The core methodology discussed involves using consistent metadata and tagging as the foundational link. The speaker stresses that during the content authoring step—when content is created in programs like InDesign and moved into the production channel—it is critical to ensure that every tag, metadata field, or attribute is consistently inserted in the correct location. This consistency allows downstream systems, particularly business intelligence dashboards, to reliably pull the execution information back for tracking and analysis. Once this standard is established, the document number inside PromoMats becomes the "key" that unlocks the entire data flow. By tracing back to this single document number via a data lake, the system can access all associated metadata from PromoMats and marry it with execution data gathered from the field, ultimately feeding comprehensive insights onto a dashboard. A significant point of failure addressed is the common desire for "advanced tagging" without understanding system limitations. The speaker advises marketeers to refocus the conversation on the actual capability of the distribution channel. Tagging is only valuable if the channel is built to accept and utilize that specific bit of information. For instance, a tag can tell you *what* video was watched (content authoring information), but it is the *channel's capability* that records *how long* the video was watched. Understanding this distinction is critical for effective intelligent engagement. Furthermore, the company addressed past failures in taxonomy implementation by taking the opportunity during the PromoMats launch to start from scratch, introducing a global taxonomy to standardize language and tracking across all content and channels. The integration strategy leverages the native connectivity within the Veeva platform. The beauty of the Veeva ecosystem, according to the speaker, is that PromoMats inherently "speaks" to Veeva CRM, Approved Emails, and other options. This marriage of systems is facilitated by that single, common content document number or tag, ensuring that content moves fluidly from regulatory approval to commercial execution while maintaining a traceable audit trail and providing the necessary data foundation for advanced analytics and commercial optimization. Key Takeaways: • **Standards are the Foundation for Tracking:** The ability to track content from production (PromoMats) to execution in the field and back to a dashboard is dependent on rigorous, enforced standards for metadata and tagging established during the initial content authoring phase. • **PromoMats Document Number as the Integration Key:** The unique document number assigned within PromoMats serves as the essential common identifier. Leveraging this number allows systems to trace execution data back to the original approved content and retrieve all associated metadata. • **Data Lake Facilitates System Marriage:** Utilizing a data lake is crucial for aggregating data. It acts as the central hub where the metadata retrieved from PromoMats is successfully married with the execution data captured from field channels (like CRM), enabling comprehensive insight generation via dashboards. • **Refocus Tagging Strategy on Channel Capability:** Instead of aiming for generalized "advanced tagging," commercial teams must clarify the specific capabilities of the distribution channel. A tag is only useful if the channel can accept and process that information to achieve the desired tracking goal. • **Distinguish Content Tags from Channel Data:** Understand the difference between information provided by the content itself (e.g., what video was watched, tracked via a tag) and information provided by the channel (e.g., how long the video was watched, tracked via channel functionality). • **Global Taxonomy Implementation is Critical:** Past failures in content tracking often stem from a lack of taxonomy adoption. Launching a new platform (like PromoMats) provides a strategic opportunity to start fresh and enforce a global taxonomy to ensure consistency across all content types and channels. • **Veeva Ecosystem Simplifies Integration:** The inherent connectivity of Veeva platforms (PromoMats, CRM, Approved Emails) streamlines the integration process, allowing the common content document number to serve as the consistent link across the entire commercial content lifecycle. • **Metadata Consistency Drives Insights:** Ensuring that metadata is consistent and inserted in the right place allows dashboards and BI systems to reliably pull information back, transforming raw execution data into actionable commercial insights for marketeers. Tools/Resources Mentioned: * Veeva PromoMats * Veeva CRM * Veeva Approved Emails * InDesign (Content authoring program example) * Data Lake Key Concepts: * **Global Taxonomy:** A standardized, shared classification system used across all content and platforms to ensure consistency in tagging and data retrieval. * **Intelligent Engagement:** The strategic use of data and technology (like consistent tagging and integrated systems) to deliver highly relevant and personalized content to healthcare professionals and customers. * **Metadata/Tagging:** Descriptive data embedded within content files that provides context, enabling systems to track, categorize, and integrate the content across different platforms.

TMF/eTMF Regulatory Agency Expectations, Inspections, and Findings
Kathy Barnett
/@kathybarnett4070
Nov 21, 2020
This video provides an in-depth exploration of regulatory expectations, inspections, and findings related to Trial Master Files (TMF) and electronic Trial Master Files (eTMF) in clinical investigations. Presented by Donna Dorinsky, a recognized subject matter expert in TMF and inspection readiness and a member of the TMF reference model steering committee, the session aims to equip participants with strategies for maintaining regulatory compliance and preparing for successful outcomes during TMF inspections. The overarching goal is to ensure that pharmaceutical companies are fully prepared from a TMF perspective when seeking regulatory approval for new drugs, emphasizing that the TMF is the complete narrative of a study. The presentation delves into the critical role of the TMF, describing it as "the story of your study"—a standalone set of documentation that should clearly articulate the entire trial without requiring extensive external explanation. Dorinsky shares a compelling anecdote about an FDA inspection where a meticulously remediated TMF led to an inspector concluding the TMF was in "excellent shape" after just three days, requiring minimal interaction with clinical personnel. This experience underscores the ideal state where the TMF itself provides a comprehensive and assessable record, enabling evaluation of trial conduct, data integrity, and compliance with Good Clinical Practice (GCP) standards. It is highlighted that the TMF represents a collective output of information from all functional areas involved in a study. A significant portion of the discussion focuses on essential documents, as defined by ICH E6, which are crucial for assessing trial conduct, data quality, and compliance with GCP. The video specifically references the 2016 revision, ICH E6 R2 (Integrated Addendum), which clarified expectations around TMF management. A key takeaway from this revision is the explicit requirement for both the sponsor and the investigator to maintain a record of the locations of their respective essential documents. Dorinsky emphasizes that regulatory bodies like the EMA and ICH consider the TMF to be comprised of documentation held by both the sponsor and the investigator (including site files). The speaker also addresses a practical challenge: even with the adoption of eTMF systems, it is rare for 100% of all essential documents to be consolidated in one single, human-readable format within a single system. Key Takeaways: * **TMF as the Study Narrative:** The Trial Master File (TMF) is fundamentally "the story of your study," serving as a standalone, comprehensive collection of documentation that should clearly explain the entire clinical trial without needing additional context. Its primary purpose is to ensure readiness for regulatory approval. * **Regulatory Inspection Readiness:** A well-maintained TMF is crucial for successful regulatory inspections. The speaker shared an experience where a highly organized TMF significantly streamlined an FDA inspection, demonstrating the power of a complete and accessible record. * **Core Functions of TMF:** The TMF enables the assessment of trial conduct, the evaluation of the integrity of trial data, and verification of compliance with Good Clinical Practice (GCP) standards, making it indispensable for regulatory oversight. * **Collective Effort:** The TMF is a collective output of information contributed by all functional areas involved in a clinical study, highlighting the need for cross-functional collaboration and standardized processes. * **Essential Documents Defined by ICH E6:** Essential documents, as defined in ICH E6, are those that individually and collectively permit the evaluation of trial conduct, data quality, and compliance of investigators, sponsors, and monitors with GCP standards. * **ICH E6 R2 Updates on TMF:** The 2016 ICH E6 R2 (Integrated Addendum) clarified that both the sponsor and the investigator are required to maintain a record of the locations of their respective essential documents, underscoring shared responsibility. * **Dual TMF Ownership:** Regulatory bodies like the EMA and ICH explicitly state that the TMF encompasses documentation held by both the sponsor and the investigator (including investigator site files), emphasizing a broader scope for TMF management. * **Challenges with eTMF Consolidation:** A practical challenge in TMF management is that even with electronic TMF (eTMF) systems, it is uncommon for 100% of all essential documents to be located and consolidated in a single, human-readable format within one system. * **Proactive CAPA Planning:** The presentation encourages participants to identify potential regulatory findings related to TMF and proactively develop Corrective and Preventive Action (CAPA) plans to address these issues, leading to successful inspection outcomes. * **Importance of Location Tracking:** Given that TMF documents may reside in multiple locations, maintaining an accurate record of where essential documents are held is a critical regulatory expectation. Tools/Resources Mentioned: * **TMF Reference Model:** A standardized, hierarchical model for classifying and organizing TMF documents, which the speaker is a steering committee member of. * **ICH E6 (R2) Integrated Addendum:** International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use, Guideline for Good Clinical Practice, Revision 2. Key Concepts: * **Trial Master File (TMF):** A collection of essential documents that individually and collectively permit the evaluation of the conduct of a clinical trial, the quality of the data produced, and the adherence to regulatory requirements. * **Electronic Trial Master File (eTMF):** A digital system for managing and storing TMF documents. * **Good Clinical Practice (GCP):** An international ethical and scientific quality standard for designing, conducting, recording, and reporting trials that involve the participation of human subjects. * **Corrective and Preventive Actions (CAPA):** A system for identifying, documenting, and resolving non-conformances or deviations, and preventing their recurrence. * **Essential Documents:** Documents that permit the evaluation of the conduct of a trial and the quality of the data. * **Sponsor:** The individual, company, institution, or organization that takes responsibility for the initiation, management, and/or financing of a clinical trial. * **Investigator:** The person responsible for the conduct of the clinical trial at a trial site. * **Inspection Readiness:** The state of being prepared for regulatory inspections by ensuring all documentation and processes are compliant and accessible. Examples/Case Studies: * **FDA TMF Inspection Anecdote:** The speaker recounted an experience where nine months of work to remediate a TMF resulted in an FDA inspector declaring the TMF in "excellent shape" after just three days of a four-day inspection, requiring minimal interaction with clinical personnel. This highlights the effectiveness of a well-prepared TMF in streamlining regulatory reviews.

Novo Nordisk: Content Journey with Vault PromoMats
Veeva Systems Inc
/@VeevaSystems
Nov 20, 2020
This video provides an in-depth exploration of Novo Nordisk’s strategic content journey following the implementation of Veeva Vault PromoMats. The discussion centers on how the pharmaceutical giant leveraged the platform not just for content logistics, but as a fundamental enabler for advanced multi-channel customer engagement. The speaker emphasizes that the initial driver for the project was to "change the conversation" within the organization, shifting the focus from mere content production and delivery to optimizing engagement capabilities. A core strategic pillar of Novo Nordisk's initiative is the adoption of **modular content**. This approach was identified as relevant because it directly addresses the challenge of multi-channel deployment. By breaking content down into reusable, compliant modules, the organization can easily repurpose assets across numerous channels without the significant effort traditionally associated with adapting content for different platforms. This methodology is crucial for scaling personalized and timely customer interactions across the life sciences ecosystem. Regarding the technical implementation, the speaker characterized the process of deploying PromoMats as "uneventful," which was intended as a significant compliment. This smooth rollout was attributed to clear objectives, strong internal team focus, and effective collaboration with Veeva. Key areas of focus during the implementation included simplifying complex workflows and streamlining the organization’s reference management processes. The subsequent operational learning highlighted the critical need to centralize work around both reference and content management to fully achieve the intended benefits of the Veeva Vault platform. Novo Nordisk stressed the importance of strategic partnerships in maximizing their investment. They noted that Veeva has acted as a "tremendous partner" alongside other specialized firms in the field. This partnership is vital for navigating the platform's capabilities and ensuring that the technological setup—particularly the modular content architecture—is aligned with the company’s overarching strategic direction for customer engagement. The success hinges on understanding the "bigger picture" and maintaining a clear vision of where the organization is heading strategically. Key Takeaways: • **Content as an Engagement Enabler:** Novo Nordisk views content management not as a logistical task, but as a strategic enabler for sophisticated multi-channel customer engagement, necessitating a shift in internal conversation and focus away from simple production metrics. • **Modular Content is Essential for Scale:** The adoption of modular content is critical for success in multi-channel strategies, as it drastically reduces the effort required to repurpose and deploy compliant content across various digital and traditional channels. • **Prioritize Workflow and Reference Simplification:** Successful implementation of Veeva PromoMats relies heavily on upfront efforts to simplify existing organizational workflows and establish robust, clear processes for reference management, which is foundational for compliance. • **Centralization is Key to Maximizing Vault Benefits:** Novo Nordisk learned that centralizing the management of references and content is necessary to truly unlock the efficiency and compliance benefits offered by the Veeva Vault platform. Decentralized content operations hinder the realization of the system’s full potential. • **Implementation Success Requires Clear Focus:** Describing the PromoMats implementation as "uneventful" suggests that clear objectives, strong internal team preparation, and defined collaboration parameters with the vendor are essential for a smooth, low-friction rollout. • **Strategic Partnership is Crucial:** Leveraging specialized partners, including Veeva, is necessary to fully understand the platform’s capabilities and ensure that the technical architecture (like modular content setup) aligns precisely with the company’s long-term commercial strategy. • **Focus on the Strategic End Goal:** Organizations must clearly define their strategic direction—specifically regarding multi-channel customer interaction—before and during implementation to ensure that the content management system is configured to support those high-level business objectives. • **Compliance Streamlining:** The focus on simplifying reference management workflows directly supports regulatory compliance, ensuring that all content components are properly linked to approved source materials, a critical requirement in the pharmaceutical industry. Tools/Resources Mentioned: * Veeva Vault PromoMats Key Concepts: * **Modular Content:** A content strategy where assets are broken down into small, reusable, and pre-approved components (modules). This allows for rapid assembly and deployment of compliant content across multiple channels without requiring a full review cycle for every piece. * **Multi-Channel Customer Engagement:** A commercial strategy focused on interacting with healthcare professionals (HCPs) and patients across a variety of coordinated digital and traditional channels, requiring highly flexible and rapidly deployable content. * **Reference Management:** The process of linking promotional and medical content to its approved scientific sources (references), which is a mandatory requirement for regulatory compliance (e.g., FDA, EMA) in the life sciences industry. Examples/Case Studies: * **Novo Nordisk Implementation:** The video serves as a case study detailing Novo Nordisk's experience implementing Veeva Vault PromoMats, highlighting their strategic shift toward modular content and their focus on simplifying internal processes like reference management to achieve greater efficiency and compliance.