Videos
Browse videos by topic
All Videos
Showing 1201-1224 of 1435 videos

Remote Monitoring for Sponsors and CROs
Veeva Systems Inc
/@VeevaSystems
Jun 2, 2020
This demonstration provides a detailed walkthrough of the remote monitoring workflow for sponsors and Contract Research Organizations (CROs) utilizing Veeva SiteVault Free, an eRegulatory system designed for clinical research sites. The primary purpose is to illustrate how monitors can efficiently perform Source Data Review (SDR) and Source Data Verification (SDV) remotely, streamlining the traditionally manual process of clinical trial oversight while ensuring compliance. The presentation focuses on the monitor’s perspective, highlighting the platform’s features for task management, document interaction, and reporting. The workflow begins with the site sending documents for review, triggering immediate email and homepage notifications for the assigned monitor. Upon logging into SiteVault, the monitor accepts the review task, which opens an envelope of documents. A key feature is the intuitive left-hand navigation panel, allowing the monitor to quickly move between documents within the task. The process involves active review, where the monitor can resolve existing site annotations or create new ones. For instance, if the monitor identifies a discrepancy—such as a mismatch between the visit date on the source document and the data entered into the Electronic Data Capture (EDC) system—they can highlight the specific data point and tag the site with an annotation detailing the issue. After reviewing each document, the monitor assigns a verdict, choosing from options like "resolved comment," "issues annotated and returned to the site," "no review required" (supporting risk-based monitoring strategies), or "no issues." Once the task is complete, the monitor receives a summary of all verdicts provided across the document set. Beyond individual task completion, the platform emphasizes high-level oversight through integrated reports and dashboards. Monitors can filter these dashboards by study to view the overall Source Document Review status and, critically, drill down into specific safety-related issues. The system allows monitors to easily identify documents flagged by the site as surrounding a protocol deviation or an Adverse Event (AE), enabling focused attention on high-risk data points. The final segment of the demonstration covers essential document management capabilities, particularly the integration with the Electronic Trial Master File (eTMF). The monitor can navigate the SiteVault library, which features Optical Character Recognition (OCR) functionality, enabling searches within the content of documents rather than just metadata. This is demonstrated by searching for a sub-investigator’s CV using a keyword like "Yale," quickly retrieving the necessary document. Monitors can add required documents (like CVs or source documents) to a digital "cart" and then download them in bulk. This download function facilitates the seamless transfer of verified, compliant documents out of SiteVault and into the sponsor’s eTMF system, ensuring the TMF remains current and complete. Key Takeaways: • **Streamlined Remote Monitoring Workflow:** Veeva SiteVault Free centralizes the SDR/SDV process, initiating review via automated notifications (email and homepage) and providing a structured interface for monitors to accept and manage document review tasks efficiently. • **Real-Time Discrepancy Flagging:** Monitors can annotate specific data points directly on the source documents and tag the site immediately when discrepancies are found, such as mismatches between the source document data and the EDC system entry, accelerating query resolution. • **Verdict-Based Task Completion:** The system requires monitors to assign a specific verdict to each document ("issues annotated," "no issues," "no review required"), creating a clear audit trail and supporting risk-based monitoring strategies by allowing monitors to bypass full verification on low-risk documents. • **Centralized Reporting for Oversight:** Dashboards provide a high-level view of the overall source document review status per study, allowing sponsors and CROs to track progress and identify bottlenecks across multiple sites. • **Risk-Based Monitoring Focus:** The platform enables monitors to filter reports specifically for documents related to critical safety events, such as Adverse Events (AEs) or protocol deviations, ensuring immediate attention is paid to high-risk data elements. • **OCR-Powered Document Retrieval:** The library utilizes Optical Character Recognition (OCR) capability, allowing users to search within the actual content of documents (e.g., searching for a university name on a CV), significantly improving the speed and accuracy of locating specific compliance records. • **Seamless eTMF Integration:** The "cart" feature allows monitors to batch select and download verified source documents and essential regulatory documents (like CVs), facilitating rapid transfer and integration into the sponsor’s Electronic Trial Master File (eTMF) system. • **Audit Trail and Compliance:** By managing the entire review and verification process within a validated system like SiteVault, the platform inherently supports regulatory compliance by maintaining a clear, time-stamped record of all review actions, annotations, and final verdicts. Tools/Resources Mentioned: * Veeva SiteVault Free (eRegulatory system for clinical research sites) * Electronic Data Capture (EDC) * Electronic Trial Master File (eTMF) Key Concepts: * **Source Data Review (SDR):** The process of reviewing source documents to ensure the data is accurate, complete, and consistent with the protocol and regulatory requirements. * **Source Data Verification (SDV):** The process of comparing source documents against the data entered into the EDC system to confirm accuracy. * **Optical Character Recognition (OCR):** Technology used to enable text searchability within images or scanned documents, allowing the system to index and retrieve documents based on their content. * **Protocol Deviation:** An instance where the conduct of a clinical trial deviates from the approved protocol. * **Adverse Event (AE):** Any untoward medical occurrence in a patient or clinical investigation subject administered a pharmaceutical product.
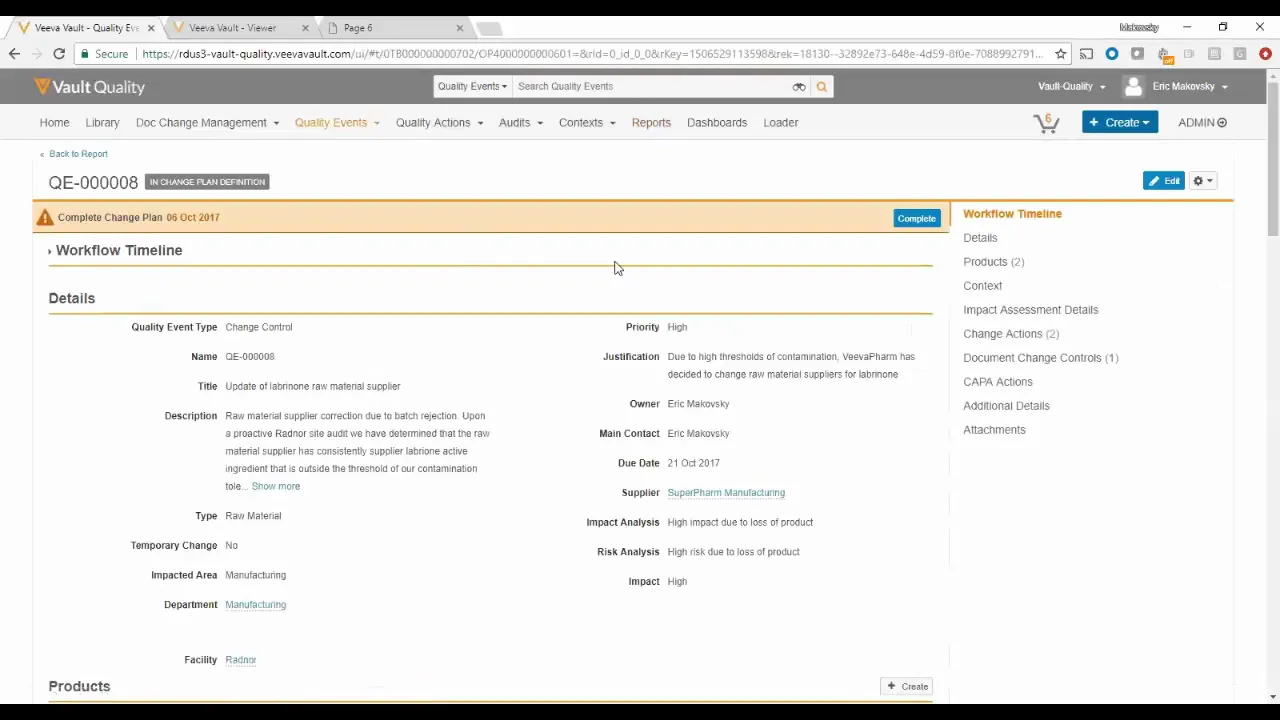
Eliminate System, Site, and Country Silos with Veeva Development Cloud
Veeva Systems Inc
/@VeevaSystems
Jun 1, 2020
The video provides a detailed demonstration of how the Veeva Development Cloud unifies critical business processes across Quality, Regulatory, and Clinical functions within the life sciences enterprise, effectively eliminating system and site silos. The presentation follows a single, interconnected workflow initiated by a significant quality event: the discovery of discolored pills leading to batch destruction and halted production at a facility. The core purpose of the demonstration is to showcase the power of a connected platform to manage complex, cross-functional compliance and operational changes rapidly and efficiently. The workflow begins with a Quality Event lodged regarding product discoloration. Upon reviewing the severity, which included visual evidence of the defect, the team agrees to launch a formal investigation. Crucially, the system immediately links the quality event data to historical supplier performance. By reviewing the supplier dashboard, the team confirms that the manufacturer, "Super Farm Manufacturing," has a history of infractions, including a previous issue with "bug parts" and hitting a threshold of four deviations, which automatically triggered a Change Control process. This seamless transition from quality investigation to supplier management highlights the platform's ability to provide empirical evidence supporting operational decisions, moving beyond anecdotal concerns. The demonstration then transitions into the regulatory domain, focusing on the active Change Control process initiated due to the supplier's poor performance. A key change action identified is the filing of a Chemistry, Manufacturing, and Controls (CMC) variation for the US market. Within the Veeva platform, the regulatory team can view the submission status and the associated Content Plan. A significant feature showcased is the use of Vault Publishing, which enables continuous, incremental validation and publishing of submission documents. Instead of waiting until all documents are collected to begin the arduous publishing process, the system validates and publishes documents to the submission archive as they are collected. The presenters illustrate resolving a missing document placeholder (marked as "half yellow" because there was "no match document") by manually matching the correct file from the library. Once the final document is added, the system immediately generates the complete, validated eCTD format output, ready for submission to the FDA or distribution to affiliates, demonstrating an end-to-end process—from deviation to published regulatory output—completed in approximately five minutes. Key Takeaways: • **Unified Enterprise Workflow:** The Veeva Development Cloud enables a single, interconnected process flow linking Quality Events, Supplier Management, Change Control, and Regulatory Submissions, ensuring that actions taken in one functional area immediately inform and trigger necessary steps in others. • **Data-Driven Quality Decisions:** The system facilitates moving beyond anecdotal evidence by providing immediate access to empirical data, such as the supplier dashboard, which confirmed a history of infractions (e.g., four deviations) for "Super Farm Manufacturing," justifying the initiation of a change control process. • **Automated Change Control Triggering:** Hitting predefined thresholds (e.g., four deviations) can automatically initiate complex processes like Change Control, ensuring proactive management of risks associated with suppliers or internal operations. • **Continuous Regulatory Publishing:** Vault Publishing eliminates the high-risk, time-consuming "big bang" publishing event at the end of a submission cycle. Documents are continuously and incrementally validated and published to the submission archive in the required eCTD format as they are collected. • **Real-Time Submission Status:** The Content Plan view provides a clear, color-coded status of submission readiness, indicating which documents are collected and successfully validated/published (green) versus those requiring manual matching or collection (half yellow/missing). • **Seamless Regulatory Output Generation:** The platform automatically generates the full, validated eCTD format, complete with leaf information, immediately upon the final document being added, allowing the output to be pushed directly to the gateway (e.g., FDA) or downloaded for affiliate distribution without further manual steps. • **Efficiency Gains in Compliance:** The demonstration highlighted the ability to execute a complex, cross-functional process—from initial quality deviation review to generating a validated regulatory submission output—in approximately five minutes, dramatically reducing cycle time and risk. • **Elimination of Silos:** By connecting clinical, regulatory, and quality data, the platform ensures that all relevant departments are working off the same, current information, preventing delays and compliance risks associated with disparate systems. Tools/Resources Mentioned: * **Veeva Development Cloud:** The overarching platform integrating various life sciences functions. * **Vault Publishing:** The specific module responsible for automating the continuous validation and generation of regulatory submission formats (eCTD). Key Concepts: * **Quality Event:** An incident requiring investigation and documentation, such as the reported discoloration of pills. * **Change Control:** A formal process used to manage and document changes to validated systems, products, or processes, often triggered by deviations or supplier issues. * **CMC Variation (Chemistry, Manufacturing, and Controls Variation):** A regulatory filing required when changes are made to the manufacturing process, facility, or supply chain of a marketed drug product. * **Content Plan:** A structured outline within the regulatory system detailing all required documents for a submission. * **eCTD Format (Electronic Common Technical Document):** The standardized structure required by regulatory bodies (like the FDA and EMA) for electronic submissions. * **Continuous Publishing:** A methodology where submission documents are incrementally validated and published in real-time as they are collected, rather than waiting for the entire package to be complete. Examples/Case Studies: * **Quality Incident:** Discoloration of pills found in the Brandner facility, leading to halted production and batch destruction. * **Supplier Risk:** Super Farm Manufacturing was identified as a high-risk supplier due to a history of multiple infractions, including a previous issue with "bug parts," which triggered the Change Control process.

Isolocity - EQMS
Isolocity
/@isolocity
May 27, 2020
This video provides an overview of Isolocity’s Electronic Quality Management System (EQMS), positioning it as a modern, automated solution designed to replace taxing and complicated paper-based or outdated systems used for regulatory compliance and production management. The core purpose of the EQMS is to streamline operations, particularly for large enterprises and small batch production facilities in regulated industries, by leveraging globally recognized compliance certifications and a modern approach to quality assurance. The system is presented as the future of production management, focusing heavily on security, centralization, and workflow automation. The EQMS functions as a secure, central access point for all operational data and documentation. A key feature highlighted is the robust change control procedure, which is essential for regulated environments, ensuring that updates and modifications occur without causing disruption of services or inefficient use of resources. Furthermore, the platform incorporates a multi-stage document approval system, mandating that critical documents are formally signed off by designated department heads or document owners before being released for circulation, thereby maintaining strict version control and accountability necessary for GxP compliance. A significant portion of the system’s value lies in its automated management capabilities for critical quality events. The platform automates the handling of Corrective and Preventive Actions (CAPA), deviations, change requests (CR), and complaint management. This automation allows users to rely on the system to proactively catch errors and manage the entire lifecycle of a quality event. Beyond incident management, the EQMS manages the frequency and due dates for recurring compliance activities, including reports, approvals, mandatory training, and inspections. Uniquely, the system can also automate requests sent directly to suppliers, significantly streamlining supplier quality management and reducing manual administrative load. Finally, the video emphasizes the ease of managing personnel training and production data. The platform features a template builder and document linking feature for designing training programs. This allows users to easily link and update new versions of compliance documents, ensuring training materials adapt instantly with evolving industry standards, which can then be scheduled for personnel with a single click. For production oversight, the EQMS facilitates the management of batch paperwork digitally, providing real-time digital analytics for immediate quality insights, moving beyond time-consuming paper trails. ### Key Takeaways: * **Automation of Core Compliance Processes:** The Isolocity EQMS focuses on automating the most burdensome compliance tasks, specifically CAPA, deviation tracking, change requests (CR), and complaint management, allowing organizations to shift from reactive error correction to proactive system oversight. * **Centralized and Secure Access:** The system acts as a single, secure repository for all operational data, documentation, and quality records, which is crucial for maintaining data integrity and facilitating efficient audits in regulated environments. * **Robust Change Control:** Integrated change control procedures are designed to mitigate operational risk by managing resource allocation and preventing service disruptions when system or process modifications are implemented. * **Mandatory Multi-Stage Document Approval:** To ensure regulatory adherence, documents must pass through a multi-stage approval workflow, requiring sign-off from designated department heads or document owners before they are officially circulated. * **Proactive Task and Due Date Management:** The EQMS automatically tracks the frequency and due dates for all mandatory compliance action items, including internal reports, approvals, training cycles, and external inspections, significantly reducing the risk of non-compliance due to missed deadlines. * **Integrated Supplier Quality Management:** The platform extends its automation capabilities to the supply chain by allowing the system to generate and send requests directly to suppliers, streamlining the process of gathering necessary compliance documentation from external partners. * **Dynamic Training Program Management:** Training programs are simplified using template builders and a critical document linking feature that automatically updates training modules when the underlying compliance documents (like SOPs) are revised, ensuring employees are always trained on the latest standards. * **Real-Time Batch Analytics:** The digitization of batch paperwork enables the use of real-time digital analytics, providing immediate quality control insights and moving away from retrospective, paper-based review processes that often delay production release. * **Focus on Global Regulatory Standards:** The system explicitly leverages "globally recognized compliance certifications," indicating that the EQMS architecture is designed to meet international regulatory requirements, which is essential for pharmaceutical and biotech companies operating across multiple jurisdictions (e.g., FDA and EMA). ### Tools/Resources Mentioned: * **Isolocity EQMS:** An Electronic Quality Management System designed for automating compliance and production processes. ### Key Concepts: * **EQMS (Electronic Quality Management System):** A software system that manages and automates quality-related processes and documentation, replacing traditional paper-based methods to improve efficiency and compliance. * **CAPA (Corrective and Preventive Actions):** A system for investigating, documenting, and resolving nonconformities (corrective actions) and preventing potential future nonconformities (preventive actions). * **Change Control:** A formal process used to manage and document changes to critical systems, documents, or processes to ensure quality and regulatory compliance are maintained. * **Deviation Management:** The process of identifying, documenting, evaluating, and resolving departures from approved procedures or specifications during manufacturing or testing. * **Batch Paperwork:** The comprehensive set of records and documentation required to prove that a specific batch of product was manufactured, tested, and released according to defined procedures and regulatory requirements.

COVID-19’s Impact on Scientific Engagement interview
Veeva Systems Inc
@VeevaSystems
May 26, 2020
This video provides an in-depth exploration of the profound and sudden impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on scientific engagement within the pharmaceutical industry, focusing specifically on the role of Medical Science Liaisons (MSLs) and Medical Affairs organizations. The discussion, featuring Brian Harper, VP of Medical Content Strategy at Veeva Systems, frames the pandemic as the "ultimate digital restructure," forcing immediate and long-term changes in how pharmaceutical companies disseminate scientific data and interact with Healthcare Professionals (HCPs). The immediate effects included the near-total cessation of face-to-face engagements, canceled conferences and congresses, and a rapid pivot to virtual platforms like Zoom and Skype for scientific exchange. The analysis highlights that this shift necessitated MSLs to quickly adopt new skills to ensure virtual interactions remained effective, efficient, and maintained continuity with previous field discussions. A key insight derived from an MSL Society study validated the rapid uptake of virtual platforms and revealed significant shifts in MSL activities. With reduced travel and in-office visits, MSLs dedicated more time to reviewing scientific literature to strengthen their therapeutic knowledge and supported other functions within Global Medical Affairs (GMA). Notably, Medical Information teams experienced a spike in activity and requests, particularly those related to COVID-19, leading to MSLs being redeployed to support these functions and manage increased demand. A critical finding regarding virtual engagement was the duration of these interactions. MSLs were able to carry on conversations with HCPs ranging from five to thirty minutes. This finding has significant implications for content strategy, requiring organizations to fuel these engagements with highly effective, compliant, and correctly versioned content tailored for shorter, focused virtual interactions. Furthermore, the speakers noted that scientific experts (HCPs) demonstrated a newfound receptivity to virtual engagements, likely influenced by their own shift to telemedicine with patients. This suggests that virtual engagement is not a temporary fix but will become a permanent, strategic component of scientific and thought leader engagement plans moving forward, requiring companies to optimize their business processes accordingly. The video also addresses the challenge of data dissemination in the absence of traditional medical conferences. The cancellation of these large-scale events forces organizations to develop non-traditional methods to get their data out to a broad audience in a meaningful way. This environment elevates the value of Medical Information teams, which remain the primary conduit for fielding specific medical requests. The need to staff and flex Medical Information teams—potentially by integrating MSLs or other GMA experts—to meet increased demand underscores the necessity for robust, scalable systems and processes to manage the influx of scientific inquiries and ensure timely, compliant responses. Key Takeaways: • **Digital Restructure Acceleration:** The pandemic acted as the "ultimate digital restructure," immediately eliminating traditional face-to-face MSL engagements and forcing a rapid, industry-wide pivot to virtual platforms (Zoom, Skype) for scientific exchange. • **New MSL Skill Requirements:** MSLs must acquire and refine new skills specifically for delivering engaging and effective virtual interactions to maintain business continuity and ensure discussions with HCPs are efficient and productive. • **Shift in MSL Focus:** With reduced travel, MSLs are spending more time on internal activities, including deeper dives into scientific literature to strengthen therapeutic knowledge and supporting other Global Medical Affairs (GMA) functions. • **Spike in Medical Information Demand:** Medical Information teams saw a significant increase in call volume and requests, particularly those related to COVID-19, necessitating organizations to assess and potentially flex staffing models by leveraging MSLs to support the increased demand. • **Optimizing Content for Virtual Engagement:** The duration of virtual conversations (5 to 30 minutes) requires organizations to rethink content strategy, ensuring MSLs have access to compliant, high-quality, and appropriately versioned content tailored for shorter, highly focused digital interactions. • **HCP Receptivity to Virtual:** Scientific experts are now generally receptive to virtual engagements, suggesting a permanent shift in interaction preference, likely influenced by their own adoption of telemedicine. • **Permanent Component of Strategy:** Virtual engagement is not a temporary measure but will become a fixed, strategic component of future scientific engagement and thought leader plans, requiring long-term optimization of business processes. • **Non-Traditional Data Dissemination:** The cancellation of major congresses forces companies to explore and implement non-traditional, digital methods for disseminating critical scientific data to a broad audience effectively. • **Value of Medical Information:** The Medical Information function is critical in the new environment, serving as the primary channel for fielding specific medical requests and demonstrating its value by ensuring customers receive necessary information despite disruptions to traditional channels. • **Systemic Optimization Required:** Companies must look beyond immediate fixes and focus on optimizing their core business processes to integrate virtual engagement seamlessly, ensuring long-term efficiency and compliance in the new hybrid environment. Tools/Resources Mentioned: * Veeva Systems (Host and context provider) * Zoom (Virtual engagement platform) * Skype (Virtual engagement platform) * MSL Society (Source of the study quantifying the impact on MSL activities) * Veeva Commercial & Medical Summit Online (Upcoming industry event focused on medical affairs strategy) Key Concepts: * **Scientific Engagement:** The interaction between pharmaceutical company representatives (like MSLs) and Healthcare Professionals (HCPs) to exchange scientific and medical information. * **MSL (Medical Science Liaison):** Field-based professionals within Medical Affairs who engage with key opinion leaders (KOLs) and HCPs to discuss scientific data and therapeutic areas. * **Global Medical Affairs (GMA):** The department responsible for ensuring the scientific and medical integrity of a company's products, including managing MSLs and Medical Information. * **Medical Information:** The team responsible for receiving, documenting, and responding to unsolicited requests for medical information from HCPs and consumers. * **Digital Restructure:** The forced, rapid transformation of business models and processes toward digital methods, catalyzed by external events like the pandemic.

Conexus - What We've Learned From Implementing Veeva
Anthony Bianciella - CNX
/@conexussolutionsinc.1740
May 20, 2020
This video provides an in-depth exploration of best practices and critical lessons learned from implementing and configuring Veeva CRM systems and associated modules within the pharmaceutical industry. Presented by Praveen Seneca, the Chief Information Officer of Connexus, the insights are drawn from over 30 successful Veeva CRM system and module deployments over the past three years. The primary goal of the presentation is to share actionable advice to ensure future Veeva projects—whether new implementations or module additions—run more efficiently and smoothly, focusing heavily on commercial operations and regulatory adherence. The presentation immediately addresses the rapid shift in pharmaceutical commercial engagement driven by the COVID-19 pandemic, specifically the dramatic increase in the use of "approved emails" as face-to-face detailing became restricted. The speaker notes that clients are typically utilizing around 15 distinct email templates for a variety of communications, including branded and non-branded messaging, clinical data follow-up, invitations to online detailing sessions, and general thank you notes. A key observation is the corresponding rise in email open rates. However, the success of this digital channel hinges on a critical operational detail: ensuring a reliable and validated source of email addresses. This often overlooked data engineering task must be prioritized, and any purchased email lists must be regularly validated, opted-in, and fully compliant with the Can-Spam Act. Beyond general email hygiene, the video highlights a specific and complex regulatory challenge: compliance with the Colorado Wholesale Acquisition Cost (WAC) disclosure requirements. If an email is used to market a drug, the WAC information must be made available to the targeted Healthcare Professional (HCP). The speaker provides a practical, targeted solution for managing this state-specific regulation: instead of applying the disclosure to all email templates, companies should use targeted email templates specifically designed for HCPs practicing in Colorado. This approach ensures regulatory compliance without unnecessarily complicating communications for the broader, non-Colorado audience. Finally, the presentation offers strategic advice for implementing complex Veeva modules, such as Veeva Vault and the Events module. The recommendation is to initially leverage the out-of-the-box (OOTB) functionality for a period. This strategy allows the organization to quickly bring core functionality online and gain familiarity with the system's standard capabilities. Only after this initial phase should the business modify or customize the workflows to suit unique business processes, thereby accelerating the time-to-value for the new functionality. Key Takeaways: * **Prioritize Email Data Quality:** Despite often being placed on the back burner, securing a reliable, valid, and opted-in source of HCP email addresses is paramount for successful Veeva Approved Email implementation and commercial outreach. * **Approved Email Usage Volume:** Clients are typically deploying approximately 15 different approved email templates to cover the range of commercial communications, including clinical data sharing, invitations, and branded/non-branded follow-up. * **Can-Spam Compliance is Mandatory:** All email marketing practices within Veeva CRM must strictly adhere to the requirements of the Can-Spam Act to maintain legal compliance and data integrity. * **Address Colorado WAC Requirements:** Pharmaceutical companies marketing drugs via email must ensure the Wholesale Acquisition Cost (WAC) disclosure information is accessible to HCPs practicing in Colorado. * **Targeted Compliance Solution:** The most efficient way to meet the Colorado WAC disclosure requirement is by creating and utilizing targeted email templates specifically for Colorado-based HCPs, avoiding unnecessary disclosure complexity for the entire national audience. * **Leverage OOTB Functionality First:** When implementing complex modules like Veeva Vault or the Events module, begin by utilizing the out-of-the-box functionality to achieve quick deployment and system familiarity. * **Phased Customization Strategy:** Customization and modification of workflows to suit unique business needs should be undertaken only after the organization has successfully deployed and used the standard, out-of-the-box functionality for a period. * **Digital Engagement Surge:** The shift away from face-to-face detailing during the COVID-19 lockdown led to a significant increase in the use of approved emails and a corresponding rise in observed open rates, highlighting the importance of robust digital channels. * **Focus on Workflow Complexity:** Workflows associated with advanced modules like Veeva Vault and Events can be inherently complex; starting with standard functionality reduces initial implementation friction and accelerates the time-to-value. Tools/Resources Mentioned: * Veeva CRM * Veeva Vault * Veeva Events Module Key Concepts: * **Approved Emails:** A core Veeva CRM functionality allowing pharmaceutical sales and medical teams to send pre-approved, compliant email communications to HCPs. * **Can-Spam Act:** U.S. law setting the rules for commercial email, establishing requirements for commercial messages, giving recipients the right to have emails stopped, and outlining penalties for violations. * **Colorado Wholesale Acquisition Cost (WAC) Disclosure:** A specific state-level regulatory requirement mandating that pharmaceutical companies disclose drug pricing information (WAC) to HCPs in Colorado when marketing drugs. * **Face-to-Face Detailing:** Traditional method of pharmaceutical sales where representatives meet directly with HCPs; the video notes this was largely replaced by digital methods during the pandemic. * **Out-of-the-Box (OOTB) Functionality:** The standard features and capabilities of a software system (like Veeva) before any custom configuration or modification is applied.
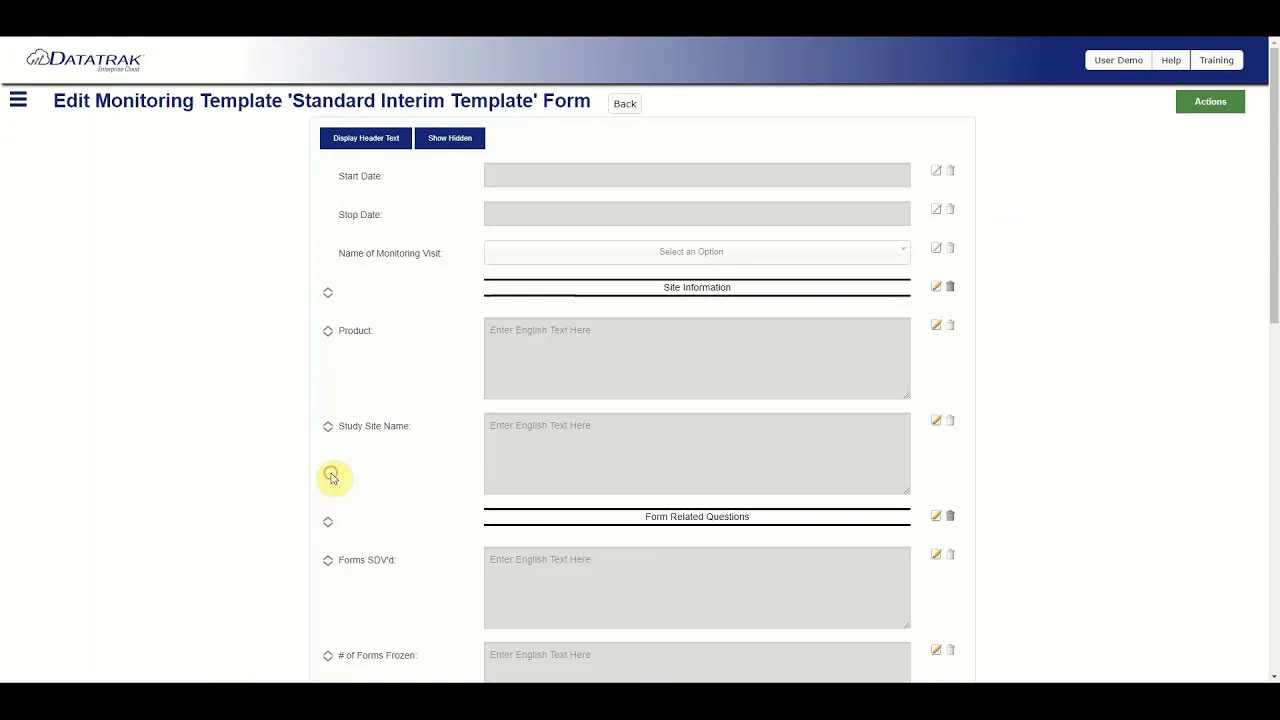
Datatrak CTMS Monitoring Overview
Datatrak International
/@datatrakinternational7104
Apr 23, 2020
This video provides an in-depth overview of how the Datatrak Clinical Trial Management System (CTMS) is leveraged to streamline the creation, management, and maintenance of monitoring visit reports, emphasizing the critical role of proper monitoring in ensuring overall study success. The system is presented as a powerful tool designed to eliminate the tedious, manual tasks traditionally associated with generating these regulatory-critical documents. The core functionality revolves around user empowerment, allowing clinical operations teams to become the "architects" of their trial management experience through highly flexible and customizable tools. The platform focuses heavily on template management and customization, which is essential for accommodating diverse study protocols and regulatory requirements. Users are given the capability to build and maintain an unlimited number of report templates tailored to specific study requirements or site needs. A key feature highlighted is the 'copy function,' which allows users to duplicate existing templates, preserving the original while enabling study or site-specific modifications to the new version. Report template creation is simplified through a drag-and-drop form building functionality, enabling the easy addition of new form questions and the utilization of section headers for visually appealing and organized reports. This architectural flexibility ensures that the monitoring experience, and indeed all aspects of trial management within the system, can be precisely configured to the organization's standard operating procedures (SOPs). A significant efficiency gain detailed in the overview is the system's ability to integrate data seamlessly across clinical systems, specifically mentioning the Electronic Data Capture (EDC) system. The CTMS is configured to automatically pull data from the EDC or other internal CTMS locations, eliminating the need for data duplication. Crucially, data that has already passed the data cleaning process within the EDC can be imported with a single click. This integration capability extends to capturing the work of co-monitors, ensuring all relevant monitoring data is consolidated efficiently. Furthermore, the system enforces compliance and quality control by allowing teams to build custom workflows, dictating the required statuses reports must pass through, and defining who is permitted to move reports between statuses, thereby ensuring adherence to internal quality gates and regulatory standards before finalization. Key Takeaways: • **Elimination of Data Duplication:** The Datatrak CTMS integrates directly with the EDC system, allowing monitoring reports to automatically pull cleaned data, significantly reducing manual data entry errors and saving substantial time during the report generation process after site visits. • **Customizable Report Templates:** The system supports the creation and maintenance of an unlimited number of monitoring report templates, offering a 'copy function' to facilitate rapid iteration and customization for specific studies or sites while maintaining a standardized core structure. • **Workflow-Driven Compliance:** Clinical teams can architect custom workflows that define the necessary status progression for monitoring reports, ensuring adherence to internal SOPs and regulatory requirements by controlling who can approve and advance a report through its lifecycle. • **User-Centric Form Building:** The platform utilizes a drag-and-drop functionality for form building, empowering clinical operations staff to easily configure report structures, add form questions, and utilize section headers for improved organization and visual clarity. • **Consolidated Monitoring Data:** The CTMS is designed to consolidate all relevant monitoring data, including contributions from co-monitors, ensuring a comprehensive and unified record of the monitoring activities for each site visit. • **Data Engineering Opportunity:** The reliance on pulling cleaned data from the EDC highlights a critical data engineering requirement for robust, reliable data pipelines between the EDC and CTMS, a key area where specialized AI and data services can optimize integration performance and data quality checks. • **Operational Efficiency in Clinical Trials:** By automating the data transfer and streamlining the report generation process, the CTMS directly contributes to the operational efficiency of clinical trials, allowing monitors to focus more on quality assurance and less on administrative, data-entry tasks. • **Importance of System Architecture:** The video emphasizes that users are the "architects" of their trial management experience, underscoring the need for flexible, configurable enterprise software solutions in the regulated life sciences environment to meet evolving trial needs. • **Focus on Study Success:** The foundational premise is that proper monitoring is crucial to study success, positioning the CTMS as an essential tool for maintaining data integrity and regulatory standards throughout the trial lifecycle. Tools/Resources Mentioned: * Datatrak CTMS (Clinical Trial Management System) * EDC (Electronic Data Capture) Key Concepts: * **Monitoring Visit Reports:** Formal documentation created by clinical research associates (CRAs) or monitors following site visits, detailing site performance, data review, and compliance with the protocol and regulatory standards. These are critical GxP documents. * **CTMS (Clinical Trial Management System):** Enterprise software used by sponsors and CROs to manage and track the operational aspects of a clinical trial, including site information, regulatory documents, budget, and monitoring activities. * **Data Cleaning:** The process within the EDC system where raw data is reviewed, queried, and corrected to ensure accuracy and consistency before being finalized for analysis or transfer. The CTMS leverages this pre-cleaned data for report accuracy.

Automate Tasks for CRAs and Study Managers with Vault CTMS
Veeva Systems Inc
/@VeevaSystems
Apr 20, 2020
This video provides a demonstration of how Veeva Vault CTMS (Clinical Trial Management System) leverages the Vault platform to automate routine, manual tasks for Clinical Research Associates (CRAs) and study managers. The core objective of these automation features is to significantly reduce monitoring effort and associated costs by simplifying cross-functional processes and ensuring that site and trial statuses are accurately updated based on designated completed milestones. The presentation systematically walks through key areas of the clinical trial lifecycle—site setup, monitoring, and site closeout—to illustrate how the system systematically moves work streams forward with minimal manual intervention. During the initial site setup phase, Vault CTMS streamlines the management of the study team roster. The system allows CRAs and study managers to quickly add principal investigators (PIs) to a site. A crucial automation feature is triggered immediately upon this addition: any existing documentation associated with that PI, which has already been collected within the system, is automatically pulled into the site’s list of documents and filed in the appropriate location within the Trial Master File (TMF) structure. This ensures immediate documentation compliance and reduces the administrative burden of manual filing and cross-referencing. The video then shifts focus to the monitoring and closeout phases, highlighting automation within the closeout visit trip report process. When completing the closeout trip report, a dedicated section allows the monitoring team to document any newly identified protocol deviations. As these deviations are logged, the user designates them as either "major deviations" or "minor deviations." This designation triggers a critical automated workflow: upon saving the report, the deviation is automatically escalated, and notifications are sent to the appropriate stakeholders, such as the study manager assigned to the trial. These notifications include a quick link, ensuring the study manager always has the most up-to-date information regarding major protocol deviations at the site, facilitating rapid response and oversight. Finally, the demonstration concludes by detailing the system-triggered actions that occur upon the formal approval of the closeout trip report. Vault CTMS performs two simultaneous, automated actions following approval. First, the system automatically creates the final trip report document and files it appropriately within the structured TMF. Second, and critical for lifecycle management, Vault CTMS automatically triggers the site to transition to the "closed phase" in its life cycle. This end-to-end automation, from roster management to final site closure, minimizes manual effort for the monitoring team while maintaining regulatory compliance and data integrity. Key Takeaways: • **Reduced Monitoring Burden:** Vault CTMS is designed to automate mundane tasks, allowing CRAs and study managers to focus on critical activities rather than manual data entry and process management, ultimately reducing monitoring effort and cost. • **Systematic Workflow Progression:** The platform ensures that work streams move forward systematically, relying on designated completed milestones (e.g., trip report approval) to trigger subsequent actions and status updates. • **Automated TMF Integration during Site Setup:** When a principal investigator (PI) is added to a site roster, any previously collected documentation associated with that individual is automatically pulled and filed into the correct location within the Trial Master File (TMF) structure. • **Streamlined Protocol Deviation Management:** During the closeout visit trip report, users can designate new protocol deviations as "major" or "minor," which dictates the subsequent automated escalation workflow. • **Automatic Escalation and Notification:** Designating a deviation triggers automatic escalation and sends notifications, including a quick link to the deviation record, to relevant groups (e.g., the study manager) to ensure immediate awareness and oversight of critical issues. • **Two-Part Closeout Automation:** Upon approval of the closeout trip report, Vault CTMS executes two system-triggered actions: the automatic creation and appropriate filing of the trip report document within the TMF structure, and the automatic transition of the site's lifecycle status to the "closed phase." • **Data Integrity and Compliance:** By automating document filing and status changes based on system milestones, the platform helps ensure that documentation is consistently filed and audit trails are maintained, supporting regulatory compliance requirements. • **Enhanced Visibility for Study Managers:** Automated notifications regarding major protocol deviations provide study managers with immediate, actionable insights, allowing them to maintain the most up-to-date information on trial risks and site status. Tools/Resources Mentioned: * Vault CTMS (Clinical Trial Management System) * Vault Platform * TMF (Trial Master File) Key Concepts: * **CRA (Clinical Research Associate):** Professionals responsible for monitoring clinical trials, ensuring compliance with protocols, and verifying data accuracy. * **Protocol Deviation:** Any change, divergence, or departure from the study design or procedures defined in the protocol. Designating them as major or minor determines the required regulatory reporting and internal escalation. * **Site Lifecycle:** The progression of a clinical trial site through various phases, such as startup, active monitoring, and closeout. Automated status changes ensure accurate tracking and reporting.
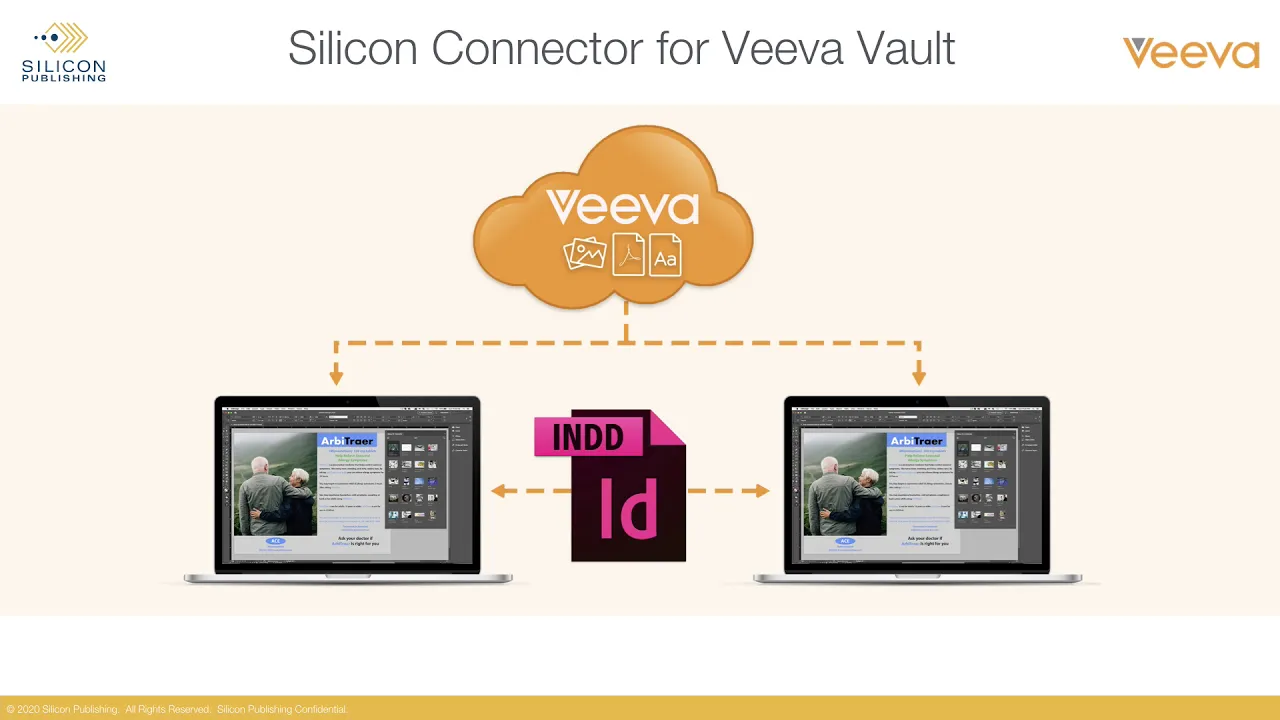
Silicon Connector for Veeva Vault
siliconpublishing
/@siliconpublishing
Apr 13, 2020
This video provides a demonstration of the "Silicon Connector for Veeva Vault," an integration tool designed to streamline the creative workflow for regulated content by connecting Veeva Vault PromoMats directly with Adobe Creative Cloud applications, specifically InDesign, Illustrator, and Photoshop. The primary purpose of this connector is to allow authoring groups—often responsible for creating marketing and medical materials in the pharmaceutical sector—to access, utilize, and manage approved assets without leaving their native design environment, thereby enhancing efficiency and maintaining compliance. The core functionality showcased is the ability to navigate and search the same assets available in the Veeva Vault PromoMats interface directly through a dedicated panel within Adobe InDesign. Users can select pre-defined sets of assets, such as those in their "cart," "favorites," or "library." A critical technical advantage is demonstrated when an image is dragged into an InDesign document: the connector automatically establishes a true URL-based link to the asset residing in the Vault. This methodology avoids the necessity of downloading graphic assets to the local file system, a feature highlighted as having "huge value" for authoring groups, as it significantly improves security, consistency, and version control, which are vital in regulated environments. Beyond simple asset retrieval, the connector facilitates advanced document management workflows essential for regulated content creation. The tool supports opening, editing, and saving back packaged InDesign documents. Furthermore, the check-in process for an InDesign package is integrated with an automated preflighting step. This preflighting mechanism ensures that the file meets quality and compliance standards before being stored in the Vault, specifically checking for missing fonts or links and verifying that graphic assets are of suitable quality. This automated quality assurance step is crucial for maintaining GxP and regulatory compliance within the pharmaceutical marketing and medical affairs content lifecycle. The video concludes by confirming that similar navigation and search capabilities are available within Photoshop and Illustrator, enabling the management of individual graphic assets, including opening files for editing and saving them back to the Vault, or adding them as new layers in existing documents. Key Takeaways: • **Veeva Vault Integration for Creative Workflow:** The Silicon Connector provides a direct, seamless bridge between the regulated content repository (Veeva Vault PromoMats) and the primary creative tools (Adobe InDesign, Illustrator, Photoshop), drastically reducing friction in the content creation lifecycle for pharmaceutical commercial operations. • **Elimination of Local Asset Downloads:** By creating true URL-based links directly to assets within the Vault, the system prevents the proliferation of unmanaged copies on local file systems, enhancing security and ensuring that creative teams are always utilizing the most current, approved versions of regulated materials. • **Automated Preflighting for Compliance:** The integration automates a critical compliance step by preflighting packaged InDesign documents upon check-in, verifying the integrity of the file (checking for missing fonts, broken links, and asset quality) before it enters the formal review and approval process within PromoMats. • **Enhanced Asset Management and Search:** Users gain the ability to navigate and search the entire Veeva Vault asset library from within the Adobe environment, utilizing existing Vault organizational structures like carts, favorites, and libraries, improving efficiency and reducing time spent switching between applications. • **Support for Packaged Document Workflow:** The connector supports the full cycle of packaged InDesign documents, allowing users to open, edit, and save the entire package back into the Vault, which is essential for complex, multi-component marketing materials common in life sciences. • **Consistency in Regulated Content Creation:** By enforcing the use of Vault-linked assets and automating quality checks, the tool helps pharmaceutical companies maintain consistency and adherence to brand guidelines and regulatory requirements (e.g., 21 CFR Part 11). • **Value Proposition for Authoring Groups:** The integration offers significant value to creative and authoring teams by allowing them to focus on design within their preferred tools while the connector handles the necessary linking, version control, and pre-compliance checks required by the regulated environment. • **Individual Graphic Asset Management:** The connector extends its utility to individual graphic assets within Photoshop and Illustrator, allowing designers to check out, edit, and save back images directly to the Vault, maintaining a clear audit trail for every asset modification. Tools/Resources Mentioned: * Veeva Vault PromoMats * Adobe InDesign * Adobe Illustrator * Adobe Photoshop * Silicon Connector (the integration tool) Key Concepts: * **Veeva Vault PromoMats:** A module within the Veeva Vault platform used by life sciences companies to manage the creation, review, and distribution of promotional materials and medical content, ensuring regulatory compliance. * **Preflighting:** The process of checking digital files for potential errors or quality issues (such as missing fonts or low-resolution images) before they are finalized or submitted for regulatory approval. * **URL-Based Linking:** A method of referencing assets by their permanent web address within the Veeva Vault system rather than embedding a local copy, which is crucial for maintaining version control and auditability in regulated content.

Ending the paper trail with REDCap: optimized workflows for screening, consenting, and compensating
MGH Martinos Center
/@MGHMartinosCenter
Apr 11, 2020
This video explores the successful digital transformation of administrative workflows in clinical research at the MGH Martinos Center, specifically focusing on replacing paper-based processes with REDCap. Olivia Rowe, a Clinical Research Coordinator, details how her team optimized subject screening, consenting, and compensation by leveraging REDCap's capabilities. The presentation highlights the numerous inefficiencies and compliance risks associated with paper forms, such as space consumption, outdated information, HIPAA vulnerabilities, and lack of flexibility. The implemented REDCap solution introduces digital safety screening, dynamic branching logic for tailored questionnaires (e.g., pregnancy screening), real-time eligibility feedback for participants, digital sign-offs for MRI technicians, and an integrated subject payment system. This initiative aims to alleviate administrative burdens, enhance data accuracy, and significantly improve regulatory compliance through robust audit trails and streamlined processes. Key Takeaways: * **Digital Transformation in Clinical Research:** The video directly addresses the administrative burden and compliance risks of paper-based workflows in clinical research, demonstrating a clear need for digital solutions to optimize operations within the life sciences sector. * **Workflow Optimization and Automation:** REDCap is effectively utilized to streamline critical processes like subject screening, consent, and compensation, showcasing the value of automating traditionally manual tasks through digital forms with features like branching logic and real-time feedback. * **Enhanced Regulatory Compliance:** Moving to digital platforms like REDCap significantly improves HIPAA compliance, provides thorough audit trails, and simplifies IRB approval processes through templated amendments, aligning with the strict regulatory requirements (e.g.ai helps clients navigate. * **Improved Participant Experience and Data Quality:** Digital forms empower participants to provide documentation, receive immediate eligibility feedback, and ensure more accurate and relevant data collection, reducing administrative overhead for research staff and improving overall data integrity. * **Interoperability and Customization Potential:** The discussion touches upon the ability to integrate with EMRs (like Epic) and the customizability of REDCap forms, highlighting the flexibility required for diverse research needs and the potential for broader data engineering initiatives. * **Scalability through Data Dictionaries:** The concept of sharing forms via a "data dictionary" allows for efficient replication and customization of standardized questionnaires across different labs, reducing redundant effort in setting up digital tools and promoting best practices.

InstantQMS™: Quality Management and Vendor Management Software for Virtual Biotech Companies
InstantGMP , Inc.
/@instantgmpinc.6394
Apr 6, 2020
This video introduces InstantQMS™, a specialized Quality Management System (QMS) and Vendor Management software designed specifically for the unique needs of virtual biotech companies operating in the preclinical to early clinical stages of drug development. The primary purpose of the software is to provide a virtual, centralized hub for accountability and documentation, which are essential requirements for FDA compliance and risk mitigation for sponsors of GxP activities. The presentation emphasizes that the FDA holds sponsors directly accountable for any issues arising during clinical trials or manufacturing, necessitating robust, easily accessible supporting documentation. The core argument presented is that a comprehensive quality system is non-negotiable for effective research and financial stewardship, ensuring that all outsourced work—a common model for virtual biotechs—is held accountable. InstantQMS provides the foundational requirements to build an expedited quality system, shifting the sponsor’s responsibility from defining and creating the entire system to simply defining the specific quality parameters and Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) for their organization, vendors, and outsourced manufacturing partners. The software package includes pre-written SOPs and forms for GxP compliance, accelerating the implementation process. The InstantQMS package is structured around five foundational pillars designed to ensure continuous audit readiness and personal risk mitigation for the sponsor. These pillars include the Document Management System, which controls SOPs; the Quality Management aspect, which records and organizes all quality parameters related to the production process and the product itself; the Vendor Management system, which tracks quality parameters for vendors of goods or manufacturing services; and the Vault system, a centralized hub for storing all documentation required for auditing or historical data purposes. The integrated nature of these systems, coupled with guided workflows and autonomous operations, aims to streamline compliance tracking, incident management, CAPA (Corrective and Preventive Actions), change control, and customer complaint handling. The system is positioned as the fastest way for early-stage companies to establish quality management, integrating a complete set of SOPs that work in concert with processes and logs. By providing a web-based hub for the collection and organization of all sponsor responsibilities and FDA regulations, InstantQMS allows virtual companies to maintain continuous audit readiness, thereby significantly mitigating the sponsor's personal and organizational risk associated with regulatory scrutiny and clinical development challenges. Key Takeaways: • **Sponsor Accountability is Paramount:** The FDA holds the sponsoring biotech company directly accountable for all problems occurring during clinical trials or manufacturing, necessitating a robust, documented quality system to supply supporting evidence immediately upon request. • **QMS as Risk Mitigation:** Implementing a virtual QMS that captures all documentation is the simplest way for virtual biotechs to reduce their risk threshold and ensure effective use of research funding and capital. • **Five Pillars of InstantQMS:** The software package is built on five core components: Document Management (SOP control), Quality Management (production process quality tracking), Vendor Management (vendor quality tracking), the Vault (centralized audit documentation storage), and pre-included GxP SOPs and forms. • **Defining vs. Creating the QMS:** The software shifts the sponsor's burden from the complex task of defining and creating the entire quality system infrastructure to the simpler task of defining the specific quality parameters and SOPs relevant to their unique organization and outsourced partners. • **GXP Compliance Focus:** The system is explicitly designed to manage GxP activities, providing guided workflows and autonomous operations for essential compliance functions like incident logging, customer complaints, CAPAs, and change control. • **Audit Readiness:** The centralized, organized documentation (the "Vault") ensures that the virtual company can maintain continuous audit readiness, a critical operational state for companies in the preclinical and early clinical phases. • **Targeted for Virtual Biotechs:** The solution acknowledges the operational model of virtual biotechs, which heavily rely on outsourced manufacturing and clinical activities, making the integrated Vendor Management and centralized documentation hub essential. • **Accelerated Implementation:** The inclusion of pre-written SOPs and forms for GxP compliance significantly expedites the process of establishing a functional quality system, allowing early-stage companies to focus on drug development rather than foundational compliance infrastructure creation. Key Concepts: * **QMS (Quality Management System):** A formalized system that documents processes, procedures, and responsibilities for achieving quality policies and objectives. In the life sciences, it ensures product safety, efficacy, and regulatory compliance (GxP). * **GxP (Good Practices):** A general term for quality guidelines and regulations covering various aspects of the life sciences industry, including Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP), Good Clinical Practice (GCP), and Good Laboratory Practice (GLP). * **Sponsor:** The individual, company, institution, or organization that takes responsibility for the initiation, management, and/or financing of a clinical trial or drug development activity. * **CAPA (Corrective and Preventive Actions):** A system for improving organizational processes, often used to eliminate the causes of non-conformities or other undesirable situations. Tools/Resources Mentioned: * **InstantQMS™:** Quality Management and Vendor Management Software. * **Learning Management System (LMS):** Mentioned as integrated, suggesting training and documentation control for personnel.

Remote Monitoring in Clinical Trials - SiteTalks Webcast
Veeva Systems Inc
@VeevaSystems
Mar 31, 2020
This video provides an in-depth discussion on the rapid adoption and best practices of remote monitoring in clinical trials, primarily driven by the operational necessity imposed by the COVID-19 pandemic. Moderated by Bri Burks of Veeva Systems, the panel features leaders from diverse research sites—including Duke School of Medicine, Vanderbilt Coordinating Center, Javara (an integrated research organization), and Keystone Clinical Research—who share their immediate challenges, infrastructural advantages, and long-term strategic recommendations. The core purpose of the webcast is to create an informal platform for researchers to exchange ideas on practical ways to continue critical work when monitors cannot access files on-site. The discussion begins by detailing the immediate impact of COVID-19, forcing sites like Duke and Vanderbilt to issue mandates blocking external monitors and quickly converting to remote monitoring protocols. Sites with existing infrastructure, such as Duke, were able to leverage pre-existing remote monitoring capabilities and streamline IRB approval processes for remote EMR access without extensive amendments. Conversely, sites like Keystone, which historically relied on paper-based systems (especially in niche areas like ophthalmology), faced significant challenges in transitioning staff and contracted physicians to electronic systems for source documentation and signatures. A central theme emerged: the pandemic is acting as a rapid accelerator for digital adoption, forcing the industry to overcome historical hesitation rooted in entrenched practices and vendor resistance. The panelists emphasized that the shift to remote monitoring offers substantial long-term benefits beyond crisis management. These benefits include reduced travel costs and time for sponsors, decreased burnout and improved job satisfaction for CRAs (who are constantly traveling), and enhanced quality control for sites. Vanderbilt shared that their long-term adoption of remote monitoring since 2012 allowed them to identify data errors and implement changes earlier, often in near real-time, improving overall trial quality. The conversation culminated in actionable advice for sites, differentiating between short-term crisis management (using existing systems like encrypted email, HIPAA-compliant telehealth, or shared drives) and long-term strategic planning (implementing comprehensive digital strategies encompassing eRegulatory, eSource, and patient engagement tools). A key regulatory insight shared was the need for sites to meticulously check IRB approvals, clinical trial agreements, and patient consent forms to ensure PHI sharing via remote methods is compliant, especially in light of new FDA and MHRA guidance encouraging remote practices. ### Detailed Key Takeaways * **Remote Monitoring is an Industry Accelerator:** The COVID-19 crisis has forced the rapid adoption of remote monitoring, overcoming years of industry hesitation and entrenched paper-based practices. This momentum should be leveraged to drive permanent enterprise-level change, benefiting both sites and sponsors by potentially accelerating timelines and reducing costs. * **Immediate Crisis Action Plan:** Sites must immediately assess their current electronic capabilities (e.g., encrypted email, HIPAA-compliant telehealth, shared drives) and identify what institutional policies and agreements (like EMR access forms) are needed to facilitate remote access for monitors, ensuring a consistent message across the research community. * **Long-Term Digital Strategy is Crucial:** For sustained success, sites must develop a comprehensive technology strategy that integrates eRegulatory systems (eISF), eSource documentation, patient engagement tools, and internal communication platforms. This strategy should be planned over a 1, 3, and 5-year horizon rather than focusing solely on immediate fixes. * **Regulatory Compliance for PHI Sharing:** Sharing Protected Health Information (PHI) remotely requires a meticulous, study-by-study regulatory check: verifying IRB application approvals, reviewing the PHI section of the Clinical Trial Agreement (CTA), and ensuring patient consent forms cover the method and scope of remote data access. * **Address CRA Burnout and Efficiency:** Remote monitoring offers a significant opportunity to improve the quality of life for CRAs by reducing constant travel, potentially lowering turnover rates, and allowing them to focus on higher-value monitoring activities, which ultimately benefits site operations and data quality. * **Start with eRegulatory (eISF):** For sites beginning their digital transformation, implementing an eRegulatory system is a practical starting point. Sites should look for solutions that fit their budget, including free or low-cost options, and avoid "analysis paralysis" by taking immediate action and iterating on the process later. * **Justify Budget Renegotiations:** If remote monitoring increases site burden (e.g., time spent redacting documents or uploading to new systems), sites should confidently renegotiate study budgets with sponsors, providing detailed justification for the additional time and effort required, leveraging the current industry need for data continuity. * **Controlled EMR Access is a Site Decision:** Granting remote access to the Electronic Medical Record (EMR/EHR) is entirely controlled by the site and its institutional privacy officer. Sites must be cautious about granting open-ended access that might expose sensitive, non-study-related patient data beyond what is covered by the study consent. * **Quality Improvement through Early Detection:** Remote monitoring, especially when supported by robust eSource systems, enables earlier identification of data errors and protocol deviations, allowing sites to implement corrective actions in near real-time, leading to higher overall trial quality compared to traditional on-site cycles. * **Standardize Processes via SOPs:** Sites should use this opportunity to update SOPs to reflect remote monitoring capabilities, ensuring that processes are standardized across all studies rather than treating remote monitoring as a "one-off" exception, which is unsustainable and increases compliance risk. * **Leverage Existing HIPAA-Compliant Systems:** Before investing in new software, sites should check if their institution offers HIPAA-compliant versions of shared drives (like Box or Dropbox) or telehealth platforms, as these can be utilized immediately for secure document sharing and virtual patient visits. * **Proactive Sponsor Communication:** Sites must proactively communicate their remote monitoring plan and capabilities to their sponsor and CRO partners, running through the study-specific regulatory checks (consent, CTA) together to ensure alignment and speed up the implementation process. ### Tools/Resources Mentioned * **Veeva Systems:** The channel and moderator are associated with Veeva, whose products support clinical trial operations and site solutions. * **Epic Health Connect:** Mentioned as a system used by Vanderbilt to connect some EHR capability remotely. * **WebEx/Zoom:** Used for virtual patient visits and internal team meetings, though security concerns regarding PHI recording were noted. * **Ver Trials:** Mentioned as a specific, marketed solution for supporting remote telehealth visits for clinical trial patients. * **Box/Dropbox:** Suggested as potential HIPAA-compliant shared drive solutions if already available institutionally. * **ACRP Nets Website:** Mentioned as a community resource for sites to share best practices and advice. ### Key Concepts * **eSource (Electronic Source Documentation):** The practice of capturing clinical trial data directly into an electronic format, eliminating the need for paper charts and facilitating remote review. * **eRegulatory (eISF):** Electronic Investigator Site File systems used to manage and share essential regulatory documents securely with sponsors and monitors. * **PHI (Protected Health Information):** Health information protected under HIPAA and GDPR, requiring explicit consent and secure methods for remote sharing. * **Analysis Paralysis:** The state of being unable to make a decision or start a project due to over-analyzing or seeking a perfect solution, a pitfall sites are warned to avoid when implementing digital systems. * **Sponsor Monitoring Agreement:** The contractual agreement defining the terms, frequency, and methods of monitoring, which may need updating to explicitly allow for remote access.

Veeva Systems CEO talks assissting life sciences industry in the race to find a COVID-19 cure
CNBC Television
/@CNBCtelevision
Mar 26, 2020
This video provides an in-depth exploration of Veeva Systems' critical role in supporting the life sciences industry, particularly during the initial phase of the COVID-19 pandemic. Featuring an interview with Veeva CEO Peter Gassner, the discussion highlights how the cloud-based software company empowers pharmaceutical and biotech firms to manage clinical trial data, ensure regulatory compliance, and enhance commercial operations. The context of the interview is a volatile market, with the host, Jim Cramer, emphasizing Veeva's perceived indispensability despite stock fluctuations. Gassner elaborates on how Veeva's customers were at the forefront of addressing COVID-19, working on new tests, treatments, and vaccinations. He explains that the pandemic significantly disrupted traditional in-person interactions essential for both commercial activities (sales reps engaging healthcare providers) and clinical trials (researchers conducting studies). In response, Veeva rapidly enabled virtual engagement through its "Veeva Engage" product, which facilitates compliant remote connections between pharmaceutical sales representatives and doctors, as well as researchers. Notably, this Zoom-based solution was offered free to the industry for a period, leading to a tenfold increase in usage within just two weeks, underscoring its immediate and vital utility. The conversation also delves into Veeva's impressive business growth, having achieved a $1 billion revenue milestone ahead of schedule and setting an ambitious new target of $3 billion by 2025. Gassner clarifies that Veeva's product portfolio has expanded significantly beyond its initial "Vault" offering, now encompassing a broad suite of solutions. He characterizes the life sciences industry as largely counter-cyclical, maintaining consistent demand for medicines even during economic downturns, although temporary disruptions to new clinical trials can occur. Gassner stresses that challenging times often serve as a catalyst for innovation, driving companies to become more productive and adaptable. Furthermore, Gassner provides concrete examples of Veeva's impact, citing its work with major pharmaceutical companies like Bristol-Myers Squibb. This includes assisting with large-scale mergers (e.g., Celgene integration), streamlining quality and manufacturing processes, supporting clinical trials, and optimizing interactions with healthcare professionals. He also introduces a significant new offering, the "Veeva Data Cloud," which focuses on leveraging data science and big data related to patient information. This initiative is crucial for advancing precision medicine by enabling companies to better understand patient populations and deliver targeted therapies, showcasing Veeva's commitment to cutting-edge data solutions. Key Takeaways: * **Veeva's Foundational Role in Life Sciences:** Veeva Systems provides essential cloud-based software solutions that enable pharmaceutical and life sciences companies to effectively manage clinical trial data, ensure adherence to complex regulations, and optimize their commercial operations. This comprehensive support positions Veeva as a critical partner across the drug development and commercialization lifecycle. * **Adaptation to Virtual Engagement during Crisis:** The COVID-19 pandemic necessitated a rapid shift from in-person to virtual interactions for both pharmaceutical sales and clinical research. Veeva played a pivotal role in facilitating this transition, demonstrating the immediate need for robust, compliant virtual engagement platforms in the industry. * **Veeva Engage: A Critical Virtual Solution:** Veeva Engage, a product built on Zoom, was offered free to the industry during the pandemic to enable compliant remote connections between pharmaceutical sales reps and doctors. Its rapid adoption, with a 10x increase in usage, highlights its effectiveness and the urgent demand for such tools. * **Resilience and Counter-Cyclical Nature of Life Sciences:** The life sciences industry is characterized as largely counter-cyclical, meaning the demand for medicines generally remains stable even during economic downturns. This inherent stability makes the sector resilient, though temporary disruptions, such as the postponement of new clinical trials, can occur. * **Innovation as a Response to Adversity:** Challenging periods, like the pandemic, act as powerful catalysts for innovation within the life sciences sector. Companies are driven by necessity to find new, more efficient, and productive ways to operate, leading to technological advancements and process improvements. * **Significant Growth and Ambitious Future Goals:** Veeva Systems has demonstrated remarkable growth, achieving $1 billion in revenue ahead of its 2020 target and setting an ambitious new goal of $3 billion by 2025. This trajectory underscores its strong market position, expanding influence, and confidence in continued growth. * **Diversified Product Portfolio Beyond Veeva Vault:** While Veeva Vault was a foundational product, Veeva's offerings have significantly broadened. The company now provides a comprehensive suite of solutions that address various aspects of pharmaceutical operations, from R&D and quality to commercial and patient data management. * **Enterprise-Level Support for Major Pharma:** Veeva provides critical support for complex, large-scale initiatives for major pharmaceutical clients, such as assisting Bristol-Myers Squibb with the integration of a significant merger (Celgene). This demonstrates its capability to handle intricate enterprise requirements and drive operational efficiency. * **End-to-End Solutions Across the Pharma Value Chain:** Veeva's services span the entire pharmaceutical value chain, including quality and manufacturing, clinical trials, and commercial interactions with healthcare providers. This integrated approach helps clients streamline operations from drug development through market delivery. * **Veeva Data Cloud for Precision Medicine:** The introduction of Veeva Data Cloud signifies a strategic move into advanced data science and big data analytics focused on patient information. This product is crucial for the advancement of precision medicine, enabling pharmaceutical companies to better understand patient populations and develop more targeted and effective therapies. * **Importance of Compliant Remote Interactions:** A core tenet of Veeva's offerings, particularly during the pandemic, is ensuring that remote interactions between pharmaceutical sales representatives and healthcare professionals are conducted in a fully compliant manner, adhering to strict industry regulations. Tools/Resources Mentioned: * Veeva CRM * Veeva Engage (based on Zoom) * Veeva Vault * Veeva Data Cloud Key Concepts: * **Cloud-based software:** Software delivered over the internet, accessible from any device. * **Life sciences industry:** Encompasses pharmaceutical, biotech, medical device, and diagnostics companies. * **Clinical trial data:** Information collected during human clinical trials to assess the safety and efficacy of new drugs or treatments. * **Regulatory compliance:** Adherence to rules and regulations set by bodies like the FDA and EMA, crucial in the pharmaceutical sector. * **Commercial operations:** Activities related to marketing, sales, and distribution of pharmaceutical products. * **Virtual engagement:** Conducting business interactions and activities remotely using digital platforms. * **Counter-cyclical industry:** An industry whose performance is inversely related to the overall economic cycle. * **Precision medicine:** An approach to disease treatment and prevention that takes into account individual variability in genes, environment, and lifestyle for each person. * **Data science and big data:** Methodologies and technologies for analyzing large, complex datasets to extract insights, particularly relevant for patient data in healthcare. Examples/Case Studies: * **Bristol-Myers Squibb (BMS):** Veeva assisted BMS with its merger with Celgene, facilitating an expeditious integration. Veeva also supports BMS across various functions, including quality and manufacturing, clinical trials, and interactions with doctors' offices.

eTMF
Sarjen Systems Pvt. Ltd.
/@SarjenSysPvtLtd
Mar 26, 2020
This video provides an in-depth exploration of Electronic Trial Master Files (eTMFs), contrasting their benefits and regulatory acceptability against the significant challenges posed by traditional paper-based TMF systems. The presenter begins by establishing the regulatory context, highlighting that eTMF standards are acceptable to authorities, specifically referencing Directive 2005/28/EC and related guidance in Volume 10 of the rules governing medicinal products in the EU. This foundational premise sets the stage for understanding why a shift to electronic systems is not just an operational improvement but a regulatory imperative. The core of the presentation then pivots to detailing the "actual scenario" where TMFs are commonly maintained on hardcopy for both bioequivalence (BA/BE) and clinical trial (CT) studies. This traditional approach is plagued by several critical issues: the unavailability of standard templates, making it difficult to inherit structures for similar products; cumbersome version management of documents, leading to confusion; limited accessibility of documents across multiple departments; and a critical lack of a robust audit trail. These challenges collectively hinder efficiency, increase operational risk, and complicate regulatory oversight, underscoring the urgent need for a more streamlined and compliant solution. The video then introduces the electronic TMF as a simplified approach designed to address these pervasive challenges. It elaborates on how an eTMF system facilitates a quick and efficient review process compared to paper TMFs. Key advantages include allowing inspectors and auditors direct access to documents, ensuring that eTMF documents are evidently authentic, complete, and legible copies of originals. Furthermore, eTMF systems incorporate validated methods to prevent unauthorized changes, track the status of all TMFs conveniently, and enable organizations to effectively manage post-submission queries from regulatory authorities. The system's design emphasizes easy accessibility through intuitive folder and file naming conventions, reducing the need for inspectors to open numerous documents. It also supports opening multiple documents simultaneously for comparison, providing access to the same document type across various studies, sponsors, and internal departments for review and comment, and comprehensive TMF lifecycle management. The culmination of these features is the ability to generate customizable reports, which significantly assists in overall proficiency. The tangible benefits of adopting an eTMF system are quantified and emphasized, illustrating a substantial positive impact on operational efficiency and cost reduction. The video claims a reduction in operational costs by up to 60% and a decrease in efforts related to maintaining multiple versions of eTMFs, thereby avoiding confusion regarding the latest version for submission. A particularly significant advantage highlighted is the aid in developing virtual inspections, which can improve the efficiency of the inspection process by up to 80%. The system also ensures easy and continual updates for ongoing trials, reinforcing its utility throughout the clinical trial lifecycle. The presentation concludes with a call to action for a demo, suggesting the immediate applicability and value of such a system. Key Takeaways: * **Regulatory Acceptance of eTMFs:** Electronic Trial Master Files are officially recognized and accepted by regulatory authorities, specifically citing EU Directive 2005/28/EC and Volume 10 guidance, making their adoption a compliant and strategic move for pharmaceutical companies. * **Critical Pain Points of Paper TMFs:** Traditional hardcopy TMFs suffer from significant drawbacks including a lack of standard templates, poor version control, limited document accessibility across departments, and the absence of a reliable audit trail, all of which impede efficiency and compliance. * **Enhanced Review and Accessibility:** eTMF systems enable quick and efficient document review, providing inspectors and auditors direct access to TMF documents, which are guaranteed to be authentic, complete, and legible copies of originals. * **Document Integrity and Auditability:** A robust eTMF system incorporates validated methods to prevent unauthorized changes to documents and provides comprehensive tracking of the status of all TMFs, ensuring data integrity and a clear audit trail. * **Streamlined Query Management:** Organizations can significantly benefit from eTMFs by effectively managing post-submission queries raised by regulatory authorities, thanks to improved document organization and accessibility. * **Intuitive Document Organization:** eTMFs utilize easy accessibility with logical folder and file naming conventions, allowing inspectors and auditors to readily identify and locate needed documents without sifting through numerous irrelevant files. * **Comparative Analysis Capability:** The ability to open and view more than one document at a time within an eTMF system facilitates direct comparison, which is crucial for thorough review and analysis during inspections or internal audits. * **Cross-Study and Departmental Access:** eTMFs allow for providing access to the same type of document across all study sponsors, products, and internal departments, fostering collaboration and consistent document review and comment processes. * **Comprehensive TMF Lifecycle Management:** The system supports full lifecycle management of TMF documents, from creation through archiving, ensuring all stages are managed efficiently and compliantly. * **Customizable Reporting for Proficiency:** The capability to generate customizable reports from the eTMF system assists in overall proficiency, offering valuable insights into document status, compliance, and operational metrics. * **Significant Cost and Efficiency Gains:** Adopting an eTMF can lead to substantial operational cost reductions, cited as up to 60%, and significantly reduced efforts in managing multiple document versions, minimizing confusion and errors. * **Facilitation of Virtual Inspections:** eTMFs are instrumental in aiding the development and execution of virtual inspections, improving the efficiency of the inspection process by up to 80%, a critical advantage in modern regulatory environments. * **Continuous Updates for Ongoing Trials:** The electronic nature of eTMFs allows for easy and continual updates for ongoing trials, ensuring that the TMF remains current and compliant throughout the duration of a study. Key Concepts: * **eTMF (Electronic Trial Master File):** A digital system for managing and storing essential documents and records related to a clinical trial, ensuring regulatory compliance and operational efficiency. * **TMF (Trial Master File):** A collection of essential documents that individually and collectively permit the evaluation of the conduct of a clinical trial and the quality of the data produced. * **Directive 2005/28/EC:** An EU directive laying down principles and detailed guidelines for good clinical practice as regards investigational medicinal products for human use, as well as the requirements for authorization of the manufacturing or importation of such products. * **Volume 10 of the Rules Governing Medicinal Products in the EU:** A comprehensive set of guidelines and regulations for medicinal products within the European Union, providing detailed guidance on various aspects including clinical trials and documentation.

Accelerate time to site activation with Vault Study Startup
Veeva Systems Inc
/@VeevaSystems
Mar 17, 2020
This video provides an in-depth exploration of the challenges inherent in clinical trial study startup and introduces Veeva Vault Study Startup as a specialized solution designed to accelerate site activation. The presentation begins by establishing the high cost and complexity associated with managing study startup activities manually, often relying on disparate spreadsheets and emails. This fragmentation makes it difficult for clinical operations teams to determine the critical path for a study, leading to delays that can cost pharmaceutical companies up to $2 million per month. The core purpose of the application is to streamline these processes, ensuring the rapid identification and activation of suitable trial sites. The solution, Veeva Vault Study Startup, focuses on creating a unified, intuitive interface for managing the entire process. Users gain access to a personalized study startup homepage that provides a comprehensive view of all studies and milestones, clearly outlining daily priorities and tasks. This centralization is crucial for identifying and resolving operational bottlenecks quickly, facilitating collaboration among team members from a single source of truth. The platform addresses a significant pain point in the site selection process by enabling the direct distribution of feasibility surveys from within the application, thereby eliminating the manual effort and wasted hours typically spent reconciling survey results from external sources. The video emphasizes the platform's utility for global studies through the inclusion of built-in workflows and country-specific milestones, which are essential for navigating diverse regulatory and operational requirements worldwide. The acceleration of the site activation process is further supported by real-time dashboards and reports, providing immediate progress tracking and enabling data-driven decision-making. Crucially, Vault Study Startup is positioned within Veeva's unified suite of clinical operations applications, ensuring seamless information exchange and integration with related systems such as the Clinical Trial Management System (CTMS) and the electronic Trial Master File (eTMF). This integration improves overall collaboration and increases operational efficiency, ultimately helping to get therapeutic products to patients faster. Key Takeaways: • **High Cost of Delay:** Delays in clinical trial study startup are extremely costly, potentially reaching $2 million per month, underscoring the necessity of optimizing site activation timelines and identifying the critical path quickly. • **Centralized Management:** The platform replaces fragmented tracking methods (spreadsheets and emails) with a single, intuitive interface, offering a full view of studies, milestones, and daily priorities to minimize complexity and friction. • **Personalized Workflow:** A personalized study startup homepage allows users to see their specific tasks and priorities, enabling efficient task completion and immediate identification of issues or bottlenecks requiring action. • **Automated Feasibility Surveys:** The system eliminates the manual burden of site selection by allowing teams to send feasibility surveys directly from the application, drastically reducing the time spent reconciling results and identifying the right sites. • **Global Study Acceleration:** The application supports complex global trials by incorporating built-in workflows and country-specific milestones, ensuring compliance and accelerating the site activation process across different jurisdictions. • **Real-Time Visibility:** Real-time dashboards and reports provide immediate tracking of site activation progress, enabling clinical operations teams to make better, more informed decisions based on current data rather than outdated reports. • **Unified Clinical Ecosystem:** Vault Study Startup is integrated into Veeva’s unified suite of clinical operations applications, facilitating seamless information sharing across core systems like CTMS and eTMF, which enhances collaboration and operational efficiency. • **Focus on Bottleneck Resolution:** The centralized interface is specifically designed to help users quickly find and resolve issues and bottlenecks that traditionally slow down the study timeline, ensuring the critical path remains clear. Tools/Resources Mentioned: * Veeva Vault Study Startup * Veeva Vault CTMS (Clinical Trial Management System) * Veeva Vault eTMF (electronic Trial Master File) Key Concepts: * **Study Startup:** The initial phase of a clinical trial that encompasses site selection, regulatory document submission, contract negotiation, and site activation before patient enrollment can begin. * **Site Activation:** The formal process of granting a clinical trial site permission to begin study activities, typically following regulatory approval and completion of all necessary documentation and training. * **Critical Path:** The sequence of dependent activities in a project (like study startup) that determines the shortest possible time needed for completion; delays on the critical path directly extend the overall study timeline. * **Feasibility Surveys:** Questionnaires sent to potential clinical sites to assess their capability, resources, patient population access, and interest in participating in a specific clinical trial.

Top Considerations When Evaluating Cloud based Quality Management Systems
Veeva Systems Inc
/@VeevaSystems
Mar 16, 2020
This video provides an in-depth exploration of the critical considerations when evaluating cloud-based Quality Management Systems (QMS) in the life sciences sector. Mike Jovanis, VP of Vault Quality at Veeva Systems, traces the evolution of electronic QMS from its inception with 21 CFR Part 11 in the late 1990s, through its maturation into web-based applications, to the current landscape dominated by cloud solutions. He establishes that the industry has reached a significant inflection point, necessitating a fundamental shift in how organizations approach QMS vendor selection and system implementation. Jovanis elaborates on the historical context, noting that early eQMS implementations were often fragmented and not viewed as strategic enterprise systems. While some organizations later consolidated these systems, they often did so on older technologies. The recent advent of cloud-based solutions, such as Veeva Vault, has created immense pressure on legacy vendors, many of whom are private equity-owned and struggle with the high investment and cultural "cloud DNA" required to adapt. He argues that history shows previous leaders in a technology space rarely become future leaders during major technological turnovers, highlighting the inherent difficulties legacy companies face in reinventing themselves. From Veeva's perspective, the video emphasizes the "industry cloud" approach, where a mature and stable platform like Vault is used to commercialize purpose-built applications for quality systems. This methodology focuses on delivering demonstrated best practices, driving industry standardization, and ensuring rapid time to value without the extensive requirements definition and configuration processes typical of older technologies. Jovanis details how Veeva has consolidated solutions for quality document management, QMS, CGXP training, and manufacturing shop floor content delivery onto a single Vault platform, enabling sophisticated business process connections—such as linking change control between QDM and QMS, or triggering training based on specific events—that were impossible with siloed legacy systems. The core message underscores that organizations must approach QMS evaluations with a long-term strategic mindset, selecting a partner for the next decade or more. This requires granular evaluations that not only assess core functional differences but also understand the transformative benefits that modern cloud solutions can offer. Jovanis stresses the importance of recognizing that the industry has fundamentally changed, and traditional thinking about QMS vendors and implementations is no longer adequate for achieving strategic advantages and future-proofing operations in a highly regulated environment. Key Takeaways: * **Evolution of eQMS:** The electronic Quality Management System (eQMS) market emerged with 21 CFR Part 11 in the late 1990s, initially comprising client-server software that evolved into single-instance, web-based applications. These systems were often implemented incrementally and lacked enterprise-wide strategic integration. * **Industry Inflection Point:** The QMS landscape has reached a critical inflection point due to the introduction of cloud-based solutions, which has fundamentally altered vendor dynamics and competitive pressures. This necessitates a fresh perspective on QMS evaluations. * **Challenges for Legacy Vendors:** Incumbent technology leaders rarely become future leaders during significant technological shifts. Legacy QMS vendors often face substantial hurdles, including the need for high profitability (especially if private equity-owned), insufficient investment for re-platforming, and a lack of inherent "cloud DNA" in their organizational structure and processes. * **Importance of "Cloud DNA":** Successfully operating in the cloud requires a distinct organizational culture, development methodology, and delivery model. Companies lacking this "cloud DNA" struggle to adapt, even with acquisitions, making their transformation efforts often ineffective. * **Veeva's Industry Cloud Strategy:** Veeva leverages its mature Vault platform to deliver purpose-built applications for quality systems, embodying an "industry cloud" approach. This strategy focuses on providing demonstrated best practices, driving industry standardization, and enabling rapid time to value. * **Transformative Outcomes:** Modern cloud QMS solutions aim for transformative outcomes beyond mere technology replacement. They address standardization challenges, consolidate disparate applications, and streamline complex workflows, offering strategic advantages over incremental improvements. * **Integrated Platform Benefits:** Consolidating various quality solutions (e.g., quality document management, QMS, CGXP training, shop floor content delivery) onto a single platform like Veeva Vault enables powerful business process connections. This allows for seamless integration, such as linking change control between different quality functions or triggering training based on specific events. * **Broader Ecosystem Integration:** The benefits extend beyond quality, with integrated platforms facilitating sophisticated business process connections between regulatory and quality functions, enhancing overall compliance and operational efficiency across the life sciences value chain. * **Long-Term Vendor Partnership:** Organizations should evaluate QMS vendors as strategic partners for a decade or more. This requires a critical assessment of the vendor's long-term viability, adaptability to future technology, and genuine cloud capabilities, rather than just current feature sets. * **Granular and Transformative Evaluations:** Due diligence must involve granular-level evaluations that not only scrutinize core functional differences but also deeply understand the transformative benefits that modern cloud solutions can unlock. These benefits are crucial for building a compelling business case for a significant, long-term investment. * **Rethink QMS Strategy:** Given the dramatic changes in the industry, organizations must adopt a new mindset for QMS evaluations, moving beyond the incremental, iterative approaches of the past 20 years. The focus should be on strategic, future-proof solutions that leverage the full potential of cloud technology. Tools/Resources Mentioned: * **Veeva Vault:** A mature and stable platform serving as the foundation for Veeva's industry-specific cloud applications. * **Veeva Vault Quality Applications:** Specific solutions built on the Vault platform, including Quality Document Management, QMS, CGXP Training, and tablet-based content delivery on the manufacturing shop floor. Key Concepts: * **21 CFR Part 11:** A U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulation governing electronic records and electronic signatures, which significantly influenced the early development of eQMS. * **Client-Server Software:** An older software architecture where applications run on individual computers ("clients") and connect to a central server for data and services, contrasting with modern web and cloud models. * **Industry Cloud:** A specialized cloud computing model tailored to meet the unique requirements, regulations, and best practices of a specific industry, such as life sciences, offering purpose-built applications and integrated workflows. * **Cloud DNA:** Refers to the intrinsic organizational culture, operational processes, and technological expertise required to effectively develop, deploy, and maintain cloud-native products and services. * **Transformative Outcomes:** Significant and fundamental improvements in business processes, efficiency, and strategic capabilities, rather than just minor or incremental enhancements. * **Rapid Time to Value:** The speed at which an organization can realize tangible benefits and a return on investment from implementing a new system or solution. Examples/Case Studies: * **Veeva Vault Integrated Quality Solutions:** The video highlights how Veeva Vault consolidates quality document management, QMS, CGXP training, and shop floor content delivery onto a single platform. This integration enables specific business process connections, such as linking change control between quality document management and QMS, or triggering training based on specific events. * **Regulatory and Quality Connections:** Veeva has also developed sophisticated business process connections between regulatory and quality applications within its broader ecosystem, demonstrating the power of an integrated platform to streamline workflows across different functions.

2020 Veeva Quality Management Trends for Biopharma
Veeva Systems Inc
/@VeevaSystems
Mar 16, 2020
This video provides an in-depth analysis of the quality management trends driving significant technological and operational transformation within the biopharmaceutical industry, particularly focusing on the shift away from legacy systems toward modern cloud solutions. Mike Jovanis, VP of Vault Quality at Veeva Systems, frames the historical context by noting that system adoption over the last two decades followed a "sine curve" pattern: periods of incremental investment followed by complacency, leading to a patchwork of aging technology across most organizations. This reactive, fragmented approach has resulted in over-engineered processes, corresponding manual workarounds, and a critical need for large-scale modernization. The acceleration toward re-platforming and adopting multi-tenant, industry cloud software is driven by three primary factors. The first is the necessity for significant business process engineering and modernization. Many existing systems and processes were implemented reactively, creating inefficient, complex workflows that require expensive overhauls. The investment required for this process overhaul often justifies the simultaneous implementation of modern, unified technology platforms. The second critical driver is the reality of globalization and outsourcing. Modern organizations rely heavily on global suppliers, contract manufacturers, and various contract service providers. Legacy applications are fundamentally incapable of facilitating the necessary interactions and control required to maintain a unified quality picture across these third parties, forcing organizations to append additional manual processes around the system perimeter. The third factor compelling transformation is simple technological obsolescence and the compelling benefits of unifying multiple disparate solutions onto a single platform. These combined pressures are leading to an acceleration of large-scale, transformative projects—a marked difference from the incremental investments of the past. These new initiatives require organizations to clearly understand and articulate the business value of the transformation, as they represent a major strategic shift rather than a simple system upgrade. Looking ahead, the industry is predicted to look significantly different within the next few years. The speaker forecasts a widespread proliferation of cloud technology, the establishment of modern, standardized best practices across the sector, and the universal engagement of third-party partners and service providers directly within the core quality processes. This digital transformation aims to eliminate risk-adverse manual hand-offs, improve compliance, and ensure better communication and control across the entire global quality ecosystem. Key Takeaways: • **The End of Incremental Investment:** The historical pattern of reactive, incremental investment in quality systems has created a landscape of legacy, patchwork technology that is no longer sustainable for modern global operations. • **Justifying Transformative Projects:** Organizations must shift from justifying small, incremental upgrades to demonstrating the clear business value of large-scale, transformative projects, which require significant process overhaul alongside technology adoption. • **Three Drivers for Re-Platforming:** The move to modern cloud solutions is primarily fueled by: 1) the need for business process engineering to eliminate over-engineered, manual workflows; 2) the requirement to digitally engage global suppliers and contract partners in quality processes; and 3) the obsolescence of aging technology. • **Globalization Demands Digital Inclusion:** Legacy quality applications fail to adequately facilitate interactions with global suppliers and contract manufacturers, necessitating the adoption of platforms capable of directly engaging these third parties to maintain regulatory control and visibility. • **Cloud as the Unifying Solution:** Multi-tenant, industry cloud software is emerging as the preferred solution for unifying multiple disparate quality systems onto a single platform, offering standardization and modernization benefits that legacy systems cannot match. • **Process Modernization is Key:** Technology implementation should be viewed as an opportunity to conduct significant business process engineering, moving away from reactive, over-engineered processes that often rely on manual workarounds. • **Future State: Standardization and Control:** The biopharma industry is moving toward a future defined by the proliferation of cloud technology, standardized best practices for quality management, and the universal, digital engagement of all external service providers within the quality ecosystem. • **Eliminating Manual Hand-offs:** Digitalization and automation are essential trends aimed at eliminating risk-adverse manual hand-offs and inefficient forms of information sharing, which currently cause delays and communication gaps between partners. • **Focus on Quality, Compliance, and Operations:** The ultimate goal of these transformative projects is to achieve simultaneous improvements in quality control, regulatory compliance adherence, and overall business operational efficiency. Tools/Resources Mentioned: * Veeva Vault Quality * Multi-tenant and Industry Cloud Software Key Concepts: * **Sine Curve of Incremental Investment:** The historical pattern of technology adoption in quality management, characterized by periods of small investments followed by complacency, resulting in fragmented, outdated systems. * **Multi-tenant Cloud Software:** Modern software architecture where a single instance of the software serves multiple customers, enabling rapid updates, standardized best practices, and easier integration across the industry. * **Business Process Engineering (BPE):** The fundamental rethinking and redesign of business processes to achieve dramatic improvements in critical measures of performance, often necessitated by the inefficiencies created by reactively implemented legacy systems.

Practical experience with Cloud Qualification
Epista Life Science
/@epistalifescience6136
Feb 27, 2020
This video provides an in-depth exploration of practical cloud qualification within regulated GxP environments, particularly for the life sciences industry. Epista Life Science, a consultancy focused on improving regulatory compliance, presents a structured approach to address the complexities of moving IT solutions to the cloud. The discussion begins by establishing that while cloud adoption offers numerous benefits, it does not inherently eliminate compliance challenges. Instead, it shifts the nature of control and responsibility, necessitating a robust oversight strategy from the regulated company. The presentation delves into various "as a Service" models, from colocation to Software as a Service (SaaS), highlighting how the degree of control relinquished to the cloud service provider increases with each model. A core theme is the critical importance of oversight, as regulated companies transfer procedural controls for aspects like patching, version upgrades, and underlying IT stack maintenance to the provider. The speakers emphasize that a successful cloud transition requires a comprehensive plan encompassing vendor assessment, service level agreement (SLA) negotiation, and a crucial, often overlooked, exit strategy to ensure data control and portability. A significant portion of the webinar is dedicated to a unique "cloud compliance verification" framework. This framework utilizes a detailed spreadsheet to systematically link relevant regulatory requirements (such as EU Annex 11 and 21 CFR Part 11) to the specific responsibilities of both the cloud service provider and the regulated customer. A practical case study involving the qualification of Office 365 for GxP activities illustrates how this framework is applied, referencing Microsoft's standard SLAs and SOC 2 reports. The video concludes by introducing "Automated Boost," a tool designed to automate manual compliance tasks and periodic reviews, demonstrating its use for checking multi-factor authentication (MFA) status and monitoring Microsoft's Message Center for critical updates, thereby enabling continuous control and compliance in the cloud. Key Takeaways: * **Cloud Adoption Shifts, Not Eliminates, Compliance Burden:** Moving to cloud solutions like Office 365 or Veeva does not make GxP compliance challenges disappear; it transforms them, requiring regulated companies to maintain vigilant oversight and adapt their control strategies. * **Oversight is Paramount in Cloud Environments:** When relinquishing control over underlying IT infrastructure (e.g., patching, OS maintenance, firewall configurations) to a cloud service provider, the regulated company must establish robust oversight mechanisms to ensure the provider's procedures meet compliance standards. * **Structured Cloud Qualification Process:** A successful cloud transition should follow a familiar IT implementation process, including a detailed planning phase (cloud strategy, vendor assessment, SLA negotiation), an explicit exit strategy, and a tailored implementation phase. * **The Importance of an Exit Strategy:** A clear exit strategy is an integral part of cloud transition planning, addressing how data will be extracted and retained in a usable format if the company decides to change providers or return to an on-premise solution, ensuring continued data control. * **"Light IQ" for Cloud Solutions:** For cloud implementations, the Installation Qualification (IQ) can be a "light IQ," focusing primarily on the client-specific configuration of the cloud account, environment, users, groups, and integrations, rather than extensive testing of the underlying infrastructure managed by the provider. * **Cloud Compliance Verification Framework:** A "massive spreadsheet" approach is recommended to systematically link general regulatory requirements (e.g., EU Annex 11, 21 CFR Part 11) to specific interpretations, additional client-specific requirements, and the documented procedural responsibilities of both the cloud service provider and the customer. * **Leveraging Cloud Service Provider Documentation:** Regulated companies should rely on and reference documentation provided by the cloud service provider, such as standard SLAs and third-party audit reports (e.g., SOC 2 reports for Microsoft Office 365), to demonstrate the provider's adherence to controls. * **Continuous Operation and Maintenance (O&M) with a "Control Wheel":** Cloud compliance requires ongoing O&M activities, which can be organized using a "control wheel" defining daily (e.g., general cloud management), monthly (e.g., account cleanup), quarterly (e.g., account access reviews), and yearly (e.g., re-verification of cloud compliance) recurring tasks. * **Automating Repetitive Compliance Tasks:** Many recurring cloud O&M tasks, such as checking system health, user configurations (like MFA status), or monitoring provider updates, are manual and time-consuming. Automation tools can significantly save time and money by performing these "point-and-click" activities. * **Monitoring Provider Updates (Microsoft Message Center):** For SaaS solutions like Office 365, it is critical to regularly monitor the provider's message center (e.g., Microsoft Message Center) for notifications on updates, issues, and planned changes, assessing their impact on control and compliance. * **Data Lifecycle and Cloud Retirement:** Just like on-premise systems, cloud systems require consideration for data lifecycle management and system retirement, ensuring data integrity and accessibility even after a system is decommissioned or a cloud service is terminated. **Tools/Resources Mentioned:** * **Automated Boost:** A record and replay test automation tool demonstrated for monitoring and automating compliance tasks in cloud environments. * **Microsoft Office 365:** Used as a practical case study for cloud qualification and automation. * **Microsoft Azure:** Mentioned in the context of Microsoft's cloud infrastructure responsibilities. * **Microsoft Message Center:** A platform for Microsoft to communicate updates, issues, and planned changes to its services. **Key Concepts:** * **XaaS (Everything as a Service):** A broad category of cloud computing services, encompassing Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS), each with varying levels of control shared between provider and customer. * **Cloud Qualification:** The process of formally documenting that a cloud-based system or service meets predefined regulatory requirements and is fit for its intended GxP-regulated purpose. * **Cloud Compliance Verification:** A methodology, exemplified by a detailed spreadsheet, for systematically mapping regulatory requirements (e.g., GxP, 21 CFR Part 11, EU Annex 11) to the controls and responsibilities of both the cloud service provider and the regulated customer. * **Light IQ (Installation Qualification):** A streamlined approach to IQ for cloud solutions, focusing on the configuration and integration aspects managed by the customer, rather than extensive testing of the underlying infrastructure which is the provider's responsibility. * **Control Wheel:** A visual framework used to define and schedule recurring operational and maintenance activities necessary to maintain continuous compliance and control over cloud solutions, categorizing tasks by frequency (daily, monthly, quarterly, yearly). * **GxP (Good x Practice):** A collection of quality guidelines and regulations for various aspects of regulated industries, particularly life sciences, including Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP), Good Clinical Practice (GCP), and Good Laboratory Practice (GLP). * **21 CFR Part 11:** Regulations from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) that set forth the criteria under which electronic records and electronic signatures are considered trustworthy, reliable, and equivalent to paper records and handwritten signatures. * **EU Annex 11:** An annex to the European Union's Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) guidelines, providing specific requirements for computerized systems used in pharmaceutical manufacturing. * **MFA (Multi-Factor Authentication):** A security system that requires more than one method of authentication from independent categories of credentials to verify the user's identity for a login or other transaction.

Streamline Change Control and Variation Management
Veeva Systems Inc
/@VeevaSystems
Feb 20, 2020
This video provides an in-depth exploration of streamlining change control and variation management within the biopharmaceutical industry, focusing on how Veeva's unified Quality and Regulatory Information Management (RIM) solutions address long-standing challenges. The presentation, led by Veeva's Quality and Regulatory strategy teams, highlights the complexities of managing product changes that often have significant regulatory impact. It emphasizes that traditional, manual, and siloed approaches lead to inefficiencies, compliance risks, and delayed product availability, setting the stage for Veeva's integrated platform as a transformative solution. The core of the discussion revolves around Veeva's vision to build an "industry cloud for Life Sciences," offering best-of-breed applications designed with industry best practices and compliance in mind. The speakers detail the functionalities of Veeva's Vault Quality Suite (including Quality Docs, Station Manager, Training, and QMS) and the Vault RIM Suite (Registrations, Submissions, Submissions Publishing, and Submissions Archive). A key message is that while these are presented as separate applications for licensing, they are built on a single Vault platform and data model, enabling seamless data flow and process unification, particularly for complex processes like change control. The video then delves into a specific workflow demonstrating how a change request initiated in Vault QMS triggers a regulatory impact assessment within Vault Registrations. This bi-directional integration allows quality teams to quickly understand the regulatory implications (impacted licenses, local market requirements) and regulatory teams to update filing statuses, which are then visible in real-time within QMS. This automation significantly reduces manual effort, improves compliance, optimizes costs, and enables more informed product shipment decisions, ultimately preventing potential short supply situations for critical medicines. The Q&A session further clarifies technical aspects, integration capabilities (e.g., with ERP systems), and Veeva's roadmap for regulatory standards like IDMP. Key Takeaways: * **Complexity of Change Control:** Change control in biopharma is a highly complex, multi-step process that can take anywhere from six months to two years to complete. Large organizations may evaluate tens of thousands of change requests and approve upwards of 15,000 changes annually, many with significant downstream regulatory impact. * **Challenges of Legacy Systems:** Traditional approaches rely on separate, siloed quality and regulatory systems, leading to manual "swivel-chair" processes, data duplication, and a lack of real-time visibility. Regulatory impact assessments, often managed via spreadsheets, are cumbersome and prone to errors, hindering compliance and extending cycle times. * **Veeva's Unified Platform Approach:** Veeva aims to provide an "industry cloud for Life Sciences" with best-of-breed applications (Vault Quality and Vault RIM suites) built on a single, multi-tenant cloud platform. This unified approach manages content, data, and business processes seamlessly, ensuring consistency and compliance. * **Vault Quality Suite Components:** The suite includes Vault Quality Docs for GxP document management, Vault Station Manager for shop floor access, Vault Training for managing training matrices, and Vault QMS for structured data management of quality events like deviations, CAPA, audits, risk management, and change control. * **Vault RIM Suite Components:** Designed to overcome regulatory fragmentation, the RIM suite comprises Vault Registrations (for tracking, regulatory impact assessments, xEVMPD/IDMP), Vault Submissions (for content planning, authoring), Vault Submissions Publishing, and Vault Submissions Archive, all leveraging a single data model for end-to-end visibility. * **Streamlined QMS-RIM Integration:** A key benefit is the automated, bi-directional integration between Vault QMS and Vault Registrations. This allows for the seamless exchange of information regarding change controls and their regulatory impact, eliminating manual handoffs and reducing errors. * **Automated Regulatory Impact Assessment:** When a change request is created in QMS, the system can automatically trigger a regulatory impact assessment in Registrations. This identifies impacted licenses and local market requirements, feeding this critical information back to QMS to inform decisions on whether to proceed with the change. * **Real-time Regulatory Status Visibility:** As regulatory filings progress and approvals are received from health authorities, their status is automatically updated and made visible within QMS. This real-time information is crucial for making accurate and timely product shipment decisions. * **Significant Business Benefits:** Unifying change control across quality and regulatory leads to greater compliance, cost optimization through reduced manual effort and faster cycle times, and improved decision-making for product shipments, ultimately preventing critical medicine shortages. * **IDMP Implementation Strategy:** Veeva currently supports xEVMPD and is committed to incrementally building out IDMP functionality. The strategy involves developing features as the EMA releases clearer implementation guide details, leveraging Veeva's three-release-per-year cycle. * **GxP System Change Management:** Vault QMS fully supports managing change requests specifically related to GxP systems, offering flexibility to configure multiple types of changes within the change control workflow process. * **Productized Connector:** The integration between Vault QMS and Vault Registrations is a productized connector, not custom code. It is included with active subscriptions to both modules and requires configuration, such as mapping products and lifecycle states between the two systems. * **ERP Integration Capabilities:** Vault QMS can integrate with ERP systems for various purposes, including placing impacted batches on hold or importing master data, ensuring data consistency and streamlined processes across the enterprise landscape. * **Flexible Change Plan Definition:** While the delivered application suggests a high-level change plan for initial impact assessment, the workflow within Vault QMS can be configured to align with an organization's preference for defining a full change management plan before initiating impact assessments. Tools/Resources Mentioned: * Veeva Vault Quality Suite (Vault Quality Docs, Vault Station Manager, Vault Training, Vault QMS) * Veeva Vault RIM Suite (Vault Registrations, Vault Submissions, Vault Submissions Publishing, Vault Submissions Archive) * EMA Gateway * ERP systems (as potential integration points) * Excel spreadsheets, Microsoft Project (mentioned as legacy tools for content plans) Key Concepts: * **Change Control:** A formal, documented process to manage and track all changes made to a product, system, or process, ensuring they are introduced in a controlled and coordinated manner. * **Variation Management:** The process of managing changes to approved regulatory submissions for medicinal products, often requiring communication and approval from health authorities. * **Unified Quality and Regulatory Information Management (RIM):** An integrated approach that combines quality management systems (QMS) with regulatory information management systems to create a seamless flow of data and processes, enhancing efficiency and compliance. * **Regulatory Impact Assessment:** The critical step of evaluating how a proposed change will affect existing regulatory approvals, licenses, and submission requirements in various markets. * **Local Disposition:** The determination of specific regulatory actions or filings required in individual local markets based on the outcome of a regulatory impact assessment. * **GxP:** A comprehensive set of guidelines and regulations (e.g., Good Manufacturing Practice, Good Clinical Practice) that ensure the quality, safety, and integrity of products and processes in the life sciences industry. * **21 CFR Part 11:** A regulation from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) that sets forth the criteria under which electronic records and electronic signatures are considered trustworthy, reliable, and equivalent to paper records and handwritten signatures. * **xEVMPD (extended EudraVigilance Medicinal Product Dictionary):** A European standard for the electronic submission of medicinal product data to the European Medicines Agency (EMA). * **IDMP (Identification of Medicinal Products):** A set of international ISO standards aimed at providing a globally consistent way to identify and exchange information on medicinal products. * **Industry Cloud:** A specialized cloud computing platform tailored to the specific needs, regulations, and best practices of a particular industry, such as life sciences. * **Swivel-Chair Process:** A term used to describe inefficient manual data transfer between disconnected systems, often involving re-keying information, leading to errors and delays. Examples/Case Studies: * The video uses the example of changing a piece of manufacturing equipment to illustrate the complex regulatory impact assessment process, including identifying impacted licenses and local market requirements. * It cites real-world examples of larger organizations evaluating tens of thousands of change requests annually and approving upwards of 15,000 changes, highlighting the sheer volume and complexity involved. * Another example mentioned is a single product potentially undergoing over 200 changes in a given year, underscoring the continuous nature of change management in the industry.

Livia - AI for Veeva CRM
IT Lab Brasil
/@itlabbrasil2587
Feb 19, 2020
This video provides an introduction to Livia, an Artificial Intelligence assistant specifically designed for integration with Veeva CRM, targeting sales representatives within the pharmaceutical industry. The presentation highlights a common challenge faced by pharma sales reps: the significant time and effort required to analyze complex CRM reports and plan their daily activities, often leading to pressure and distress. Livia is positioned as a solution to this problem, aiming to streamline data exploration and insight generation, thereby enhancing sales force effectiveness and efficiency. The core functionality of Livia revolves around its ability to act as a virtual AI assistant directly within Veeva My Site. It is engineered to explore and synthesize data from the CRM system, combining it with external market and territory information. This comprehensive data analysis allows Livia to provide sales reps with relevant insights that would otherwise require extensive manual effort or specialized business intelligence skills. The user interaction model is conversational, enabling reps to either select from a predefined list of questions or type their own queries using a keyboard interface. Upon answering a question, Livia can offer further options or drill-down capabilities directly within the Veeva CRM environment, such as checking specific customer data like "Mary Clark." Furthermore, Livia operates with a robust back-office system that generates real-time reports, reflecting trends and addressing the main concerns of the sales rep team. This real-time feedback mechanism allows for continuous adjustment of Livia's answers to align with specific sales team needs and business objectives, ensuring the information provided is always relevant and actionable. The AI is also designed to be a "fast learner," implying that its accuracy and helpfulness improve with increased user interaction. The overarching goal is to empower sales reps to achieve better results faster, easier, and with significant time savings, effectively democratizing data-driven decision-making without requiring them to become business intelligence experts. Key Takeaways: * **Addressing Sales Rep Inefficiency:** The video identifies a critical pain point for pharmaceutical sales representatives: the excessive time spent analyzing complex CRM reports and planning activities, which can lead to stress and reduced productivity. * **AI for Veeva CRM Integration:** Livia is introduced as an AI assistant specifically developed to integrate seamlessly with Veeva CRM, a leading platform in the pharma industry, enhancing its utility for sales teams. * **Comprehensive Data Exploration:** The AI assistant is capable of exploring not only internal Veeva CRM data but also external market and territory information, providing a holistic view for sales planning and strategy. * **Intuitive Conversational Interface:** Sales reps can interact with Livia through a chat interface, asking questions either from a predefined list or by typing custom queries, making data access user-friendly and efficient. * **Actionable Insights within CRM:** After providing answers, Livia can offer additional options or direct actions within the Veeva CRM system, such as reviewing specific customer data, facilitating immediate application of insights. * **Real-time Reporting and Trends:** Livia is supported by a back-office system that delivers real-time reports, highlighting trends and key concerns relevant to the sales team, ensuring up-to-date information. * **Customizable and Adaptive Answers:** The AI's responses can be adjusted to meet the specific needs and business context of individual sales teams, ensuring the relevance and utility of the information provided. * **Continuous Learning Mechanism:** Livia is designed to be a "fast learner," meaning its performance, accuracy, and helpfulness improve over time as sales representatives interact with it more frequently. * **Empowering Non-BI Professionals:** A key benefit is enabling sales reps to leverage advanced data insights and analytics without needing specialized business intelligence skills, democratizing data-driven decision-making. * **Improved Sales Performance and Time Savings:** The ultimate promise of Livia is to help sales teams achieve better results faster, easier, and with significant time savings, by optimizing their planning and preparation processes. Tools/Resources Mentioned: * Veeva CRM * Livia (AI Assistant) * Veeva My Site Key Concepts: * **AI Assistant:** An artificial intelligence program designed to help users by performing tasks or providing information, often through conversational interfaces. * **Veeva CRM Integration:** The process of connecting an application or system directly with Veeva CRM to leverage its data and functionalities. * **Real-time Reporting:** The capability to generate and view reports instantly as data becomes available, providing up-to-the-minute insights. * **Data Exploration:** The process of discovering patterns, trends, and anomalies in data, often using visual methods and interactive tools. * **Commercial Operations Optimization:** The strategic improvement of processes, technologies, and people within a company's commercial functions to enhance efficiency and effectiveness. Examples/Case Studies: * The video uses the example of a sales rep needing to "check the data of Mary Clark" to illustrate how Livia can provide specific customer-related information and further options within Veeva CRM.

Catalyst Clinical Research Selects Veeva Vault Safety
Veeva Systems Inc
/@VeevaSystems
Feb 10, 2020
This video provides an endorsement and case study regarding the implementation of Veeva Vault Safety by Catalyst Clinical Research, focusing specifically on the efficiency of the deployment process and the user experience of the pharmacovigilance platform. Denise Williams, representing Catalyst, details how technology fundamentally supports safety operations by managing the intake and organization of critical data, thereby enabling medical experts and scientists to efficiently evaluate adverse event information. The central theme revolves around the contrast between traditional enterprise system deployments and the modern, rapid approach facilitated by Veeva's cloud-based architecture and methodology. A key focus of the discussion is the application's design and usability. Williams highlights that Vault Safety is "very intuitive" and visually appealing, making it easy for both experienced users and new beginners to navigate. The structure of the interface, where data is clearly presented on the right-hand side, facilitates visualization and workflow management. This emphasis on user experience (UX) is crucial in regulated environments, where efficiency and accuracy are paramount, suggesting that modern safety systems are moving away from cumbersome legacy interfaces toward highly usable, intuitive designs that reduce training time and potential errors. The most striking insight shared by Catalyst Clinical Research concerns the speed and seamlessness of the implementation process. The organization achieved a complete go-live in just 12 weeks. This timeline included all critical phases: requirements documentation, User Acceptance Testing (UAT), and training. This rapid deployment contrasts sharply with the speaker's past experiences with other commercially available systems, which often involve lengthy, complex, and unpredictable rollouts. The efficiency is attributed to Veeva’s development process, which utilizes a sandbox environment concurrently with requirements documentation. This approach ensures that when the system reaches the validation stage, there are "no surprises," drastically streamlining the UAT and final validation steps necessary for GxP compliance. This methodology provides a strong model for other life sciences companies seeking to modernize their safety infrastructure without protracted downtime or costly implementation cycles. ### Key Takeaways * **Technology is Foundational to Safety Operations:** The core role of technology in pharmacovigilance is to efficiently manage the intake, organization, and structuring of vast amounts of safety data, ensuring that medical experts and scientists can focus their efforts on evaluation and analysis rather than data wrangling. * **Intuitive Design Drives Efficiency:** Veeva Vault Safety is praised specifically for its ease-of-use, intuitive interface, and visual appeal. Highly usable systems reduce the learning curve for new users and increase the efficiency of experienced personnel, which is a critical factor in high-stakes regulatory environments. * **Rapid Deployment is Achievable in Regulated Software:** Catalyst Clinical Research achieved a full system go-live in an exceptionally fast 12 weeks, demonstrating that modern, cloud-native solutions can significantly compress the deployment timeline for GxP-critical enterprise software compared to traditional systems. * **Streamlined Validation via Concurrent Development:** The rapid deployment timeline was enabled by Veeva's methodology of utilizing a sandbox environment simultaneously with requirements documentation. This concurrent development and testing approach minimizes surprises during the final validation (UAT) phase. * **Focus on Seamless Implementation:** The deployment was described as "seamless" and "nothing like what we were used to" in comparison to previous experiences with commercially available safety systems, highlighting a significant shift in the enterprise software implementation experience within life sciences. * **Comprehensive Deployment Scope:** The 12-week timeline was comprehensive, encompassing requirements documentation, UAT, and training, indicating a highly integrated and efficient project management approach that covers all necessary regulatory steps. * **Visual Data Management Enhances Workflow:** The application’s design, which places relevant data clearly on the right-hand side, aids in visualization and allows users to easily work through cases, reinforcing the importance of thoughtful UI/UX design in complex data environments. * **CROs Seek Modern, Agile Safety Solutions:** As a Contract Research Organization (CRO), Catalyst Clinical Research’s selection of Vault Safety underscores the industry trend where service providers require modern, agile, and rapidly deployable systems to manage client data efficiently and maintain regulatory standards. ### Tools/Resources Mentioned * **Veeva Vault Safety:** A cloud-based application designed for pharmacovigilance and safety operations, managing adverse event reporting and case processing. * **Sandbox Environment:** A testing and development environment used by Veeva during the implementation phase to allow concurrent development and requirement validation, minimizing post-development issues. ### Key Concepts * **Safety Operations:** The processes and procedures within a pharmaceutical or life sciences organization dedicated to collecting, assessing, monitoring, and preventing adverse effects from pharmaceutical products. This is a core function of regulatory compliance (pharmacovigilance). * **UAT (User Acceptance Testing):** The final phase of software testing where end-users verify that the system meets the specified requirements and functions correctly in a real-world scenario, a mandatory step for GxP validation. * **GxP Compliance:** A set of regulations and guidelines (Good Practices) governing the quality and integrity of data and processes in the life sciences industry, including Good Clinical Practice (GCP) and Good Pharmacovigilance Practice (GVP). Vault Safety implementation must adhere strictly to these standards.

Defining Requirements For An EQMS
ZenQMS- Quality that Means Business
/@zenqms-qualitythatmeansbus2122
Feb 7, 2020
The video provides an in-depth analysis of the essential requirements and strategic implementation phases for an Electronic Quality Management System (EQMS) within the life sciences sector. The core argument, presented by Ryan Coleman from Dayspring Technology, centers on leveraging EQMS to replace outdated, manual, spreadsheet-based systems, thereby ensuring consistent regulatory compliance and audit readiness. Coleman identifies the most critical feature of an EQMS as its ability to enforce "quality gates" and provide mandatory notifications and stepwise guidance through defined workflow processes. These automated controls are crucial because the consistent maintenance of documentation is the first element to fail in older, spreadsheet-based environments. The speaker highlights a significant pitfall of manual systems: the tendency for documentation maintenance to be neglected for months, leading to a frantic, last-minute update rush right before an audit. This practice, often joked about in the industry ("documentation was magically updated two days ago"), signals to auditors that the organization lacked continuous quality control for the preceding 11 months. An effective EQMS solves this by providing automated consistency, ensuring that tasks are completed on time and documentation is current, thus mitigating audit risk and demonstrating continuous adherence to GxP standards. Coleman recommends two primary scenarios for adopting an EQMS. The first is for companies that are "just starting out" and have not yet developed the "bad habit of spreadsheets." This provides an ideal opportunity to automate processes from the outset, either by defining new workflows or absorbing predefined quality management system processes directly into the business structure. The second scenario targets larger organizations with deeply embedded, spreadsheet-based tools. In this case, he advises a phased approach focusing heavily on organizational change management. For established organizations, the recommendation is not to implement every aspect of the EQMS simultaneously—such as change control, internal auditing, and corrective actions (CAPA). Instead, companies should identify one process ripe for a "revamp," such as their corrective action processes, and use that as the initial focus. This allows the organization to slowly put away legacy spreadsheets and roll out different EQMS functionalities over a longer, manageable roadmap, ensuring successful adoption and minimizing disruption. Key Takeaways: • **Critical EQMS Feature:** The most important functionality of an EQMS is the inclusion of "quality gates," mandatory notifications, and stepwise guidance through workflow processes. These features enforce consistency and prevent critical quality tasks from being neglected, a common failure point in manual systems. • **Mitigating Audit Risk:** Manual, spreadsheet-based systems typically result in documentation being updated only right before a regulatory or ISO audit. This lack of continuous maintenance is a red flag for auditors, suggesting non-compliance for the majority of the year. • **Consistency is Key:** An EQMS ensures consistent documentation maintenance throughout the year, removing the need for last-minute "cramming" and providing a transparent, compliant audit trail that demonstrates continuous adherence to quality standards. • **Ideal Implementation Scenario 1 (Startups):** Companies that are newly formed should implement an EQMS immediately to establish compliant processes from the start, avoiding the development of "bad habits" associated with manual spreadsheet management. • **Ideal Implementation Scenario 2 (Established Firms):** Larger organizations with deeply embedded spreadsheet tools must approach implementation through organizational change management, focusing on slowly rolling out the EQMS in manageable phases. • **Phased Rollout Strategy:** Instead of attempting to implement all EQMS components (e.g., change control, internal auditing, CAPA) at once, organizations should select one process that requires a revamp (such as corrective actions) and use that as the initial module to transition away from spreadsheets. • **Automated Task Management:** An EQMS significantly improves efficiency by replacing external, manual reminders (like Outlook notifications) with direct email notifications that contain links, allowing users to quickly access and update required documentation within the system. • **Leveraging Predefined Workflows:** New organizations can expedite the establishment of compliant quality practices by absorbing predefined quality management system processes directly into their EQMS workflows, rather than building them from scratch. • **Roadmap for Change:** For established companies, the transition to an EQMS should follow a longer, strategic roadmap, gradually rolling out different functionalities to ensure successful user adoption and minimize operational disruption. Key Concepts: * **EQMS (Electronic Quality Management System):** A software system designed to manage and automate quality processes and documentation (e.g., CAPA, change control, training, audits) to ensure regulatory compliance (e.g., GxP, 21 CFR Part 11). * **Quality Gates:** Mandatory checkpoints within a workflow process that require specific actions or approvals before the process can advance, ensuring adherence to quality standards. * **Regulatory Technology (RegTech):** Technology solutions focused on helping organizations manage regulatory compliance and reporting requirements efficiently and effectively. * **Organizational Change Management:** The process of preparing, equipping, and supporting individuals to successfully adopt change in order to drive organizational success and outcomes (critical when moving from spreadsheets to a structured EQMS).

Regulatory Services: Submission and Product Lifecycle Considerations
Innomar Strategies
/@innomarstrategies2523
Feb 4, 2020
This video provides an in-depth exploration of critical regulatory considerations for pharmaceutical product submissions and lifecycle management within the Canadian market, specifically focusing on Health Canada’s processes. The speaker, Anne Tomalin, Vice President of Quality, Regulatory and Safety at Innomar Strategies, outlines key mechanisms for accelerating approval, the evolving cost structure for New Drug Submission (NDS) review, and the specifics of data protection exclusivity that supplement patent rights. The discussion is framed around the strategic planning required by sponsors to navigate regulatory pathways efficiently and maximize commercial value. A significant portion of the presentation details the Priority Review process, Canada's mechanism for accelerated approval. This status is highly sought after as it reduces the standard review timeline from ten months down to six months. To qualify, a drug must meet stringent criteria: it must address a severely debilitating or life-threatening condition, and either there must be no other medication available for that condition, or the drug must be demonstrably superior to existing treatments based on head-to-head clinical study results. Meeting these conditions allows the sponsor to apply for Priority Review status, effectively moving their submission ahead of others in the queue. The video also addresses the financial realities of regulatory filing, noting a substantial shift in the cost burden for New Drug Submissions. Historically, the concept was for the industry (sponsor) to cover 50% of the review cost, with the public covering the remaining 50%, resulting in fees of approximately $300,000 to $350,000 for a new chemical entity (NCE). However, regulatory policy is transitioning toward sponsors paying closer to 100% of the review cost. This change is being phased in over about a five-year period, projecting NCE review costs to rise significantly to approximately $700,000. This increase underscores the need for sponsors to ensure submission quality and efficiency to avoid costly delays. Finally, the speaker outlines the specifics of data protection in Canada, which serves as a crucial supplement to patent protection. Data exclusivity is granted for a period of eight years, but it applies exclusively to new chemical entities. This eight-year period includes a critical six-year "no file" window during which generic companies are legally barred from filing a generic submission. Health Canada is prohibited from issuing an approval until the full eight years have elapsed. Furthermore, the video highlights a key incentive for sponsors: submitting work related to a pediatric application can potentially extend the data exclusivity period by an additional six months, offering valuable extended market protection. Key Takeaways: • **Accelerated Approval Mechanism:** Canada offers a Priority Review process that shortens the New Drug Submission review timeline from the standard 10 months to 6 months, representing a 40% reduction in regulatory time-to-market. • **Criteria for Priority Review:** To qualify for accelerated review, the drug must treat a severely debilitating or life-threatening condition and must either address an unmet medical need (no existing medication) or prove superiority over available drugs in head-to-head clinical studies. • **Rising Regulatory Costs:** The cost structure for reviewing a New Chemical Entity (NCE) submission is shifting from a shared burden to nearly 100% sponsor responsibility, leading to projected costs rising from approximately $300,000–$350,000 to around $700,000. • **Strategic Submission Quality:** The significant increase in regulatory fees necessitates that pharmaceutical companies invest heavily in high-quality, compliant submissions to minimize the risk of costly re-submissions, delays, or outright rejection. • **Data Exclusivity Period:** Canada grants eight years of data protection for New Chemical Entities (NCEs), a vital commercial asset that supplements patent protection and restricts generic market entry. • **Generic Filing Restriction:** The first six years of the eight-year data exclusivity period constitute a "no file" period, during which generic companies cannot even submit an application to Health Canada, providing robust initial market protection. • **Pediatric Exclusivity Incentive:** Sponsors can gain an additional six months of data exclusivity by submitting work dealing with a pediatric application, providing a regulatory incentive to conduct studies in younger populations and extending the product’s commercial lifecycle. • **Compliance and Data Strategy Integration:** Effective regulatory strategy requires integrating clinical development plans (like pediatric studies) with commercial objectives (maximizing data exclusivity) and ensuring all data handling meets regulatory standards for submission. Key Concepts: * **Priority Review Process:** An accelerated regulatory pathway in Canada designed for drugs treating severe or life-threatening conditions where there is an unmet need or demonstrated superiority over existing treatments. * **New Drug Submission (NDS):** The formal application submitted to Health Canada seeking approval to market a new drug. * **New Chemical Entity (NCE):** A drug containing an active substance that has not previously been authorized for sale in Canada. * **Data Protection/Exclusivity:** A regulatory measure that prevents a regulatory body (Health Canada) from relying on the originator's clinical data to approve a generic version for a specified period (8 years for NCEs). * **Pediatric Gap Application:** Submission of data related to the use of a drug in pediatric populations, which can trigger an extension of data exclusivity.

Vault Station Manager: Delivering the Right Content to the Right Manufacturing Station
Veeva Systems Inc
/@VeevaSystems
Jan 30, 2020
This demonstration focuses on Veeva Vault Station Manager, a modern, mobile application designed for the manufacturing shop floor within the pharmaceutical and life sciences sectors. The primary goal of the application is to ensure that manufacturing operators consistently have access to the correct, latest approved content—including procedures, work instructions, and videos—at the exact point of use, thereby enhancing compliance and operational efficiency. Station Manager is integrated into the broader Veeva Vault Quality Suite, working specifically in conjunction with Veeva Quality Docs to manage content distribution and control. The application functions as a critical digital interface for operators. Upon accessing the app on a tablet, users are presented with documents and videos specifically assigned to their station. A key feature is its robust offline capability; the application pulls down standard metadata and viewable renditions of documents, storing them encrypted on the device's disk. This ensures continuous access to critical procedures, even in environments with spotty connectivity or during system outages. Operators can easily scroll through lists, utilize built-in search functions based on criteria, and perform in-document searches. The application supports standard finger gestures for navigation, including pinch-to-zoom, and can display supporting documents and videos, demonstrating native support for multimedia content on platforms like iOS. From an administrative and compliance standpoint, Vault Station Manager significantly streamlines the management of controlled documentation. The business administrator manages document assignment and distribution through the familiar Vault Quality Docs interface. A station can be flexibly defined as a piece of equipment, a manufacturing line, or even a specific role, accommodating diverse business needs. Once a document is assigned, the system automatically handles version control: when a document is revised to a new version in Quality Docs, the old version is automatically superseded and updated on the tablet. This automated process directly replaces the manual, high-risk process of managing physical paper binders filled with controlled copies that require laborious reconciliation when superseded or obsolesced. Furthermore, the system provides powerful data engineering and business intelligence capabilities. The application automatically syncs with Vault every 15 minutes, though users can also manually force a sync. Administrators can view connected devices, track device IDs, and monitor the last successful sync time from the administrative view within Quality Docs. All this operational data is available through Vault’s built-in reporting and dashboard features. Examples of actionable insights available include tracking document types by station, identifying devices that have not synced recently (e.g., in the last seven days), monitoring the total number of documents assigned per station, and analyzing device distribution by location. These dashboards provide the necessary oversight to maintain compliance and proactively address potential documentation gaps. Key Takeaways: • **Automated Compliance for GxP Documentation:** Vault Station Manager ensures continuous compliance by automatically distributing the latest approved versions of standard operating procedures (SOPs) and work instructions directly to the point of use on the manufacturing floor, eliminating the risk associated with outdated paper copies. • **Offline Access for Operational Resilience:** The application downloads and encrypts viewable document renditions locally on the tablet, guaranteeing that manufacturing operators maintain access to critical procedures and documentation even during network outages or in areas with poor Wi-Fi connectivity. • **Elimination of Manual Paper Processes:** The system directly replaces the manual management of controlled paper binders, which traditionally required complex reconciliation processes when documents were revised, superseded, or obsoleted, leading to significant time savings and reduced compliance risk. • **Flexible Station Definition:** The underlying data model allows administrators to define a "station" flexibly—as a piece of equipment, a manufacturing line, or a specific operational role—ensuring the system can be tailored to the unique physical and procedural layout of any facility. • **Seamless Integration with Quality Docs:** Station Manager is an extension of the Vault Quality Suite, relying on Vault Quality Docs for centralized content management, version control, and document assignment, ensuring a single source of truth for all manufacturing documentation. • **Automated Version Control and Distribution:** When a business administrator revises a document in Quality Docs, the system automatically pushes the new version to the assigned tablets, ensuring that operators are always working with the current, approved procedure without manual intervention. • **Enhanced Search and Usability:** The mobile application provides operators with intuitive search capabilities, both across the list of assigned documents and within the document content itself, alongside support for multimedia content like training videos. • **Actionable Business Intelligence:** Operational data, including device connectivity status, last successful sync times, and document distribution metrics, is captured and made available through Vault's reporting and dashboard capabilities. • **Proactive Compliance Monitoring:** Administrators can utilize built-in dashboards to monitor key metrics, such as "devices not synced in the last seven days" and "number of documents by station," enabling proactive intervention to maintain system integrity and compliance readiness. Tools/Resources Mentioned: * Veeva Vault Station Manager (Mobile application) * Veeva Vault Quality Suite * Veeva Vault Quality Docs (Content management system) * iOS Platform (Supported operating system for the mobile app) Key Concepts: * **Station Manager:** A mobile application designed to deliver controlled documentation and work instructions directly to manufacturing operators at their specific station or equipment. * **Controlled Copies:** Documents (SOPs, procedures) that must adhere to strict regulatory requirements (like GxP) regarding version control, approval, and distribution, ensuring only the latest approved version is used. * **Viewable Renditions:** Digital copies of documents optimized for viewing on a mobile device, which are downloaded and stored locally to facilitate offline access. * **Sync Now:** A function allowing the user to manually force an immediate synchronization between the mobile device and the central Vault system, supplementing the automated 15-minute sync schedule.

Webinar Preview: Streamline Change Control and Variation Management:
Veeva Systems Inc
/@VeevaSystems
Jan 30, 2020
This webinar preview outlines a critical challenge for large biopharma organizations: managing the complex, multi-step process of change control and variation management. These companies often execute tens of thousands of changes annually, many of which carry significant downstream regulatory impact. The core problem addressed is the reliance on manual processes to manage these touchpoints, which leads to fragmented information, massive distribution delays, issues with regulatory compliance, and ultimately, increased operational risk. The solution proposed by Veeva Systems is the unification of discrete business processes by connecting Quality and Regulatory systems through an integrated platform. The central theme of the presentation, featuring Mike Jovanis (VP of Vault Quality) and Marc Gabriel (Sr. Director of Vault RIM), is demonstrating how a unified Quality and Regulatory solution automates information exchange across business functions. This integration is designed to streamline the evaluation of changes to approved products, ensuring that regulatory impact is assessed efficiently and accurately. By moving away from siloed, manual management, organizations can achieve greater transparency throughout the change lifecycle, which is crucial for effective decision-making and risk mitigation. The key benefits highlighted revolve around measurable improvements in operational performance and compliance posture. Specifically, attendees are promised insights into how to reduce the cycle time required for changes, significantly increase overall efficiency, and reduce regulatory risk by leveraging better intelligence regarding the regulatory impact of each change. The session includes a demonstration of the integrated change control and variation management functionality within the Veeva Vault platform, illustrating how automation and centralized data management can transform what is traditionally a complex and high-risk process into a streamlined, compliant workflow. Key Takeaways: • **High Volume of Changes:** Large biopharma organizations routinely handle tens of thousands of changes yearly, many of which necessitate careful evaluation due to their potential regulatory consequences on approved products. • **Inefficiencies of Manual Processes:** Managing change control through manual methods results in critical failures, including incomplete information transfer, substantial delays in distribution and implementation, and severe risks to regulatory compliance. • **Value of Unification:** The primary strategy for improvement is unifying traditionally discreet business processes, specifically connecting Quality Management Systems (QMS) with Regulatory Information Management (RIM) systems. • **Automation for Compliance:** A unified Quality and Regulatory solution automates the necessary information exchange between these critical business functions, ensuring that regulatory teams are immediately aware of quality changes and vice versa. • **Improved Decision Making and Risk Reduction:** Streamlining change control processes directly improves the quality of decision-making by providing comprehensive, real-time data, thereby lowering the overall regulatory and operational risks associated with product changes. • **Cycle Time Reduction:** Implementing an integrated system is shown to reduce the cycle time required to execute and approve changes, leading to faster operational agility and quicker implementation of necessary product updates. • **Enhanced Regulatory Intelligence:** The integration provides "better intelligence around regulatory impact," allowing organizations to accurately assess and predict the regulatory consequences of a proposed change before implementation, ensuring proactive compliance. • **Veeva Vault Integration:** The solution leverages specific modules within the Veeva ecosystem, namely Vault Quality and Vault RIM, to provide a seamless, integrated platform for managing the entire change control and variation lifecycle. Tools/Resources Mentioned: * **Veeva Vault Quality:** A component of the Veeva Vault suite designed to manage quality processes, including documentation, training, and change control within a regulated environment. * **Veeva Vault RIM (Regulatory Information Management):** A component of the Veeva Vault suite focused on managing regulatory submissions, registrations, and variations globally. * **Integrated Change Control and Variation Management:** The specific integrated functionality demonstrated in the webinar, which bridges the gap between Quality and Regulatory functions. Key Concepts: * **Change Control:** A formal, systematic process used to manage all changes made to a system, product, or process within a regulated environment (like biopharma) to ensure that quality and compliance are maintained. * **Variation Management:** The process of managing regulatory submissions and updates required when changes (variations) are made to approved medicinal products, ensuring compliance with global health authority requirements (FDA, EMA, etc.). * **Unifying Quality and Regulatory Systems:** The strategic integration of QMS and RIM platforms to ensure that changes initiated in the quality domain are automatically assessed for regulatory impact, eliminating manual handoffs and data fragmentation.