Videos
Browse videos by topic
All Videos
Showing 1225-1248 of 1435 videos

Webinar Preview: Modernizing Quality Management
Veeva Systems Inc
/@VeevaSystems
Jan 29, 2020
This video provides an in-depth exploration of the necessity and methodology for modernizing quality management (QM) systems within the pharmaceutical and life sciences manufacturing sectors. Presented by Veeva Systems, the discussion centers on how contemporary pressures—such as addressing drug shortages, developing complex novel therapies, and navigating continuously shifting regulations—are forcing organizations to undertake unprecedented modernization and unification programs for their quality infrastructure. The core message emphasizes that legacy, paper-based systems are insufficient for maintaining compliance and achieving operational efficiency in the current complex regulatory landscape. The speakers, leaders from Veeva Vault Quality, position modern quality systems as essential tools for achieving manufacturing agility. This transformation is driven by the need to reduce costs and increase efficiencies while simultaneously managing regulatory complexity. A key focus area is the automation of critical business processes, which allows companies to move away from manual, error-prone workflows. Furthermore, the webinar highlights the importance of connecting global partners and suppliers through unified systems, a crucial step for maintaining quality control across increasingly complex and distributed supply chains. The content is specifically tailored for quality professionals, GxP compliance officers, and employees within pharma manufacturing, generics, and Contract Manufacturing Organizations (CMOs). The discussion promises to deliver actionable insights into key industry trends driving this transformation, practical opportunities for digitizing manufacturing operations to improve quality, and real-world examples illustrating the benefits companies realize from adopting modern quality systems. Ultimately, the goal of this modernization effort is to eliminate the volume of paper and manual processes that currently hinder efficiency and compliance, thereby creating a robust, unified, and agile quality framework capable of supporting advanced therapeutic development and stringent regulatory requirements. Key Takeaways: • **Drivers for Quality Transformation:** The industry is currently experiencing a period of "unprecedented modernization" driven by three primary pressures: the complexity of novel new therapies, the burden of continuously shifting global regulations, and the imperative to reduce operational costs and increase overall efficiencies. • **Focus on Unification and Digitization:** Organizations are actively pursuing unification programs to consolidate disparate quality systems and processes. A major component of this effort is digitization, specifically targeting the reduction of paper-based and manual processes that introduce risk and inefficiency. • **Automation of GxP Processes:** Modern quality systems are essential for automating core GxP business processes. This automation is critical not only for reducing human error and increasing speed but also for ensuring that audit trails and compliance tracking are robust and readily available for regulatory scrutiny (e.g., 21 CFR Part 11 requirements). • **Supply Chain Connectivity:** Achieving manufacturing agility requires systems that can effectively connect global partners and suppliers. Modern quality systems facilitate this by providing a unified platform for quality documentation, change control, and deviation management across the extended enterprise. • **Operational Efficiency Opportunities:** The webinar identifies key business process efficiency opportunities that arise from modernization, including faster turnaround times for quality events (CAPAs, deviations) and streamlined documentation management, directly impacting time-to-market and operational throughput. • **Target Audience Alignment:** The content is explicitly aimed at quality professionals, quality operations staff, and those responsible for GxP Compliance within manufacturing organizations, confirming the high regulatory and operational focus of the discussion. • **Veeva Vault Quality Ecosystem:** The involvement of Veeva Vault Quality leadership indicates that the proposed solutions and best practices are centered around the capabilities of the Veeva Vault platform, emphasizing its role in managing regulated content and quality processes. • **Intermediate Learning Level:** The content is designed for individuals who already possess basic knowledge of quality management topics, suggesting the discussion will move quickly into higher-level concepts, synthesis, and application of modern quality frameworks. Tools/Resources Mentioned: * **Veeva Vault Quality:** The platform is the implied central technology solution for achieving the discussed modernization goals, focusing on quality systems, operations, and GxP compliance management. Key Concepts: * **Quality Management Transformation:** A strategic initiative involving the overhaul of quality systems, processes, and technology infrastructure to meet modern regulatory and operational demands, moving away from legacy, paper-based methods. * **Manufacturing Agility:** The ability of a manufacturing organization to rapidly adapt to changes in demand, supply chain disruptions, or regulatory requirements while maintaining high standards of quality and compliance. * **GxP Compliance:** Adherence to Good Practices (e.g., Good Manufacturing Practice, Good Clinical Practice) regulations, which are central to quality control in the life sciences industry and a core focus of modern quality system design.

Gens and Associates - 2020 World Class RIM - Structured Data Submissions
Gens and Associates
/@gensandassociates3638
Jan 24, 2020
This video provides an in-depth exploration of Section six, "Structured Data Submissions," from the 2020 World Class RIM (Regulatory Information Management) survey conducted by Gens and Associates. The speaker, Kelly NAT, guides viewers through nine questions designed to assess approaches, costs, and resource requirements related to both existing and upcoming structured data submission mandates within the pharmaceutical and life sciences industries. The primary objective is to gather comprehensive data on how organizations are currently managing these critical regulatory submissions and their preparedness for future requirements, particularly those from the European Medicines Agency (EMA). The discussion begins by addressing current structured data submission requirements, focusing on the capabilities and solutions companies have in place. Question 33 probes the status of existing capabilities, listing various submission types and the diverse solutions employed, such as manual population of internal tools, direct electronic submission from internal systems, reliance on external vendors, or direct entry into Health Authority portals. The survey allows for multiple selections per row, acknowledging that companies often utilize hybrid approaches. Following this, Question 34 specifically targets the handling of xevMPD third acknowledgment records received from the EMA after quality reviews of submitted xevMPD data, offering several options for how these acknowledgments are processed. The latter half of the section shifts focus to future and upcoming structured data submission requirements. Questions 35 through 37 delve into initiatives and strategies companies are employing to prepare for these evolving mandates. The survey lists common strategies observed across the industry but also invites participants to share internally developed approaches, recognizing the unique challenges and solutions companies might devise. The video then highlights specific major initiatives: the EU IDMP SPOR initiative (Question 38) and UDEMED (Question 39). For these, the survey asks participants to estimate the number of months required to achieve full readiness for compliant submissions to the EMA, providing a range of timeframes for selection. The final questions, 40 and 41, address the anticipated costs associated with preparing for IDMP SPOR and UDEMED, respectively. These questions differentiate between costs already incurred and additional expected spend, specifying cost categories such as software, external consultants, external service providers, and data remediation/migration, while explicitly excluding internal resource costs to ensure consistent data comparison. Participants are also asked to indicate their level of confidence in future cost estimates. Key Takeaways: * **Criticality of Structured Data Submissions:** The video underscores the ongoing and increasing importance of structured data submissions for regulatory compliance in the pharmaceutical and life sciences sectors, particularly with mandates from bodies like the EMA. * **Diverse Management Approaches:** Companies employ a variety of methods for managing existing structured data submissions, ranging from manual processes and internal tools to leveraging external vendors or direct interaction with Health Authority portals. Many organizations utilize a combination of these approaches. * **Specific Regulatory Focus on xevMPD:** The survey specifically investigates how companies handle xevMPD third acknowledgment records from the EMA, highlighting the granular detail required for managing post-submission regulatory feedback. * **Proactive Preparation for Future Mandates:** A significant portion of the survey is dedicated to understanding how companies are strategically preparing for upcoming structured data submission requirements, such as the EU IDMP SPOR initiative and UDEMED. * **Strategic Planning for Compliance:** Companies are encouraged to articulate their specific initiatives and strategies for future compliance, including internally developed approaches, indicating a need for tailored solutions beyond generic industry practices. * **Estimating Readiness Timeframes:** Organizations are asked to estimate the time (in months) required to achieve full readiness for compliant submissions to the EMA for major initiatives like IDMP SPOR and UDEMED, providing insight into project timelines and resource allocation. * **Comprehensive Cost Estimation:** The survey requires a detailed breakdown of anticipated costs for compliance, including software, external consultants, contractors, external service providers, and data remediation/migration. This provides a holistic view of financial investment. * **Exclusion of Internal Resource Costs:** To ensure data consistency across survey responses, companies are specifically instructed not to include internal resource costs in their budget estimates, allowing for clearer benchmarking of external expenditures. * **Tracking Current vs. Future Spend:** The survey distinguishes between dollars already spent and additional dollars expected to be spent, offering a phased view of financial commitment towards regulatory readiness. * **Confidence in Cost Estimates:** Participants are asked to provide a level of confidence (high, medium, low) for their future cost estimates, acknowledging the inherent uncertainty in projecting future expenditures for complex regulatory projects. * **Value of Aggregated Data:** The survey emphasizes that all collected data is blinded, encouraging companies to share sensitive budget and strategy information to contribute to valuable industry-wide benchmarks and insights. * **Evolving Regulatory Landscape:** The continuous introduction of new sections and questions in the World Class RIM survey reflects the dynamic and evolving nature of regulatory information management and compliance requirements. Key Concepts: * **Structured Data Submissions:** Data submitted to regulatory authorities in a predefined, machine-readable format to ensure consistency and facilitate processing. * **xevMPD:** Extended EudraVigilance Medicinal Product Dictionary, a database of medicinal product data in the European Union, managed by the EMA. * **EMA (European Medicines Agency):** The agency responsible for the scientific evaluation, supervision, and safety monitoring of medicines in the European Union. * **EU IDMP SPOR Initiative:** The European Union's implementation of ISO Identification of Medicinal Products (IDMP) standards, focusing on Substances, Products, Organizations, and Referentials (SPOR) data. * **UDEMED:** The European Database on Medical Devices, a central database developed by the European Commission to enhance market surveillance and transparency for medical devices. * **Health Authority Portal:** Online platforms provided by regulatory bodies (like the EMA) for direct submission and management of regulatory data. * **Data Remediation and Migration:** Processes involved in correcting errors or inconsistencies in data and transferring data from one system or format to another, often a significant part of preparing for new regulatory requirements.

Gens and Associates - 2020 World Class RIM - Organization
Gens and Associates
/@gensandassociates3638
Jan 24, 2020
This video provides an in-depth review of Section 2, "Organization Background and Strategies," from the 2020 World Class RIM (Regulatory Information Management) survey conducted by Gens and Associates. The primary goal of this section is to establish baseline organizational data regarding the structure, size, and reporting relationships of regulatory functions within life sciences companies. By collecting this data, the survey aims to facilitate comparisons of organizational strategies, particularly concerning efficiency and the operational models of dedicated RIM groups. The speaker, Steve Ganz, guides participants through key questions related to internal regulatory headcount and the specific remit of dedicated RIM teams. The analysis begins with Question 7, which focuses on internal regulatory headcount. This question seeks to quantify the number of regulatory personnel across various locations, including headquarters, regional offices, local offices, and other locations. For medical device companies, the terminology expands to include business divisions and design centers. A significant addition to the 2020 survey is the inclusion of an estimated non-employee headcount. This modification aims to capture the total size of the regulatory organization, allowing for a clear split between full-time employees and external resources like contractors, consultants, and temporary staff, expressed as a full-time equivalent (FTE). The speaker notes the potential difficulty in quantifying non-employees, especially those involved in broad service contracts, and clarifies that the focus is only on those external resources that can be reasonably quantified as FTEs. The second major focus area highlighted is the exploration of the dedicated RIM group, following up on a similar question from the 2018 survey. This section moves beyond simply asking if a dedicated group exists (yes/no/planned within two years) to exploring the specific "remit" or purpose of the Regulatory Information Group (RIG) or team. The speaker emphasizes that this group does not necessarily imply a centralized function; it can be distributed globally, and its size can range from a single individual in small organizations to ten or more in larger enterprises. The survey provides multiple rows listing various potential responsibilities for the RIM group, requiring participants to scale their response based on whether the activity is the sole responsibility of the group, a shared responsibility with another organizational unit, or an area that is not currently managed but is anticipated within the next two years. This detailed breakdown allows for a nuanced understanding of how RIM functions are scoped and managed across the industry. Finally, the speaker stresses the importance of accurately defining the scope of the RIM group's responsibilities. The survey uses a structured scale to capture whether a function is the sole responsibility of the RIM group or shared with another group, regardless of whether the RIM group is primary or secondary. A crucial element for capturing comprehensive data is the inclusion of an "other" field, allowing participants to manually add responsibilities that are primary to their RIM group but not listed in the predefined options. This mechanism ensures that the survey captures the full spectrum of RIM activities, providing a robust dataset for benchmarking organizational strategies and efficiency comparisons. Key Takeaways: • **Holistic Regulatory Headcount Measurement:** The 2020 survey introduced the requirement to estimate non-employee headcount (contractors, consultants, temps) quantified as Full-Time Equivalents (FTEs), moving beyond internal employees to capture the true scale and resource allocation of the total regulatory organization. • **Organizational Strategy Benchmarking:** The primary objective of collecting organizational data (headcount, structure, reporting) is to establish a baseline for comparing different organizational strategies, particularly in relation to efficiency metrics explored elsewhere in the World Class RIM survey. • **Geographic Distribution of Regulatory Staff:** Internal regulatory headcount is segmented by location (headquarters, regional, local, other), acknowledging the global nature of regulatory operations and the specific terminology used by medical device companies (business division, design center). • **Defining the RIM Group's Remit:** The survey shifts focus from the mere existence of a dedicated RIM group to defining its specific purpose and scope of responsibility, which is critical for understanding operational models and resource deployment. • **RIM Group Structure Flexibility:** The concept of a "dedicated regulatory information group" is flexible; it does not mandate a central structure and can be distributed globally, accommodating organizations ranging from very small teams (one person) to large, multi-functional units. • **Quantifying Shared Responsibilities:** The survey utilizes a specific scale to distinguish between functions that are the *sole responsibility* of the RIM group and those that are *shared* with other groups in the organization, providing clarity on cross-functional dependencies. • **Future Scope Planning:** Participants are asked to identify areas that are not currently under the RIM group’s responsibility but are anticipated to be within scope in the next two years, offering insight into strategic planning and future technology needs. • **Exiting Non-Applicable Questions:** A mechanism is provided for required questions (marked with an asterisk) to be exited if they do not currently apply to the organization's situation or are out of scope, ensuring data accuracy and avoiding forced responses. • **Customizing Responsibility Capture:** The inclusion of an "other" field is vital for capturing unique or specialized responsibilities where the RIM group holds primary accountability, ensuring the survey accurately reflects the diversity of RIM functions across the industry. Key Concepts: * **RIM (Regulatory Information Management):** The systematic management of all information and processes related to regulatory compliance, submissions, and product lifecycle within the life sciences industry. * **Dedicated RIM Group:** A specific team or organizational unit tasked primarily or solely with managing regulatory information and related processes, which can be centralized or distributed. * **FTE (Full-Time Equivalent):** A unit of measure used to express the workload of an employed or contracted person in a way that makes workloads comparable across various contexts, often used to quantify contractors and consultants. * **Remit:** The area of authority or responsibility assigned to a specific group or committee, in this context, defining the specific tasks and functions of the dedicated RIM group.

Aquila University The eCTD Publishing Process
Aquila Solutions
/@aquilasolutions6783
Jan 17, 2020
This video explores the intricate and often underestimated eCTD (Electronic Common Technical Document) publishing process, which is critical for regulatory submissions like NDAs to agencies such as the FDA. The speaker highlights the common misconception among sponsors regarding the time and resources required to convert years of clinical data into a compliant and reviewable eCTD, emphasizing that inadequate planning significantly increases project risk. The discussion details the essential components for eCTD creation, including specialized publishing systems, advanced PDF tools, eCTD validators, and a dedicated team of experienced regulatory operations publishers. The process is broken down into four major activities: lifecycle planning, document remediation, quality control, and project management, with remediation consuming the vast majority of the effort. Key Takeaways: * **Underestimated Complexity:** eCTD publishing is a highly complex, resource-intensive process, with sponsors frequently underestimating the 2,000 man-hours and minimum four months required for a typical 505 B1 NDA (100,000+ pages, 300+ documents). * **Critical Resource Requirements:** Successful eCTD publishing necessitates a robust technology stack (publishing system, advanced PDF tools, dual eCTD validators) and a skilled team comprising experienced manager-level and associate-level regulatory publishers. * **Remediation is King:** Document remediation, involving cleaning, formatting, bookmarking, and intricate linking of individual PDFs, accounts for approximately 70% of the total project time, underscoring its manual and meticulous nature. * **QC is Non-Negotiable:** Cutting corners on the 15% allocated for quality control introduces substantial risk of non-compliance, incorrect versions, broken links, or inconsistent content, which can severely impact reviewer satisfaction and approval chances. * **Operational Challenges:** Beyond document processing, significant challenges include managing large file transfers (often 10-20+ GB per submission, requiring multiple transfers) and ensuring seamless integration of new submissions with previous ones. * **Strategic Compliance:** Proper eCTD planning and execution are not just technical tasks but strategic imperatives that directly influence regulatory approval timelines and outcomes by ensuring a clear, consistent, and easily reviewable application for regulatory bodies.

Growing Adoption of Cloud Quality Systems
Veeva Systems Inc
/@VeevaSystems
Nov 20, 2019
This video explores the accelerating trend of cloud adoption within quality management systems (QMS) across the pharmaceutical and life sciences industries, emphasizing how modernization drives compliance, improves product quality, and mitigates risk. The discussion targets various segments of the market, including established pharmaceutical companies, emerging biotech firms, and medium-sized manufacturers, noting that while many companies recognize the need to adapt to new business models, the journey of migrating legacy quality systems is often fraught with complexity. The core challenge highlighted is overcoming the inertia associated with deeply entrenched, often manual, processes and the difficulty of implementing significant operational change within highly regulated environments. The speaker emphasizes that successful modernization requires more than just lifting and shifting existing data; it necessitates a fundamental re-evaluation of processes and the replacement of outdated systems with structured, modern cloud architectures. This transition is crucial because legacy systems often struggle to handle the complexity and volume of modern quality data, leading to compliance risks and operational inefficiencies. The presentation suggests that companies should not attempt to merely "ensure informanten leer in groep" (likely meaning incremental, localized fixes), but rather commit to a comprehensive overhaul, viewing the migration as an opportunity to implement entirely new, optimized workflows. A key focus of the discussion is the methodology for achieving this transition, introducing a specific, pre-validated solution package—referred to as "V-Qualvis and Groots"—which appears to be a structured implementation framework for cloud quality systems (likely Veeva Vault Quality Suite). This framework is presented as providing an implementation support perspective, focusing on robust, proven quality processes that ensure adherence to all applicable regulatory requirements. The methodology stresses the importance of establishing a solid foundation, ensuring that the new cloud system is not only robust and compliant but also includes necessary "after care" and centralized knowledge management to sustain the benefits post-implementation. Key Takeaways: • **Mandate for Cloud QMS Adoption:** Cloud adoption is rapidly increasing across all segments of the life sciences market, driven by the need for enhanced regulatory compliance, risk reduction, and improved product quality, particularly among biotech and medium-sized manufacturing companies. • **Complexity of Legacy Migration:** The primary barrier to modernization is the inherent complexity of existing quality processes and the difficulty in managing organizational change, requiring companies to move beyond incremental fixes and embrace full system replacement. • **Process Re-engineering is Essential:** Successful cloud QMS implementation demands a commitment to establishing entirely new, structured processes rather than attempting to replicate outdated, inefficient workflows within a new cloud environment. • **Structured Implementation Frameworks:** The use of pre-validated, specific package solutions—such as the referenced "V-Qualvis and Groots" (likely a Veeva implementation methodology)—is critical for ensuring a proven, robust, and compliant transition. • **Regulatory Assurance:** The chosen cloud solution and implementation process must guarantee adherence to all applicable regulatory frameworks, ensuring that the resulting quality process is robust and auditable from day one. • **Focus on Robust Quality Processes:** The goal of modernization is to implement a "proven and robust quality process" that inherently supports compliance, minimizing manual intervention and the risk of human error. • **Implementation Support and Aftercare:** Effective deployment requires comprehensive implementation support and a defined "after care" strategy, including centralized knowledge management, to ensure long-term system stability and user adoption. • **Strategic System Replacement:** Companies must be prepared to "replace systems and look at like a new process," recognizing that legacy systems often act as a bottleneck and must be fully decommissioned to realize the benefits of cloud quality management. • **Addressing Diverse Market Needs:** The cloud QMS solutions must be adaptable to the varying needs and scales of different segments, from large pharmaceutical enterprises to smaller, agile biotech firms and manufacturers. Tools/Resources Mentioned: * **V-Qualvis and Groots:** A specific, pre-flight package or implementation methodology designed for deploying cloud quality systems, emphasizing robustness and compliance. (Contextually, this refers to Veeva Vault Quality Suite implementation). * **Veeva R&D Summit, Europe:** Mentioned as a resource for learning about the latest industry trends in quality. Key Concepts: * **Cloud Quality Systems (Cloud QMS):** Modern, internet-based platforms for managing quality documentation, processes (CAPA, deviations, training), and compliance, offering greater scalability and accessibility than traditional on-premise systems. * **Regulatory Compliance:** Ensuring that quality processes and systems adhere to stringent industry regulations (e.g., FDA, EMA, GxP, 21 CFR Part 11), which is a key driver for QMS modernization. * **Process Complexity:** The inherent difficulty and intricacy of established quality workflows within life sciences companies, often necessitating significant process simplification and standardization during cloud migration.

A day in the life of a patient with Medable Digital Trial Platform
Medable
/@medable
Nov 13, 2019
This video provides a detailed simulation of the patient experience within a Decentralized Clinical Trial (DCT) using the Medable Digital Trial Platform. The primary purpose is to showcase how modern technology facilitates a patient-centric approach to clinical research, moving away from traditional, site-heavy models toward flexible, remote participation. The demonstration illustrates the seamless integration of various digital tools—mobile applications, telemedicine, and remote data capture—into the daily life of a trial participant. The core progression of the video focuses on the patient journey, starting with initial engagement and continuing through daily study activities. Key themes include enhanced accessibility and convenience, which are critical for improving patient recruitment and retention rates in complex studies. The platform is shown managing essential study functions, such as electronic consent (eConsent), scheduling virtual visits with study coordinators, and providing timely reminders for medication adherence and required tasks. By bringing the trial to the patient, the platform minimizes the logistical burden of travel and time off work, addressing two major historical barriers to clinical trial participation. The technological framework highlighted involves robust data collection mechanisms. The platform enables electronic Patient-Reported Outcomes (ePROs) and Clinician-Reported Outcomes (eCOAs) to be captured directly via the patient’s mobile device. Furthermore, the system likely integrates with wearable devices or sensors to passively collect continuous, high-fidelity physiological data. This shift from intermittent, site-based data collection to continuous, real-time data streams fundamentally changes how clinical data is managed and monitored. The video emphasizes the platform’s role as a central hub for communication, ensuring that patients feel connected and supported by the clinical site staff, thereby maintaining compliance and data quality throughout the study duration. Ultimately, the demonstration underscores the industry-wide necessity for sophisticated, compliant digital infrastructure in clinical operations. The platform serves as a critical bridge between the patient, the site, and the sponsor, ensuring that all interactions and data transfers adhere to stringent regulatory standards (such as GxP and 21 CFR Part 11). This digital transformation in clinical research creates significant opportunities for specialized technology firms to provide custom integration, advanced data analytics, and AI-driven monitoring solutions to manage the complexity and volume of decentralized trial data effectively. Key Takeaways: • **Data Engineering Requirements for DCTs:** Decentralized trials generate massive, diverse data sets (e.g., continuous sensor data, ePRO text entries, video visit transcripts) that require specialized data engineering services to integrate, standardize, and pipeline into centralized Electronic Data Capture (EDC) or clinical data management systems. • **Regulatory Compliance in Digital Trials:** The shift to eConsent, remote monitoring, and digital signatures necessitates robust, built-in compliance features to meet GxP and 21 CFR Part 11 requirements, particularly concerning audit trails, data integrity, and system validation. • **Integration with Enterprise Systems:** DCT platforms must seamlessly integrate with existing pharmaceutical enterprise software, including CTMS (Clinical Trial Management Systems), EDC systems, and potentially Veeva platforms used for commercial or medical affairs operations, requiring custom API development and system integration expertise. • **AI for Automated Monitoring:** The wealth of real-time patient data collected through DCT platforms is ideal for applying AI and machine learning models to automate safety monitoring, identify potential adverse events early, and predict patient adherence risks, allowing clinical teams to intervene proactively. • **Patient-Centric Design is Critical:** The success of a digital trial hinges on the platform’s usability; custom software development must prioritize intuitive, accessible interfaces to ensure high patient engagement and minimize dropout rates, which directly impacts study timelines. • **LLM Applications in Clinical Operations:** Large Language Models (LLMs) can be leveraged to process unstructured data from patient diaries, telemedicine transcripts, and support chat logs, providing automated summaries or flagging critical safety information for CRAs and investigators. • **Operationalizing Patient Engagement Data:** The engagement metrics captured by the digital platform (login frequency, task completion rates) provide valuable operational intelligence that can be used to optimize trial protocols and resource allocation, requiring specialized business intelligence dashboard development. • **Convergence of Clinical and Commercial Data:** As patient engagement technology matures in clinical trials, the data and lessons learned about patient interaction can inform commercial operations strategies (e.g., patient support programs, medical affairs outreach), creating a need for unified data strategies across the life sciences value chain. • **Need for Custom Software for Unique Protocols:** While platforms like Medable provide a framework, highly complex or specialized protocols often require custom software modules built on top of or integrated with the core platform to handle unique data capture or device integration needs. Tools/Resources Mentioned: * Medable Digital Trial Platform Key Concepts: * **Decentralized Clinical Trials (DCTs):** A methodology for conducting clinical research where some or all trial-related activities occur remotely, away from traditional clinical sites, often leveraging digital tools and telemedicine. * **eConsent:** The process of obtaining informed consent from a trial participant electronically, typically via a digital platform, ensuring documentation and regulatory compliance. * **ePRO/eCOA (Electronic Patient/Clinician-Reported Outcomes):** The use of electronic devices (like mobile phones or tablets) to capture data directly from patients or clinicians regarding symptoms, quality of life, or treatment effects. * **Patient-Centricity:** A design philosophy in clinical trials that focuses on minimizing the burden on the patient and maximizing their convenience and experience to improve participation and retention.

The Need for Better Regulatory Information Management in Medical Device Manufacturing
Xtalks
/@XtalksWebinars
Nov 4, 2019
This presentation explores the critical need for robust Regulatory Information Management (RIM) systems within the medical device and diagnostics manufacturing sectors, emphasizing the challenges posed by relentless global change and fragmented data sources. The speaker establishes that the regulatory landscape is constantly shifting—driven by changes in regulations, business environments, politics, and technology—necessitating that regulatory professionals maintain synchronization, transparency, and registration of product data across all global stakeholders. The core argument centers on the necessity of moving beyond siloed operations where regulatory data is treated separately from product data, stressing that "data is data" and must be shared across the enterprise to effectively communicate product acceptability and compliance worldwide. A significant portion of the discussion focuses on the complexity of managing product data throughout its lifecycle, particularly within the "sustaining organization" responsible for products already on the market. The speaker highlights that regulatory data is fundamentally product data, used to "tell the story" of why a product meets requirements. This integration is complicated by global variations, using Unique Device Identification (UDI) as a prime example. While countries worldwide adopt UDI, their specific data requirements often differ, forcing manufacturers to account for diverse global needs in their sustaining operations. The speaker notes that these sustaining teams, though crucial, are often overlooked until an issue arises, underscoring the lack of internal recognition for proactive compliance management. The speaker provides a compelling personal anecdote illustrating the stark contrast in RIM maturity across the industry. They recount moving from a large medical device company that utilized a Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) system and an existing, though outdated, RIM system, to a diagnostics company that operates primarily on paper-based processes. This shift revealed a common, problematic theme within the diagnostics world: reliance on decentralized, manual tools like individual Excel files and scattered SharePoint sites for managing critical worldwide registrations. This reliance creates severe operational risks, making it nearly impossible to accurately track the status, quantity, associated revenue, or required updates for registrations when regulations change. The presentation concludes by polling the audience to gauge the prevalence of these challenges across different industry sectors (med device, combo products, etc.), underscoring the widespread nature of the "hill to climb" in digital transformation for regulatory affairs. Key Takeaways: • **The Imperative for Synchronization:** Regulatory teams must actively work to keep product registrations, compliance data, and internal business processes synchronized with constant changes in global regulations, political environments, and emerging technology standards. • **Eliminating Data Silos:** The traditional view that regulatory data is separate from core product data must be abandoned; data should be treated as a unified asset, requiring shared, transparent access across all internal stakeholders (e.g., R&D, manufacturing, commercial, and regulatory). • **Master Sources of Information are Critical:** To ensure consistency and accuracy, organizations must establish and maintain master sources of product and regulatory information, moving away from fragmented systems like local Excel files and SharePoint sites. • **Sustaining Operations Complexity:** The sustaining organization, which manages products post-launch, faces immense pressure to maintain global compliance, often without adequate systemic support or recognition, making them highly vulnerable to regulatory gaps. • **Global UDI Fragmentation:** Although UDI standards are globally adopted, the specific data requirements associated with UDI often vary significantly by country, demanding complex, localized data management strategies from manufacturers. • **The Diagnostics Industry Lag:** A prevalent challenge, particularly noted in the diagnostics sector, is the reliance on outdated, paper-based systems for managing critical worldwide registrations, which dramatically increases risk and operational inefficiency. • **Risk of Decentralized Tracking:** Managing worldwide product registrations using manual, decentralized tools (like personal Excel files) makes it impossible to answer fundamental business questions, such as the total number of registrations managed, associated revenue, or the impact of regulatory changes. • **Assessing the Regulatory Burden:** Companies must be able to quickly assess the size of their regulatory burden—how many registrations are active, which markets they cover, and what revenue is tied to them—to prioritize resources and manage risk effectively. • **Impact of Regulatory Change:** Without a structured RIM system, regulatory changes often necessitate starting the registration process over, rather than allowing for efficient updates, leading to significant time and cost overruns. • **Digital Transformation Necessity:** The industry must recognize that the shift from paper-based and manual systems to integrated digital platforms is not optional but essential for competing globally and maintaining timely compliance in complex markets. Key Concepts: * **Regulatory Information Management (RIM):** The systems and processes used to manage, track, and submit regulatory data and documentation throughout the product lifecycle. * **Sustaining Organization:** The internal teams responsible for maintaining product quality, compliance, and market presence after the initial launch, often handling post-market changes and regulatory updates. * **Unique Device Identification (UDI):** A system used globally to mark and identify medical devices through distribution and use, though its specific data requirements vary by jurisdiction. * **Data Silos:** The isolation of data within specific departments (e.g., regulatory, R&D) preventing enterprise-wide transparency and efficient use of information.

Clinical Trials and Research News Weekly Roundup | 10-14-2019 S1 E14
To Be Frank
/@therealtobefrank
Oct 12, 2019
This video provides a weekly roundup of significant news in clinical trials and life sciences research, covering a broad spectrum of topics from vaccine development and new drug approvals to industry trends and technological advancements. A central theme is the increasing integration of technology, particularly Veeva's platforms and Artificial Intelligence, into pharmaceutical R&D and clinical operations. The discussion highlights both the opportunities and ethical challenges presented by these innovations within the regulated life sciences environment. Key Takeaways: * **Veeva's Strategic Expansion in Clinical Data Management:** Veeva is actively strengthening its position in clinical operations by offering SiteVault Free to investigator sites and showcasing its Vault CDMS for unified clinical data and document management. This indicates a growing market for specialized Veeva consulting and integration services * **Accelerated AI Adoption Across Pharma Value Chain:** The partnership between Novartis and Microsoft to leverage AI in drug development, clinical trials, manufacturing, and finance underscores the critical and expanding role of AI in the pharmaceutical industry. * **Robust Growth in Clinical Research and CRO Ecosystem:** The video highlights a thriving life sciences sector, evidenced by the increase in clinical trials and the launch of specialized Contract Research Organizations (CROs). * **Critical Importance of Data Ethics and Regulatory Compliance in AI:** The segment discussing the use of AI to analyze patient data (YouTube videos of children) without explicit consent brings to the forefront the ethical and regulatory complexities of deploying AI in research.g., GxP, 21 CFR Part 11). * **Innovation in Advanced Therapeutics:** News about Moderna's mRNA therapeutic and gene therapy trials demonstrates the ongoing push for novel treatment modalities, which often require sophisticated data infrastructure and AI-driven insights for efficient development, clinical management, and regulatory navigation.

University of Louisville: Improving Regulatory Compliance with eRegulatory
Veeva Systems Inc
/@VeevaSystems
Oct 2, 2019
This video details the University of Louisville's strategic adoption of Veeva SiteVault to address mounting pressures in clinical research, specifically focusing on the challenges associated with increasingly stringent regulatory compliance and complex protocols. The core motivation for implementing a modern eRegulatory system was the need to maintain competitiveness and responsiveness in a rapidly evolving market where regulations are becoming "tougher and tougher every day." The university recognized that their previous, decentralized methods—relying on internal servers and attempting to push end-users toward specific pathways—were unsustainable, as staff consistently reverted to individual "comfort zones," leading to a lack of standardization and inefficiency. The primary operational challenges stemmed from the inability to quickly locate essential documentation and the slow pace of task completion, exacerbated by the research teams being geographically "spread out over an entire campus." To overcome this fragmentation and lack of control, the university sought a system that could inherently support standardization and process improvement. The selection of Veeva SiteVault provided the necessary structure, immediately standardizing critical elements like document naming conventions, which was previously a major pain point. A significant benefit highlighted by the speaker is the immediate external validation and trust gained by using an industry-recognized platform. When mentioning the use of SiteVault, the sponsors and Contract Research Organizations (CROs) that the university collaborates with instantly "understand what I'm talking about," leading to positive feedback and improved collaboration. This standardization and recognized platform usage are viewed as key accomplishments in process improvement. The speaker concludes by describing SiteVault as "intuitive, top notch, innovative, easy to use, and flexible," expressing extreme satisfaction with the chosen product for enhancing regulatory compliance and operational efficiency. Key Takeaways: • **Regulatory Pressure Drives Tech Adoption:** The increasing complexity of clinical research protocols and the tightening regulatory environment necessitate the adoption of modern, specialized eRegulatory systems to maintain market competitiveness and operational viability. • **Decentralization Hinders Compliance:** Relying on decentralized storage (like internal servers) across a large campus environment severely impedes the ability to quickly find necessary documentation and complete tasks, directly impacting efficiency and compliance readiness. • **Standardization Requires System Enforcement:** Attempts to enforce standardization (e.g., specific file pathways or naming conventions) through policy alone often fail because end-users revert to familiar, non-compliant habits; robust systems like Veeva SiteVault are required to embed standardization directly into the operational workflow. • **Veeva Ecosystem Recognition:** Utilizing platforms within the established Veeva ecosystem provides immediate credibility and facilitates collaboration with external partners, as sponsors and CROs instantly recognize and trust the system's capabilities and data integrity standards. • **Process Improvement Through Standardization:** The implementation of an eRegulatory system immediately drives process improvement by standardizing foundational elements, such as document naming conventions, which streamlines operations and reduces administrative burden. • **Focus on User Experience (UX):** Successful adoption of new regulatory technology hinges on the system being intuitive, easy to use, and flexible; these attributes ensure high user compliance and maximize the return on investment in the platform. • **Competitive Advantage through Responsiveness:** Adopting a modern eRegulatory system is not just about meeting minimum compliance requirements, but about enabling the research institution to be more responsive and competitive in securing and managing complex clinical trials. • **Need for Integrated Solutions:** The challenges faced—difficulty in finding documents and slow execution—underscore the need for integrated data management and workflow solutions that can bridge the gaps caused by physical dispersion and disparate data storage methods. Tools/Resources Mentioned: * **Veeva SiteVault:** An eRegulatory system specifically designed for managing investigator site files and improving efficiency in clinical research operations. Key Concepts: * **eRegulatory System:** A digital platform used by research sites and institutions to manage essential regulatory documents, investigator site files (ISF), and maintain compliance with clinical trial regulations (e.g., FDA, ICH-GCP). * **Investigator Site File (ISF):** The collection of essential documents maintained by the research site that individually and collectively permit the evaluation of the conduct of a trial and the quality of the data produced. * **Standardization (in Clinical Research):** The process of establishing uniform procedures, document naming conventions, and data structures across all research operations to ensure consistency, quality, and regulatory compliance.

Quality and Manufacturing Highlights: 2019 Veeva R&D Summit
Veeva Systems Inc
/@VeevaSystems
Sep 27, 2019
This video provides an in-depth exploration of quality and manufacturing highlights from the 2019 Veeva R&D Summit, focusing on the transformative projects undertaken by pharmaceutical and life sciences companies. Mike Jovanis, VP of Vault Quality at Veeva, and Kent Malmros, Senior Director of Vault Training, share key reflections on modernizing and unifying quality management systems and integrating training into this unified approach. The discussion highlights a historical context where early electronic quality projects, driven by the emergence of 21 CFR Part 11 in the late 1990s, led to a fragmented landscape of homegrown applications and manual processes, creating a strong impetus for comprehensive transformation. The presentation delves into several real-world case studies illustrating these transformative initiatives. Samsung Biologics, a contract manufacturing organization, was featured as a keynote speaker, showcasing their successful implementation of Veeva's suite of quality products to modernize their manufacturing environment. Similarly, BMS and Roche presented on their respective Quality Management System (QMS) transformation projects, both aiming to consolidate multiple legacy QMS applications into a single Veeva Vault QMS. BMS specifically focused on collapsing and harmonizing R&D quality with manufacturing quality, while Roche pursued harmonization and consolidation across various previously separate lines of business within their diagnostics sector. PRA Health Sciences, a Contract Research Organization (CRO), also shared their experience with a unification and harmonization project, integrating both Vault QualityDocs and Vault QMS through a multi-phase initiative to bring disparate solution spaces into a single Vault platform. Kent Malmros then transitions to the critical role of training within this unified quality framework, emphasizing the goal of avoiding the fragmentation issues that plagued document and quality management systems. The discussion centered on improving GxP and quality training effectiveness through unified training management. Foamix shared their journey, demonstrating how their maturation from using QualityDocs to a unified training system was a natural progression, enabling them to eliminate redundant training applications and integrations. Dicerna further elaborated on achieving efficiency and effectiveness across the end-to-end lifecycle of document creation and subsequent training program development within the same application, seamlessly managing curriculum review, approval, assignment delivery, and progress tracking. Finally, Xeris and Xencor, in a panel discussion, echoed these sentiments, highlighting the strategic advantage of a unified training approach to analyze training effectiveness by combining training outcome data with other quality event data. Key Takeaways: * **Addressing Fragmented Quality Landscapes:** The pharmaceutical industry has historically suffered from an "aging fragmented solution landscape" in quality management, stemming from early electronic implementations driven by 21 CFR Part 11, which necessitates transformative projects to unify and modernize systems. * **Strategic QMS Transformation:** Companies like BMS and Roche are undertaking significant QMS transformation initiatives to consolidate multiple legacy applications into a single, unified platform (Veeva Vault QMS), leading to improved efficiency and compliance. * **Harmonization Across Business Functions:** Beyond consolidation, harmonization of quality processes across different business units, such as R&D quality with manufacturing quality (BMS) or across various lines of business (Roche), is crucial for operational consistency and regulatory adherence. * **Unified Training Management for GxP:** Effective GxP and quality training is a cornerstone of regulatory compliance. Implementing a unified training management system, such as Veeva Vault Training, helps avoid the integration complexities and inefficiencies of disparate training applications. * **End-to-End Training Lifecycle Management:** Modern unified training systems enable seamless management of the entire training lifecycle, from document creation and curriculum development to assignment delivery, progress tracking, and review/approval, all within a single application. * **Measuring Training Effectiveness:** A key advancement is the ability to combine training outcome data with other quality event data to robustly demonstrate the effectiveness of training programs, moving beyond simple completion tracking to actual impact assessment. * **Benefits for Contract Research Organizations (CROs):** CROs like PRA Health Sciences benefit significantly from unifying quality documentation (Vault QualityDocs) and QMS (Vault QMS) into a single platform, streamlining operations and ensuring consistent quality across research phases. * **The Transformative Nature of Modern Quality Projects:** Current quality projects are not merely about replacing old systems but about fundamentally transforming how quality is managed, leading to more integrated, efficient, and compliant operations. * **Leveraging Integrated Suites:** Adopting a comprehensive suite of quality products, such as those offered by Veeva Vault, allows companies to mature their quality processes naturally, moving from document management to integrated training and QMS, thereby eliminating redundant applications and integrations. * **Proactive Compliance:** The shift towards unified systems allows companies to proactively manage compliance challenges rather than reactively remediating them, as was often the case with older, fragmented systems. Tools/Resources Mentioned: * Veeva Vault Quality * Veeva Vault QMS * Veeva Vault QualityDocs * Veeva Vault Training Key Concepts: * **21 CFR Part 11:** Regulations concerning electronic records and electronic signatures for the pharmaceutical industry, which historically drove the initial adoption of electronic quality systems. * **GxP (Good Practices):** A collection of quality guidelines and regulations ensuring that products are safe and meet their intended use, encompassing areas like Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) and Good Clinical Practice (GCP). * **QMS (Quality Management System):** A formalized system that documents processes, procedures, and responsibilities for achieving quality policies and objectives, crucial for regulatory compliance in life sciences. * **Unified Training Management:** An integrated approach to managing all aspects of employee training, particularly GxP and quality-related training, within a single system to ensure consistency, efficiency, and compliance. * **Quality Event Data:** Data related to quality incidents, deviations, CAPAs (Corrective and Preventive Actions), and other quality-related occurrences, which can be analyzed to identify trends and improve processes. * **Harmonization:** The process of making different systems, processes, or standards consistent and compatible across various departments, sites, or lines of business within an organization. Examples/Case Studies: * **Samsung Biologics (Contract Manufacturing):** Implemented Veeva quality products to modernize their manufacturing environment. * **BMS (Biopharmaceutical):** Consolidated multiple legacy QMS apps into a single Vault QMS and harmonized R&D quality with manufacturing quality. * **Roche (Pharmaceutical/Diagnostics):** Harmonized and consolidated QMS across various different lines of business that were previously separate systems. * **PRA Health Sciences (Contract Research Organization - CRO):** Implemented Vault QualityDocs and Vault QMS in a three-phase initiative to unify and modernize their quality solution spaces. * **Foamix (Pharmaceutical):** Shared their story of maturing from QualityDocs to a unified training system, eliminating training applications and integrations. * **Dicerna (Biopharmaceutical):** Discussed efficiency and effectiveness in managing the end-to-end lifecycle of creating documents and developing training programs within the same application. * **Xeris (Pharmaceutical) & Xencor (Biopharmaceutical):** Shared insights on leveraging a unified training approach to combine training outcome data with other quality event data to demonstrate training effectiveness.

2019 Veeva R&D Summit Keynote: Veeva Vision
Veeva Systems Inc
/@VeevaSystems
Sep 12, 2019
This.ai offers specialized consulting. The discussion of clinical data management, regulatory compliance (e.g. This video explores Veeva's vision for an integrated "Development Cloud" for the life sciences R&D sector, delivered through a keynote address at their 2019 R&D Summit. The speaker outlines Veeva's core vision to build an industry-specific cloud for life sciences, encompassing applications, data, professional services, and an ecosystem of partners, all aimed at improving and extending human life. Key themes include Veeva's foundational values ("do the right thing," customer success, employee success, speed) and significant product innovations across various R&D domains. The presentation details advancements in clinical data management (e.g., agile study design, autosave), the introduction of Vault Safety for pharmacovigilance, and the development of "Safety AI" to automate the processing of unstructured safety content. Other innovations include continuous publishing for regulatory submissions, enhanced collaborative authoring capabilities through Microsoft Word integration, and a complete quality suite (Quality Docs, QMS, Training). The speaker emphasizes the importance of integration via "Spark" technology to connect various Vaults and external systems, and the necessity for customers to embrace business process changes alongside new technology adoption. Key Takeaways: * **Integrated Development Cloud Strategy:** Veeva is pursuing a comprehensive "Development Cloud" strategy, aiming to provide an integrated suite of modular applications that serve as the "operating system for drug development," covering clinical, safety, regulatory, and quality functions to break down silos. * **Strategic AI Investment in Pharmacovigilance:** Veeva is making a significant move into AI with "Safety AI," a specialized product designed to process unstructured content (PDFs, emails, text) using an AI engine to generate review-ready safety cases, addressing a complex and error-prone area in pharmacovigilance. * **Focus on Continuous and Incremental Innovation:** The company emphasizes "reimagining" existing processes and delivering incremental improvements (e.g., agile study design, quick view, autosave in clinical data management, continuous publishing) to enhance efficiency, user experience, and adaptability to evolving industry needs like frequent protocol amendments. * **Modernizing Regulatory and Content Management:** Innovations like "Vault Publishing" with continuous publishing capabilities for eCTD formats and tight integration with Microsoft Word for collaborative authoring demonstrate a strong commitment to streamlining regulatory submission processes and improving content management within a compliant framework. * **Importance of Integration and Ecosystem:** Veeva's "Spark" integration technology is critical for connecting various Vault applications and external systems, facilitating seamless data flow and business processes across the entire R&D lifecycle, and enabling a more unified operational environment. * **Business Process Transformation is Key:** The speaker explicitly highlights that adopting new technologies, particularly transformative ones like continuous publishing, necessitates significant changes in business processes and roles, underscoring that technology implementation is not merely a tool adoption but a fundamental shift in operations.

IDMP 2019 WHO
IOMPOfficial
/@IOMPOfficial
Aug 31, 2019
This video, presented by Adriana Velásquez and María del Rosario Pérez, serves as an invitation to celebrate the International Day of Medical Physics, organized by the International Organization of Medical Physics (IOMP). The core purpose of the address is to draw global attention to the indispensable role of medical physicists in ensuring the safety and quality of radiation interventions within healthcare. The speakers underscore the rapid advancements in radiation health technologies and the consequent imperative to elevate the education, training, availability, and recognition of medical physicists worldwide. The presentation delves into the diverse applications of radiation health technologies, encompassing diagnostic radiology, nuclear medicine, interventional radiology, and radiotherapy. It highlights their critical utility in the diagnosis and treatment of various diseases, specifically mentioning cancer care and the management of cardiovascular diseases. A central theme is the necessity for robust support systems to guarantee that these advanced technologies are not only produced correctly but also properly calibrated, absorbed into clinical practice, and effectively maintained for optimal performance. The speakers emphasize that despite the increasing availability of radiation technology and equipment in many settings, the presence of qualified medical physicists is crucial for maintaining patient care quality and mitigating health risks. Furthermore, the video stresses the vital function of medical physicists in providing radiation protection education and training for healthcare professionals. They are portrayed as key figures in implementing and upholding radiation safety standards within clinical environments. The overall message is a call to action for global recognition and support for the medical physics profession, ensuring that as radiation technologies continue to evolve and expand, patient safety and the quality of care remain paramount through the expertise and dedication of these specialists. The address concludes with a congratulatory note to medical physicists globally for their contributions, reinforcing the significance of their work. Key Takeaways: * **Critical Role of Medical Physicists:** Medical physicists are fundamental to guaranteeing the safety and quality of radiation interventions, acting as guardians of patient well-being in an increasingly technology-driven healthcare landscape. * **Scope of Radiation Health Technologies:** The field encompasses a broad spectrum of applications, including diagnostic radiology, nuclear medicine, interventional radiology, and radiotherapy, all vital for modern diagnosis and treatment. * **Addressing Major Diseases:** These technologies are crucial for managing severe conditions like cancer and cardiovascular diseases, underscoring their impact on public health. * **Global Imperative for Professional Advancement:** Rapid technological advancements necessitate a global focus on improving the education, training, availability, and recognition of medical physicists to keep pace with innovation. * **Ensuring Technology Efficacy and Safety:** Adequate support is required to ensure that radiation technologies are produced correctly, calibrated accurately, properly integrated into clinical practice, and maintained for effective and safe performance. * **Optimal Device Utilization:** Medical physicists play a key role in ensuring that radiation-emitting devices are used optimally, maximizing therapeutic benefits while minimizing risks. * **Radiation Protection Education:** They are essential educators, providing critical radiation protection training to other healthcare professionals, which is vital for a safe clinical environment. * **Implementation of Safety Standards:** Medical physicists are responsible for implementing and upholding rigorous radiation safety standards in clinical settings, ensuring compliance and best practices. * **Quality Assurance in Patient Care:** Their expertise directly contributes to the quality of patient care by minimizing health risks associated with radiation exposure and ensuring the accuracy of diagnostic and therapeutic procedures. * **Addressing Gaps in Availability:** There's a recognized need to ensure that qualified medical physicists are available in all settings where radiation technology is introduced, preventing potential safety and quality compromises. Key Concepts: * **Medical Physics:** A branch of applied physics concerned with the application of physics concepts, theories, and methods to medicine or healthcare. It involves the use of radiation and other physical principles for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. * **Radiation Health Technologies:** A collective term for medical technologies that utilize various forms of radiation for medical purposes. This includes: * **Diagnostic Radiology:** Using X-rays, CT scans, and MRI for imaging internal body structures. * **Nuclear Medicine:** Using small amounts of radioactive materials (radiopharmaceuticals) to diagnose and treat a variety of diseases. * **Interventional Radiology:** Performing minimally invasive procedures using image guidance (e.g., X-ray, ultrasound, CT, MRI). * **Radiotherapy:** Using high-energy radiation to treat cancer by damaging cancer cells. * **Radiation Safety Standards:** Guidelines and regulations designed to protect patients, healthcare workers, and the public from unnecessary exposure to radiation, ensuring that radiation use is justified and optimized. * **Calibration:** The process of configuring an instrument to provide a result for a sample within an acceptable range, ensuring accuracy and reliability of radiation doses or measurements. * **Quality Assurance:** A systematic process of checking to see whether a product or service being developed is meeting specified requirements, crucial for the safe and effective operation of medical devices. Examples/Case Studies: * The video highlights the application of radiation technologies in **cancer care**, where radiotherapy is a primary treatment modality. * It also mentions the use of these technologies in the **management of cardiovascular diseases**, indicating their broader diagnostic and therapeutic utility beyond oncology.

Drew Garty invites you to Veeva R&D Summit
Veeva Systems Inc
/@VeevaSystems
Aug 20, 2019
This video serves as a personal invitation from Drew Garty, a key figure at Veeva Systems, urging industry professionals to attend the annual Veeva R&D Summit. The primary goal of the message is to highlight the strategic value of the event for leaders in the pharmaceutical, biotech, and medical device sectors—specifically those involved in clinical, regulatory, quality, and IT functions. Garty emphasizes that the summit is not merely a series of presentations but a critical forum for discussing emerging best practices, exploring cutting-edge innovation areas, and engaging directly with the future trajectory of the Veeva platform. A central theme promoted by Garty is the opportunity for attendees to gain an "inside track" into Veeva’s strategic development via the dedicated roadmap session. This session is positioned as essential for understanding Veeva’s prioritization of business problems and the thinking behind their future product development. Crucially, Garty encourages attendees to actively challenge this thinking, positioning the summit as a collaborative environment where customer feedback directly influences the evolution of the Veeva ecosystem. This interaction is vital for consulting firms and technology providers who need to align their custom solutions and implementation strategies with the vendor's future direction. Beyond formal sessions, the speaker stresses the unparalleled networking opportunities available at the summit. He describes the event as a chance to engage in "meaningful conversations with industry colleagues," fostering collaboration and knowledge exchange among life sciences leaders. Furthermore, Garty specifically plugs a session titled "The Richard and Drew Show," which is dedicated to exploring how Veeva Vaults can solve current and near-future business challenges. This session is particularly focused on addressing **CDMS business problems** (Clinical Data Management Systems), indicating a strong focus on clinical operations and data management efficiency, which are core areas for AI-powered optimization and regulatory compliance within the life sciences sector. The comprehensive nature of the summit, covering clinical, regulatory, quality, and IT, confirms its importance as a holistic view of the R&D technology landscape. Key Takeaways: • **Veeva Roadmap Insight:** The dedicated roadmap session offers a crucial opportunity to understand Veeva’s internal prioritization of business problems and their planned technological solutions. This foresight is invaluable for consulting firms needing to anticipate platform changes and align their custom AI and software development services accordingly. • **Direct Influence on Product Development:** Attendees are explicitly invited to challenge Veeva’s thinking during the roadmap session, providing a direct channel for influencing the platform's future features and ensuring that upcoming releases address specific, high-priority client needs in areas like regulatory compliance and clinical data management. • **Focus on Veeva Vaults and CDMS:** The highlighted "Richard and Drew Show" session confirms a deep dive into the capabilities of Veeva Vaults, particularly in solving Clinical Data Management System (CDMS) challenges. This indicates that operational efficiency, data integrity, and streamlining clinical processes are major focus areas for Veeva's R&D strategy. • **Strategic Networking Opportunities:** The summit is positioned as a premier venue for meaningful conversations with industry colleagues, offering unparalleled access to potential clients, partners, and key decision-makers across clinical, regulatory, quality, and IT departments within the life sciences ecosystem. • **Innovation and Best Practices:** The event features an exceptional lineup of industry leaders discussing new and emerging best practices and innovation areas. This provides a critical mechanism for staying current on industry trends, especially concerning the integration of advanced technologies like AI/LLMs into regulated R&D workflows. • **Comprehensive R&D Scope:** The summit’s coverage spans clinical operations, clinical data management, regulatory affairs, quality management, and IT strategy, confirming its relevance as a holistic learning environment for all aspects of pharmaceutical R&D technology utilization. • **Customer Case Studies:** The event promises over 65 breakout sessions featuring customer case studies. These real-world examples offer practical insights into successful Veeva implementations and highlight specific business problems that have been solved using the platform, providing valuable reference material for consulting engagements. Tools/Resources Mentioned: * **Veeva Vaults:** The core platform suite discussed for solving R&D and CDMS business problems. Key Concepts: * **CDMS (Clinical Data Management System):** Refers to the systems and processes used to manage data generated during clinical trials. The focus on solving CDMS business problems highlights the need for improved data quality, integration, and efficiency in clinical operations, areas ripe for AI and data engineering solutions. * **Veeva R&D Summit:** An annual gathering focused on technology, innovation, and best practices across the clinical, regulatory, and quality functions within the life sciences industry.

Henry Levy invites you to R&D Summit
Veeva Systems Inc
/@VeevaSystems
Aug 20, 2019
This video serves as an invitation from Henry Levy, General Manager for Veeva Vault CTMS (Clinical Trial Management System), to the Veeva R&D Summit in Philadelphia. The primary context of the invitation is to highlight the significant progress and maturation of Veeva’s solutions in the clinical operations space, particularly focusing on their Electronic Data Capture (EDC) offering and the broader goal of revolutionizing clinical data management. Levy uses his personal experience—joining Veeva three years prior and participating in a demo of a "very, very early EDC solution"—to frame the rapid evolution of the technology. The core message emphasizes the transition from nascent technology to an established, market-tested platform. Levy provides specific, albeit brief, metrics demonstrating this growth: in the three years since the initial demo, Veeva’s EDC solution has been utilized to run almost 40 clinical studies, with nearly 10 studies having reached the lock stage. This rapid adoption and successful completion of trials underscore Veeva’s commitment to disrupting traditional clinical data management systems. The progression of ideas moves from a historical anecdote to current success metrics, culminating in a call to action for industry leaders to attend the summit to share in this journey and contribute feedback. The speaker’s perspective is one of excitement and partnership, positioning the R&D Summit not just as a showcase for innovative technology, but as a collaborative forum. The explicit request for attendees to "help us" and "tell us how we can continue to improve the data management space" highlights Veeva’s reliance on customer feedback to refine its regulated enterprise software. This approach suggests a continuous development cycle driven by the practical needs of pharmaceutical, biotech, and medical device companies, aiming to fully capitalize on the benefits of modern technology within the highly regulated clinical trial environment. The overall theme is the successful integration of technology into R&D processes to enhance efficiency and compliance in clinical data management. Key Takeaways: • **Rapid Maturation of Veeva Clinical Solutions:** The video confirms the accelerated growth and market acceptance of Veeva’s R&D suite, moving from an early-stage EDC demo to a solution running approximately 40 clinical studies and locking 10 within a three-year span. This validates Veeva’s aggressive push into the clinical operations technology market. • **Focus on Clinical Data Management Revolution:** The central strategic goal articulated is the revolutionization of clinical data management, indicating that Veeva is actively challenging traditional, often fragmented, systems with integrated, cloud-based solutions like Vault CTMS and EDC. This represents a significant shift in industry standard operating procedures. • **Importance of Integrated CTMS and EDC:** The speaker, as the General Manager for Vault CTMS, links the success of the EDC solution directly to the broader Vault platform, emphasizing the value of having core clinical trial management and data capture functions unified within a single ecosystem. This integration streamlines workflows and improves data integrity. • **Customer-Centric Development Model:** Veeva explicitly invites industry leaders to the R&D Summit to provide feedback, underscoring a commitment to a customer-driven development cycle. For consulting firms, this signals that successful Veeva implementations must incorporate client-specific operational needs and feedback loops. • **Proof Points for Adoption:** The metrics provided (40 studies run, 10 studies locked) serve as crucial proof points for potential clients and partners, demonstrating the reliability and regulatory compliance of the system for managing end-to-end clinical trials, including the critical study lock milestone. • **Strategic Opportunity in R&D Operations:** The focus on the R&D Summit confirms that Veeva is heavily investing in the clinical, regulatory, and quality sectors, moving beyond its traditional strength in commercial CRM. This expands the scope of required expertise for consultants specializing in Veeva systems. • **Technology Capitalization in Regulated Space:** The speaker stresses the need to "capitalize on the benefits of technology in this important space," which directly aligns with IntuitionLabs’ mission to deploy AI and custom software to optimize regulated processes like clinical data handling and compliance tracking. • **Target Audience Alignment:** The R&D Summit targets leaders in clinical, regulatory, quality, and IT—the precise departments within pharmaceutical and biotech companies that IntuitionLabs serves, confirming the relevance of these topics to the company’s sales and service strategy. Tools/Resources Mentioned: * **Veeva Vault CTMS (Clinical Trial Management System):** A core product within the Veeva R&D suite designed to manage the lifecycle of a clinical trial. * **Veeva EDC (Electronic Data Capture):** The specific solution mentioned for capturing and managing clinical trial data electronically. * **Veeva R&D Summit:** The annual industry event serving as a platform for sharing best practices and technology updates in clinical, regulatory, and quality operations. Key Concepts: * **Clinical Data Management (CDM):** The process of collecting, cleaning, and managing data from clinical trials in compliance with regulatory standards (e.g., GxP, 21 CFR Part 11). The video positions Veeva’s solutions as revolutionary tools for modernizing CDM. * **Study Lock:** A critical milestone in a clinical trial where the database is finalized and "locked," meaning no further changes can be made to the data before analysis and submission to regulatory bodies. Achieving 10 study locks demonstrates the system's maturity and regulatory readiness.

Why Dublin? Veeva
Dublin, Ohio, USA
/@DublinOhioUSA
Aug 12, 2019
This video provides a concise look into the operational expansion strategy of Veeva Systems, a leading provider of enterprise cloud software for the global life sciences industry. The presentation features Katherine Halls House, the Global CIO and Head of Operations for Veeva, explaining the strategic decision behind establishing Dublin, Ohio, as the company’s second major regional hub outside its San Francisco Bay Area headquarters. The core message is that Veeva’s rapid growth necessitated a significant expansion, and the selection process prioritized locations that offered both operational advantages and a high quality of life conducive to employee retention and relocation. Veeva Systems, founded 12 years prior to the video and boasting approximately 2,600 employees across 24 global offices, experienced growth so rapid that it required a substantial second location within the United States. The company undertook an extensive search, evaluating prominent tech and business centers such as Austin, Nashville, and Portland, Oregon. Ultimately, Dublin, Ohio, was selected based on a combination of logistical and cultural factors. The decision was heavily influenced by the community's appeal, which was noted to be reminiscent of some Northern California towns where Veeva maintains its primary base. The appeal of Dublin centered on its ability to attract and retain talent through lifestyle benefits. Employees who relocated cited the convenience of being able to walk to work, coupled with the community's diverse nature and small-town feel, which includes amenities like a farmers market, alongside access to quality dining, shopping, and entertainment. From an operational standpoint, Veeva highlighted Dublin’s proactive approach to supporting its business community. The city actively engages in outreach, encouraging local enterprises to network, meet, and share ideas, which fosters a close-knit, collaborative ecosystem. This supportive environment was deemed essential for sustaining the growth trajectory of a global technology company operating in a highly specialized sector like life sciences. The insights provided by the Global CIO underscore that for a specialized technology firm like Veeva, location strategy is not solely about cost or proximity to talent pools, but also about creating an environment where employees thrive and businesses can interact effectively. The choice of Dublin reflects a mature strategy focused on long-term sustainability, talent satisfaction, and leveraging local government support to enhance business connectivity. This strategic move ensures Veeva can continue to scale its operations while maintaining the cultural and community values that appeal to its workforce. Key Takeaways: • **Rapid Operational Scaling:** Veeva Systems, a major enterprise cloud software provider for the life sciences industry, required a "second big regional hub" in the U.S. to accommodate its rapid growth, highlighting the intense scaling demands within the regulated software sector. • **Extensive Location Scouting:** The selection of Dublin, Ohio, followed a rigorous evaluation process that included other high-growth markets such as Austin, Nashville, and Portland, Oregon, indicating a strategic, data-driven approach to expansion. • **Prioritizing Quality of Life for Talent:** The final decision was significantly influenced by lifestyle factors, with Dublin offering a diverse community and a small-town atmosphere that was specifically noted to be reminiscent of Veeva’s Northern California home base. • **Successful Employee Relocation:** The company noted successful employee relocations, with staff choosing Dublin not only for professional reasons but also for the quality of life, including the convenience of being able to walk to work. • **Community Amenities as a Draw:** Dublin’s blend of small-town features (like a farmers market) and urban amenities (restaurants, shopping) was crucial in appealing to a diverse, mobile workforce accustomed to high-quality living standards. • **Strategic Municipal Business Support:** A key operational advantage cited was Dublin’s strong municipal outreach to businesses, actively fostering networking and idea sharing among local companies, which creates a supportive ecosystem for technology firms. • **Leadership Validation:** Katherine Halls House, Global CIO and Head of Operations, explicitly endorsed Dublin as the "perfect place for a growing global technology company," confirming the strategic alignment of the location with Veeva's long-term corporate goals. • **Scale of Operations:** At the time of the video, Veeva operated with approximately 2,600 employees across 24 global offices, underscoring its position as one of the largest providers of enterprise cloud software globally. • **Strategic Hub Model:** Establishing a second major hub allows Veeva to diversify its operational base and mitigate risks associated with relying solely on the San Francisco Bay Area, ensuring business continuity and access to different regional talent pools. Tools/Resources Mentioned: * Veeva Systems Inc. (Cloud-based software for the global life sciences industry) Examples/Case Studies: * **Dublin, Ohio:** Selected as Veeva’s second global headquarters/regional hub in the U.S. after evaluating locations like Austin, Nashville, and Portland, Oregon. The choice was based on community fit, quality of life, and strong business outreach programs.

Bayer: Customer Data Strategies on Recommendations for Digital Transformation
Veeva Systems Inc
@VeevaSystems
Jul 26, 2019
This video provides an expert perspective from Bayer on the organizational and strategic challenges inherent in digital transformation within the life sciences sector, specifically focusing on the foundational requirement of high-quality customer reference data. The speaker emphasizes that while new systems and digital initiatives are crucial, their success hinges entirely on the underlying data quality, which touches virtually all business processes. The core challenge is not merely technical, but organizational and cultural, particularly when dealing with legacy processes that may be utilizing customer data in ineffective or "broken" ways. To successfully navigate organizational change and implement systems requiring robust data, the speaker posits that three main elements must be addressed: the **skill set**, the **tool set**, and the **mind set**. While skill development and tool implementation are manageable tasks, cultivating a true data-driven mindset across the organization is the most difficult hurdle. Consequently, significant time and resources must be dedicated to establishing effective data governance—the mechanism that allows organizations to "move the needle" on data quality and adoption. The speaker outlines three critical takeaways derived from their experience in establishing a successful governance model. First, organizations must focus on identifying and articulating **collective pain points**. Instead of getting defensive about existing broken processes, teams must collaboratively identify which processes are being hindered or prevented from succeeding due to poor data quality. Second, securing **executive leadership sponsorship and awareness** is non-negotiable, as change requires unique funds and resources. This sponsorship must be justified by a clear plan demonstrating the return on investment (ROI), ensuring leadership understands the initiative is not just an investment but a source of measurable returns. Finally, the most impactful factor for success was establishing a **common theme or single authority** empowered to make decisions across all three pillars of the data ecosystem: industry reference data standards, the tools for integration and mastering (MDM), and the receivership services. Without this centralized authority to make unified calls across these interdependent components, organizations risk struggling indefinitely with fragmented solutions. The ultimate success of digital transformation relies on shifting the organizational perspective from being a "sole ace" (working in isolation) to being part of a strategic solution, which requires stakeholders—especially sales representatives and power users—to be included in the mission and excited about the possibilities enabled by high-quality data. Key Takeaways: * **Data Quality is Foundational for Digital Transformation:** New systems and digital initiatives, particularly those relying on platforms like Veeva CRM, require high-quality customer reference data; failure to address underlying data issues will impede success. * **The Three Pillars of Change:** Successful organizational change requires balancing improvements in the **skill set** (training and expertise), the **tool set** (technology and platforms), and the **mind set** (cultural adoption of data-driven thinking). * **Mindset is the Hardest Challenge:** Cultivating a data-driven mindset is significantly more difficult than acquiring new skills or tools, necessitating focused initiatives and investment in governance to drive cultural change. * **Governance Drives Progress:** Effective data governance is the primary mechanism for moving the needle on data quality and adoption, ensuring that data standards are consistently applied across the enterprise. * **Focus on Collective Pain Points:** When initiating governance efforts, avoid defensive explanations of existing failures; instead, collaboratively identify shared pain points to clearly articulate which critical business processes are being hindered by poor data. * **Secure Executive Sponsorship with ROI:** Gaining executive leadership awareness and sponsorship is essential for securing the necessary funds for data transformation; this must be supported by a clear plan demonstrating the anticipated return on investment (ROI). * **Establish Centralized Decision Authority:** The most critical factor for success is establishing a single, common theme or authority empowered to make decisions across the entire data lifecycle (reference data, integration/mastering tools, and receivership services). * **Avoid Fragmented Solutions:** Without a unified authority overseeing all three data pillars, organizations will struggle with fragmented, interdependent solutions that fail to solve the core data quality issues. * **Shift from "Sole Ace" to "Solution Partner":** Individuals and departments must move away from isolated approaches ("sole ace") and embrace a strategic, collaborative mindset focused on being part of the overall data solution. * **Engage Stakeholders Early and Enthusiastically:** Success requires getting stakeholders, including sales representatives and power users, excited about the change by including them in the mission and "selling them the art of the possibility" enabled by improved data. Key Concepts: * **Customer Reference Data:** The foundational, high-quality data describing customers (e.g., healthcare professionals, organizations) that is essential for commercial operations, CRM systems (like Veeva), and analytics. * **Data-Driven Mindset:** A cultural shift where decision-making is consistently based on data insights, requiring organizational commitment beyond just implementing new technology. * **Governance Model:** A structured framework, including policies, procedures, and defined roles, designed to manage, control, and ensure the quality and compliance of data assets across the organization.

Bayer: Customer Data Strategies on Measuring ROI and Impact
Veeva Systems Inc
@VeevaSystems
Jul 26, 2019
This video, featuring a representative from Bayer, details the significant return on investment (ROI) and operational impact achieved through the optimization of their customer data management program, focusing heavily on data quality improvements and process efficiency. The core narrative revolves around transforming slow, bottlenecked data processes into agile, daily operations, fundamentally changing how the commercial field force interacts with critical customer reference data. The speaker highlights several key metrics demonstrating this transformation, moving beyond abstract quality goals to concrete improvements in speed, capacity, and user engagement. A major achievement discussed is the shift in data mastering cycles. Previously, mastering cycles—the process of cleaning, matching, and consolidating customer data—ran only twice a month. Through program improvements, this was accelerated to a daily mastering cycle. This daily capability is described as "very powerful," enabling the organization to immediately leverage data provided by external data vendors on a daily basis, a crucial factor in maintaining timely and accurate customer profiles (physicians, accounts, affiliations, and addresses). Concurrently, the capacity to handle Data Change Requests (DCRs) dramatically increased, moving from attending to only two types of requests to managing over ten different types, covering all data entities relevant to customer data. The speaker also addresses the initial concern that implementing stricter data change request processes might create friction or delays for the sales representatives (field force). Surprisingly, the opposite occurred. By providing the field force with access to a "bigger view" of open data on demand, the overall need for creating DCRs decreased. Furthermore, when a DCR was necessary, the turnaround time improved drastically. Historically, DCRs were processed on a monthly basis, forcing the field force to mark their calendars for data updates. This slow process was replaced with a Service Level Agreement (SLA) measured in just a few hours. This rapid turnaround fostered a change in mindset among the sales reps, who began viewing the time spent submitting quality requests as a worthwhile investment, knowing they would quickly receive accurate data to support their commercial activities. Finally, the presentation emphasizes the massive reduction in time required for data integration projects and the elimination of data silos. Data integration, which previously took close to three months—creating "red alert" situations for new data acquisitions or product launches—was reduced to just a few weeks of effort, especially when leveraging solutions like Veeva. This efficiency gain allowed the team to invest more time in strategic planning and data profiling rather than worrying about execution bottlenecks. The overall solution empowered "power users" to move out of data silos, granting them self-service access to data that was previously locked away in a "black box," thereby democratizing data access and fostering greater organizational efficiency. --- ### Key Takeaways * **Accelerated Data Mastering:** The organization successfully transitioned from a bi-monthly data mastering cycle to a daily cycle. This daily capability is essential for pharmaceutical companies that rely on timely customer data updates from external providers and is a critical metric for measuring data management program ROI. * **Increased Data Change Request (DCR) Capacity:** The ability to handle DCRs expanded significantly, moving from only two types of requests to managing over 10 different types, ensuring comprehensive coverage of all customer data entities (physician, address, affiliation, accounts). * **Dramatic SLA Improvement for Field Force:** DCR turnaround time was reduced from a monthly cycle (requiring field force calendar marking) to an SLA measured in just a few hours. This rapid response time is crucial for maintaining data relevance and supporting agile commercial operations. * **Field Force Mindset Shift:** The improved speed and quality of the data management process changed the sales reps' perception, leading them to view the investment of time in submitting quality DCRs as worthwhile, knowing they would quickly receive high-quality data in return. * **Reduced Need for DCRs via Transparency:** Providing the field force with access to a "bigger view" of open data on demand surprisingly reduced the overall volume of DCRs, suggesting that data transparency can preempt many common data quality issues. * **Massive Reduction in Integration Time:** The time required for new data integration projects was drastically cut from approximately three months to just a few weeks, particularly when leveraging platforms like Veeva. This efficiency eliminates bottlenecks that previously delayed product launches and new data acquisition. * **Strategic Focus Over Execution Worry:** By streamlining data integration and mastering processes, the team was able to shift their focus, investing more time in strategic planning and data profiling rather than being consumed by execution challenges and "red alerts." * **Elimination of Data Silos and Empowerment of Power Users:** The implemented solution provided a clear view and access mechanism to previously siloed data ("black box" data), enabling power users to perform self-service data tasks and fostering data democratization across the organization. * **Customer Data Entities Covered:** The data management program specifically addresses key customer data entities, including addresses, physicians, accounts, affiliations, and associated attributes, highlighting the comprehensive nature of the quality initiative. --- ### Tools/Resources Mentioned * **Veeva:** Explicitly mentioned as a platform that helped drastically reduce data integration efforts and is implied as the core system supporting the customer data strategy (likely Veeva Network/CRM). ### Key Concepts * **Data Mastering Cycles:** The process of cleaning, standardizing, matching, and consolidating customer data from various sources into a single, accurate master record. Accelerating this cycle (from bi-monthly to daily) is a key measure of data management maturity. * **Data Change Requests (DCRs):** Formal requests submitted by users (e.g., sales reps) to correct, update, or add customer reference data (e.g., a physician's address or affiliation). The efficiency of the DCR process directly impacts field force productivity. * **Service Level Agreement (SLA):** A commitment regarding the speed and quality of service delivery. Improving the SLA for DCRs from monthly to hourly turnaround demonstrates significant operational improvement. * **Data Silos:** Data stored in separate systems or departments that is not easily accessible or integrated, often preventing a unified view of the customer. The solution aimed to move users out of these silos. * **Data Profiling:** The process of examining the data available from an existing information source (e.g., a database or file) and collecting statistics and information about that data. This is a crucial step in data integration planning.

Bayer: Customer Data Strategies on the Impact of Speed
Veeva Systems Inc
@VeevaSystems
Jul 26, 2019
This video provides an expert perspective from Bayer on optimizing customer data strategies within the pharmaceutical industry, focusing specifically on the critical balance between the value derived from data speed and the organizational appetite for consuming that speed. The speaker outlines how Bayer has successfully navigated this challenge by redefining data access workflows for commercial teams and ensuring enterprise-wide consistency in data consumption. This strategy is rooted in shifting away from traditional, reactive data management toward proactive, high-quality data integration, which significantly impacts commercial operations like sales force effectiveness and product launch readiness. The core of Bayer’s strategy involves segmenting the data challenge into two components: "value from speed" and "appetite for speed." Achieving value from speed meant providing sales representatives with access to a fuller universe of data, fundamentally changing their daily workflows. Instead of the old-school method of creating unverified customer data and cleaning it later, the new approach empowers reps to search for and download a clean, verified profile from the outset. This immediate access to high-quality data accelerates integration timelines, particularly when onboarding new data sources like data aggregators or specialty pharmacies, and ensures the commercial team is better and faster prepared for critical events such as new product launches or the creation of new call plans. However, the speaker emphasizes that high-speed data delivery is only effective if the organization is prepared to consume it responsibly—the "appetite for speed." This necessitated implementing checks and balances within the systems consuming customer data, recognizing that data quality is only as good as its consumption by the systems interfacing with end-users. This focus on governance allowed Bayer to challenge the status quo in internal systems that were still consuming data at a slower rate or inconsistent frequency. The ultimate goal was to ensure all downstream systems consumed data at a similar frequency, establishing a common data language across the entire enterprise to maintain integrity and operational synchronization. This holistic approach highlights that technological capability (the speed of data delivery) must be paired with organizational readiness and robust data governance (the appetite for speed). By standardizing consumption frequency and ensuring clean data profiles are the starting point for commercial activities, Bayer created a more efficient, compliant, and commercially agile environment, maximizing their investment in customer reference data and related enterprise platforms. Key Takeaways: • **Balancing Speed and Governance:** Successful data strategy requires balancing the commercial value derived from rapid data access (value from speed) with the organizational capacity and control mechanisms for consumption (appetite for speed). • **Transforming Sales Workflow:** Pharmaceutical sales representatives should transition from a reactive model—creating unverified data and cleaning it later—to a proactive model where they search and download clean, verified customer profiles immediately. This shift drastically improves data quality at the source. • **Accelerated Integration:** High-speed access to quality customer data significantly reduces the time required to integrate critical third-party data sources, such as data aggregators or specialty pharmacies, into core operational systems. • **Enhanced Commercial Readiness:** Rapid data access prepares commercial teams faster and more effectively for key strategic initiatives, including new product launches and the development of optimized call plans and targeting strategies. • **Data Quality is Consumption-Dependent:** Customer data is only valuable if it is consumed correctly by the systems interfacing with end-users; therefore, governance must focus heavily on the consumption layer, not just the delivery layer. • **Challenging Internal Status Quo:** Organizations must actively identify and challenge internal systems that are consuming customer data at a slower or inconsistent frequency, as these bottlenecks undermine the investment in high-speed data pipelines. • **Establishing a Common Data Language:** A primary goal of data strategy should be ensuring that all internal systems consume data at a similar frequency and adhere to a common data language, which is essential for enterprise-wide synchronization and regulatory compliance. • **Governance through Checks and Balances:** Implementing robust checks and balances is crucial for systems consuming customer data to ensure responsible usage and maintain data integrity throughout the organization. Key Concepts: * **Value from Speed:** The tangible commercial benefits derived from having immediate access to high-quality, verified customer data (e.g., faster integration, better call plans). * **Appetite for Speed:** The organizational readiness, governance, and system capacity required to consume high-speed data consistently and responsibly across the enterprise. * **Fuller Universe of Data:** Providing commercial teams with comprehensive access to all relevant customer reference data, moving beyond siloed or incomplete records. Examples/Case Studies: * **Bayer's Sales Workflow Transformation:** The shift from "old-school way of creating unverified data and then trying to clean it at a later point" to "doing a search and downloading a clean profile to begin with," illustrating a successful implementation of data quality at the point of entry. * **Integration Acceleration:** The ability to reduce the time required to integrate data from external sources like data aggregators or specialty pharmacies, improving operational agility.

Bayer: Customer Data Strategies for Reduction in Costs and Complexity
Veeva Systems Inc
@VeevaSystems
Jul 26, 2019
This video provides an executive perspective from Bayer on their successful customer data strategy, centering on the implementation of a Veeva solution and the strategic utilization of Veeva Open Data to achieve substantial reductions in operational costs and complexity. The speaker immediately quantifies the financial impact of this transition, noting that the initial shift to the Veeva platform resulted in an immediate savings of half a million dollars. This initial success established a strong business case for further investment in data centralization and optimization. The core strategy involved getting rid of disparate reference data sources and extending the use of Veeva Open Data across multiple critical commercial and regulatory functions. Key operational areas benefiting from this integration include state license validation, which is crucial for ensuring field representatives can legally engage with healthcare professionals, and managing sample ability, which governs compliant distribution of drug samples. By centralizing this reference data, Bayer significantly streamlined these processes, reducing the manual effort and complexity historically associated with maintaining accurate, up-to-date compliance data. Furthermore, the company leveraged the Veeva Open Data platform for transparency reporting, a mandatory and data-intensive regulatory requirement tracking payments and interactions with healthcare providers. This expansion generated additional, ongoing savings by simplifying the data aggregation and reporting process. Critically, the savings realized from reducing data complexity and eliminating reliance on expensive, external reference data providers are not being retained as simple cost cuts but are being strategically channeled back into the program. These funds are earmarked for future innovation, specifically supporting projects related to data science and broader digital enablement initiatives, demonstrating a self-funding model for advanced commercial capabilities. The long-term vision involves further integration of the centralized data asset across the enterprise. The speaker mentions plans to extend the use of Open Data to the Medical CRM system, indicating a move toward unifying data governance and ensuring consistency between commercial and medical affairs activities. This strategic reinvestment into data science and digital platforms highlights how foundational data management improvements are essential prerequisites for successful AI and advanced analytics initiatives within the highly regulated pharmaceutical environment. Key Takeaways: * **Quantifiable ROI on Platform Migration:** The initial transition to the Veeva solution delivered an immediate and significant return on investment, with Bayer achieving $500,000 in savings, validating the financial benefits of modernizing core commercial data infrastructure. * **Veeva Open Data as a Cost Reduction Engine:** Strategic adoption of Open Data allowed Bayer to eliminate reliance on costly, complex third-party reference data services, directly reducing vendor spend and the internal overhead associated with data harmonization and maintenance. * **Compliance Automation for Field Operations:** The centralized data platform is instrumental in automating critical regulatory checks, specifically state license validation and sample eligibility, ensuring continuous compliance for sales representatives and reducing risk associated with non-compliant interactions. * **Streamlining Regulatory Transparency:** Extending the use of Open Data to transparency reporting simplifies one of the most data-intensive regulatory requirements in the pharmaceutical industry, yielding further operational savings and enhancing the accuracy of required disclosures. * **Self-Funding Innovation Model:** The cost savings achieved through data optimization are strategically reinvested into high-value initiatives, including data science and digital enablement, creating a sustainable financial model for continuous technological advancement. * **Foundation for Data Science:** By standardizing and cleaning customer reference data, the company establishes a high-quality data foundation, which is a prerequisite for successful deployment of AI and machine learning models in commercial operations. * **Integration with Medical Affairs:** Future plans to integrate Open Data into the Medical CRM system signal a strategic effort to unify data governance between commercial and medical teams, crucial for compliant and coordinated engagement with healthcare professionals (HCPs). * **Focus on Complexity Reduction:** Beyond monetary savings, the primary benefit is the reduction in complexity across data technology and service providers, which improves data quality, reduces IT burden, and accelerates time-to-insight for commercial teams. ### Tools/Resources Mentioned: * **Veeva Solution:** Refers generally to the suite of Veeva products utilized by the pharmaceutical industry, likely including Veeva CRM and related data services. * **Veeva Open Data:** A specific Veeva product providing verified, standardized healthcare professional (HCP) and healthcare organization (HCO) reference data, which is central to the cost-saving strategy. * **Medical CRM:** The Customer Relationship Management system used by Medical Affairs teams, indicating a planned integration point for the centralized data. ### Key Concepts: * **Reference Data:** The foundational, standardized data (like HCP names, addresses, specialties, and affiliations) required for commercial operations, compliance, and reporting. Managing this data efficiently is critical for pharma companies. * **State License Validation:** The mandatory process of verifying that healthcare professionals hold current, valid licenses in the states where they practice, a key compliance requirement for pharmaceutical interactions. * **Sample Ability:** The process of determining a healthcare professional's eligibility to receive drug samples, which is strictly governed by FDA regulations and state laws. * **Transparency Reporting:** Regulatory reporting (e.g., U.S. Sunshine Act, European equivalents) that requires pharmaceutical companies to disclose payments and transfers of value made to healthcare professionals and organizations. ### Examples/Case Studies: * **Bayer's Initial Savings:** The company achieved an immediate savings of half a million dollars simply by shifting their reference data management to the Veeva solution. * **Strategic Reinvestment:** The savings generated are being explicitly redirected to fund new projects in data science and digital enablement, demonstrating a commitment to leveraging operational efficiency gains for future innovation.

Blockchain in Action: How IQVIA Built an App Streamlining Drug Labels
Salesforce Developers
/@SalesforceDevs
Jun 26, 2019
This video explores a real-world application of blockchain technology by IQVIA, a leading life sciences company, to streamline the complex and highly regulated process of managing prescription drug labels using Salesforce Blockchain. The speakers highlight how traditional methods for label changes are inefficient, involve numerous parties, and lack consistent version control, posing significant challenges for regulatory compliance and patient safety. Blockchain is presented as a transformative solution to these issues, offering an immutable ledger, distributed network, and consensus workflows to ensure the permanence, provenance, and real-time replication of critical label information across stakeholders, including pharmaceutical companies, regulatory bodies, and design teams. Key Takeaways: * **Blockchain for Regulated Content Management:** The video demonstrates a powerful application of blockchain in the pharmaceutical industry for managing highly sensitive and regulated content like drug labels, ensuring immutable evidence, auditability, and real-time consistency across a multi-party ecosystem. * **Addressing Operational Inefficiencies in Life Sciences:** Blockchain is positioned as a solution to overcome the inherent complexities and inefficiencies of traditional drug label management, which is characterized by disparate data sources, manual processes, and challenges in maintaining version control and audit trails. * **Architectural Paradigm Shift:** The speakers advocate for viewing blockchain as a new architectural layer for enterprise systems, specifically for recording immutable events and facilitating "collaborative coding" of smart contracts among different organizations, moving beyond its common association with supply chain or cryptocurrency. * **Enhanced Regulatory Compliance and Patient Safety:** By providing a trusted, shared record of all label changes and their history, the solution significantly enhances regulatory compliance (e.g., FDA, EMA, GxP) and enables rapid, secure updates to critical drug information, directly impacting patient safety. * **Salesforce's Role in Enterprise Blockchain:** The successful prototyping of this solution on Salesforce Blockchain underscores Salesforce's capability to provide a declarative, integrated platform for enterprise-grade blockchain applications, particularly within regulated industries. * **Data Provenance and Auditability:** The "blockchain Timeline view" feature, which tracks every change and its history, offers robust data provenance and audit trail capabilities, crucial for meeting stringent regulatory requirements.

Veeva Vault – How to Integrate with Other Applications
Technology Services Group is now part of Hyland
/@tsgrp
Jun 14, 2019
This video provides a technical demonstration of integrating Veeva Vault, a leading content management system for the life sciences industry, with external enterprise applications. The core purpose of the integration is to allow external systems to access and display regulated documents stored within Vault using a streamlined, custom viewer application. The speaker showcases R&D work focused on minimizing the complexity of this integration, proving that robust access can be achieved using a minimal set of Veeva API calls. The primary business case presented is linking training materials stored in a Learning Management System (LMS), specifically SuccessFactors, directly to the authoritative Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) or detailed training documents housed in Veeva Vault. The demonstration illustrates a training slide on disaster recovery within the LMS, which contains a hyperlink designed to launch the custom Veeva Vault application. Upon clicking the link, the application uses the Veeva Document ID as a parameter to retrieve the necessary content. The application successfully pulls down the PDF document for display to the user, along with relevant metadata, such as the document title or version. This approach is contrasted with traditional methods where content is often cached or synchronized between the content management system and the LMS using complex, often brittle, synchronization logic. A key architectural advantage highlighted by the speaker is the elimination of content caching. By connecting directly to Veeva Vault via the API for every request, the system ensures that the user always accesses the latest, most current, and approved version of the document. This is critical in regulated environments where outdated SOPs or training materials can lead to compliance violations. Furthermore, the integration addresses authentication, suggesting two primary methods: prompting the user for a separate login or utilizing Single Sign-On (SSO) capabilities to provide a seamless, streamlined user experience without requiring secondary application logins. Finally, the custom application provides enhanced control over the user interface and functionality. By building a dedicated document viewer, the developers can control exactly what the user sees and limit any potential additional functionality or actions that could be performed on the document, ensuring data integrity and adherence to viewing protocols. This R&D work demonstrates a practical, lightweight solution for ensuring regulatory compliance and content currency across disparate enterprise systems within the pharmaceutical ecosystem. Key Takeaways: • **Minimalist API Integration:** The integration relies on only three essential Veeva API calls—Login, Retrieve Document, and Retrieve Metadata—demonstrating that robust, functional document access does not require complex, multi-layered API interactions. • **Elimination of Content Caching:** A primary benefit of the direct API integration is the ability to bypass content synchronization and caching logic, ensuring that external systems always display the most current, approved version of regulated documents (e.g., SOPs). • **Regulatory Compliance Assurance:** In pharmaceutical and life sciences contexts, ensuring access to the latest SOPs and training materials is a critical compliance requirement; direct integration with Veeva Vault serves as the single source of truth for these documents. • **LMS Integration Use Case:** The specific business case demonstrated involves linking a training system (SuccessFactors) directly to detailed SOPs within Vault, streamlining the training process and ensuring that employees are referencing the authoritative source material. • **Streamlined User Experience (UX):** The integration can leverage Single Sign-On (SSO) capabilities, eliminating the need for users to log into a secondary application (the custom viewer) and providing a smoother, more efficient workflow for accessing necessary documentation. • **Controlled Document View:** Developing a custom document viewer allows the organization to precisely control the user interface, limiting potential actions or functionality that could be performed on the regulated document, thereby enhancing security and adherence to viewing protocols. • **Metadata Utilization:** The custom application retrieves and displays key metadata alongside the document (e.g., title, version), providing context and verification to the user regarding the document's status. • **Architecture for Regulated Environments:** This integration pattern is highly valuable for organizations operating under GxP or 21 CFR Part 11 requirements, as it maintains the integrity and audit trail of documents within the regulated content management system (Veeva Vault). Tools/Resources Mentioned: * **Veeva Vault:** The core content management platform holding the regulated documents. * **Veeva API:** The interface used for integration, specifically mentioning Login, Retrieve Document, and Retrieve Metadata calls. * **SuccessFactors:** Mentioned as the example Learning Management System (LMS) being integrated with Veeva Vault. Key Concepts: * **Content Caching:** The practice of storing copies of content in multiple locations (e.g., within the LMS) to improve access speed, which requires complex synchronization logic to keep the copies current. The video advocates avoiding this for regulated content. * **Single Sign-On (SSO):** An authentication scheme that allows a user to log in with a single ID and password to gain access to multiple related applications, improving security and user convenience. * **SOP (Standard Operating Procedure):** Detailed, regulated instructions that govern critical operations within pharmaceutical and life sciences companies. Examples/Case Studies: * **Training System Integration:** The primary example involves a training slide within an LMS (SuccessFactors) that links directly to a detailed SOP (on disaster recovery) stored in Veeva Vault, ensuring employees always access the most current training reference material.

Regulatory Intelligence Trailer
Kathy Barnett
/@kathybarnett4070
Jun 5, 2019
This video provides an in-depth exploration of Regulatory Intelligence (RI), defining its core components, differentiating it from mere regulatory information, and outlining its critical role in shaping successful strategies for pharmaceutical and medical device companies. The presentation begins by establishing the necessity of RI in a constantly evolving regulatory landscape, setting the stage for understanding its importance beyond simply tracking regulations. It aims to equip attendees with the knowledge to identify sources, evaluate research questions, utilize RI databases, and effectively summarize and present findings to their teams. The speaker meticulously defines regulatory information as the act of gathering and analyzing publicly available regulatory data, including communicating its implications and monitoring the environment for opportunities to influence future regulations, guidance, and policy. A key distinction is drawn between this raw "regulatory information" and "regulatory intelligence." While information is the data dump—the written, published, or unpublished raw material—intelligence is the active capacity to acquire knowledge through analysis and surveillance. For instance, gathering data on competitor products (trade names, routes of administration, labeling, clinical trials, drug class, submission/approval dates) constitutes regulatory information. In contrast, regulatory intelligence involves taking this information, summarizing it into an executive report, and analyzing it to review competitor products, the current regulatory landscape, and submission routes to inform a company's strategic direction. The presentation further distills regulatory intelligence into three major guiding principles: gathering data, analyzing information, and formulating regulatory strategy. It emphasizes that RI is often one of the most misinterpreted roles within regulatory departments, particularly in consulting capacities for pharmaceutical and device companies. Far from being a passive data collection exercise, RI is presented as the "creative part of regulatory affairs," crucial for informed decision-making. The speaker clarifies what RI is not, distinguishing it from competitive intelligence (typically a marketing function), proprietary sales or marketing information, drug pricing, or reimbursement issues. Instead, RI leverages regulatory information, potentially alongside other data, to provide a comprehensive analysis that enables a company to move forward in an informed and strategic manner. Key Takeaways: * **Defining Regulatory Intelligence (RI):** RI is the systematic act of gathering, analyzing, and communicating publicly available regulatory information, monitoring the environment, and assessing implications to shape future regulations, guidance, policy, and legislation. It is crucial for developing successful regulatory strategies in a dynamic landscape. * **Information vs. Intelligence:** Regulatory information refers to the raw, published or unpublished data (e.g., competitor product details like trade names, clinical trials, approval dates). Regulatory intelligence, conversely, is the active capacity to acquire knowledge and experience through analysis and surveillance, transforming raw data into strategic insights. * **Three Pillars of RI:** Effective regulatory intelligence is built upon three fundamental components: gathering data, analyzing information, and developing a clear regulatory strategy based on these insights. These pillars guide the entire RI process. * **Strategic Value of RI:** RI is not merely compliance tracking; it is a strategic function that helps companies understand the current regulatory landscape, anticipate changes, and make informed decisions to advance their products and operations. It enables proactive rather than reactive engagement with regulations. * **Scope of RI:** The process of RI encompasses identifying diverse information sources, continuously monitoring the regulatory landscape, effectively using regulatory intelligence databases for research, and then summarizing, analyzing, integrating, and presenting the intelligence to relevant teams. * **RI as a Creative Role:** The speaker highlights RI as the "creative part of regulatory affairs," often underestimated or misinterpreted. It requires critical thinking and analytical skills to synthesize information into actionable strategies, rather than just reporting facts. * **What RI Is Not:** It's important to distinguish RI from competitive intelligence (which focuses on market and competitor strategies), proprietary sales or marketing data, drug pricing, or insurance/reimbursement information. RI specifically focuses on the regulatory implications and landscape. * **Example of RI Application:** A practical application involves gathering comprehensive information on competitor products (e.g., submission dates, labeling, clinical trials) and then generating a regulatory intelligence report with an executive summary that analyzes this data to inform a company's development and submission routes. * **Importance of Ongoing Monitoring:** Due to the "constantly changing regulatory environment," continuous monitoring and evaluation of the landscape are essential components of effective regulatory intelligence. This ensures strategies remain current and compliant. * **Structured Research Approach:** Conducting RI involves breaking down a regulatory research question into "researchable units" and then systematically using available databases and sources to gather the necessary information. Key Concepts: * **Regulatory Intelligence (RI):** The process of gathering, analyzing, and applying regulatory information to inform strategic decisions and shape future regulatory environments. * **Regulatory Information:** Raw, publicly available data, documents, and guidelines from regulatory bodies. * **Regulatory Landscape:** The current and evolving set of laws, regulations, directives, guidance documents, and policies governing an industry. * **Regulatory Strategy:** A plan developed based on regulatory intelligence to navigate the regulatory environment, achieve approvals, and maintain compliance. * **Executive Summary:** A concise overview of a regulatory intelligence report, highlighting key findings and strategic implications for decision-makers. Examples/Case Studies: * **Competitor Product Analysis:** The video uses the example of analyzing competitor products to illustrate the difference between information and intelligence. Gathering details like trade names, routes of administration, labeling, pivotal clinical trials, drug class, and submission/approval dates in various countries is regulatory information. Transforming this into an "executive summary" that reviews competitor products, the current regulatory landscape, and submission routes to guide a company's direction is regulatory intelligence.

Vertex Reduces EDC Study Build Times by 50%
Veeva Systems Inc
/@VeevaSystems
May 16, 2019
This video provides an in-depth exploration of how Vertex Pharmaceuticals significantly reduced its EDC (Electronic Data Capture) study build times and accelerated clinical data lock processes, achieving a 50% reduction in study build times. Featuring insights from Vertex's senior and associate directors of clinical data management and metrics, Vitas Galati and Michelle Garrison, alongside Richard Young from Veeva Systems, the discussion highlights Vertex's journey in optimizing clinical operations. The webinar contrasts Vertex's industry-leading performance against broader industry benchmarks, particularly referencing "Tufts data" on average timelines for data entry, query resolution, and database lock. The core of Vertex's success lies in a multi-faceted approach centered on a "sites first, patients first" philosophy. This ethos drives their operational strategies, emphasizing consistency in database creation, standardized query application, and continuous, open communication with clinical sites. Vertex actively engages sites through regular meetings, data management-specific tables at investigator meetings for live demos and feedback, and weekly newsletters for updates and training. This collaborative approach, coupled with a focus on understanding site motivations rather than imposing penalties, has led to exceptional site performance, with data entry often within 48 hours and query responses within 72 hours, significantly outperforming industry averages. A key conceptual shift discussed is the move from "database lock" to "data lock," recognizing that 70-80% of critical study data often originates from external sources outside the EDC system. Vertex prioritizes the reconciliation and locking of all relevant data, including external data, aiming for a complete, quality-assured data lock within 15 days from the last subject's last visit. This aggressive timeline is supported by proactive data review starting from the first patient screen, ensuring live data access for clinical and medical monitoring teams, and automating lab data downloads within 24 hours. The "onion slide" concept illustrates Vertex's layered, risk-based approach to data review, acknowledging that multiple checks occur at various stages, allowing for more focused attention on critical data points. The entire process requires strong organizational buy-in across clinical, medical, and vendor teams, with a culture of continuous innovation and improvement. Key Takeaways: * **Industry-Leading Performance:** Vertex achieved a 50% reduction in EDC study build times and consistently locks clinical data within 15 days, significantly faster than the industry average of 40 days. They also boast rapid data entry (within 48 hours) and query response (within 72 hours) from sites. * **Site-Centric Philosophy:** A "sites first, patients first" approach is paramount. Vertex fosters collaboration and understanding with sites, using a "carrot, not stick" method, avoiding penalty clauses, and focusing on consistent processes and clear communication to motivate high-quality data submission. * **Proactive Data Management:** Data review begins immediately from the first patient screen, not waiting for milestones. This ensures continuous monitoring and early identification of issues, allowing clinical and medical monitoring teams live access to data for real-time patient oversight. * **Emphasis on External Data:** Recognizing that 70-80% of primary and secondary endpoint data often comes from external sources (e.g., labs), Vertex redefines "database lock" to "data lock," focusing on comprehensive reconciliation and locking of all critical data, internal and external. * **Automated Data Acquisition:** Significant effort is invested in automating data downloads from primary labs, aiming to receive lab data within 24 hours of collection or report generation, drastically reducing data transfer times. * **Risk-Based Data Review:** The "onion slide" concept illustrates that data undergoes multiple layers of review (e.g., CCGs, error checks, CDM, cross-functional teams). This allows for a risk-based approach, dedicating more intensive review to critical data points while trusting the multi-layered system for general data quality. * **Organizational Buy-in is Crucial:** Achieving rapid data lock requires a coordinated effort and buy-in from the entire organization, including clinical, medical, and vendor teams, ensuring everyone is aligned with the quality and timeline goals. * **Strategic Vendor Management:** Vertex engages vendors early in the contracting process to establish expectations for timely and quality data transfers. They also explore consolidating vendors or routing specialty lab data through central labs to streamline data flow and reduce the number of interfaces. * **Continuous Improvement and Standardization:** Lessons learned from every study are applied to subsequent trials. Vertex emphasizes training, standardizing data transfer specifications, and reusing data collection standards to achieve greater efficiency and consistency. * **Innovation as a Cultural Imperative:** Vertex maintains a culture of innovation, constantly challenging internal processes and seeking better, faster ways to operate while maintaining quality, which was a key driver in their partnership with Veeva. **Tools/Resources Mentioned:** * **Veeva Systems:** The platform and software used by Vertex for their clinical data management, specifically EDC. * **Tufts Data:** Research on industry benchmarks for clinical trial timelines (data entry, query resolution, database lock). **Key Concepts:** * **EDC Study Build Times:** The time required to set up and configure an Electronic Data Capture system for a new clinical study. * **Data Lock / Database Lock:** The process of finalizing and freezing a clinical trial database or all relevant study data (including external sources) to prevent further changes before analysis and submission. Vertex advocates for "data lock" to encompass all critical data, not just what's in the EDC. * **Clinical Data Management (CDM):** The process of collecting, cleaning, and managing data from clinical trials to ensure its accuracy, completeness, and validity. * **Site-Centric Approach:** A philosophy in clinical trials that prioritizes the needs and experiences of the clinical research sites and their staff to foster better collaboration and data quality. * **Risk-Based Data Review:** A strategy for reviewing clinical trial data where resources and effort are concentrated on data points and processes deemed most critical to patient safety and study integrity, rather than uniformly reviewing all data. **Examples/Case Studies:** * **Vertex Pharmaceuticals:** The entire discussion serves as a case study of Vertex's successful implementation of advanced clinical data management strategies, showcasing their specific achievements in reducing study build times and accelerating data lock processes in their cystic fibrosis (CF) trials.
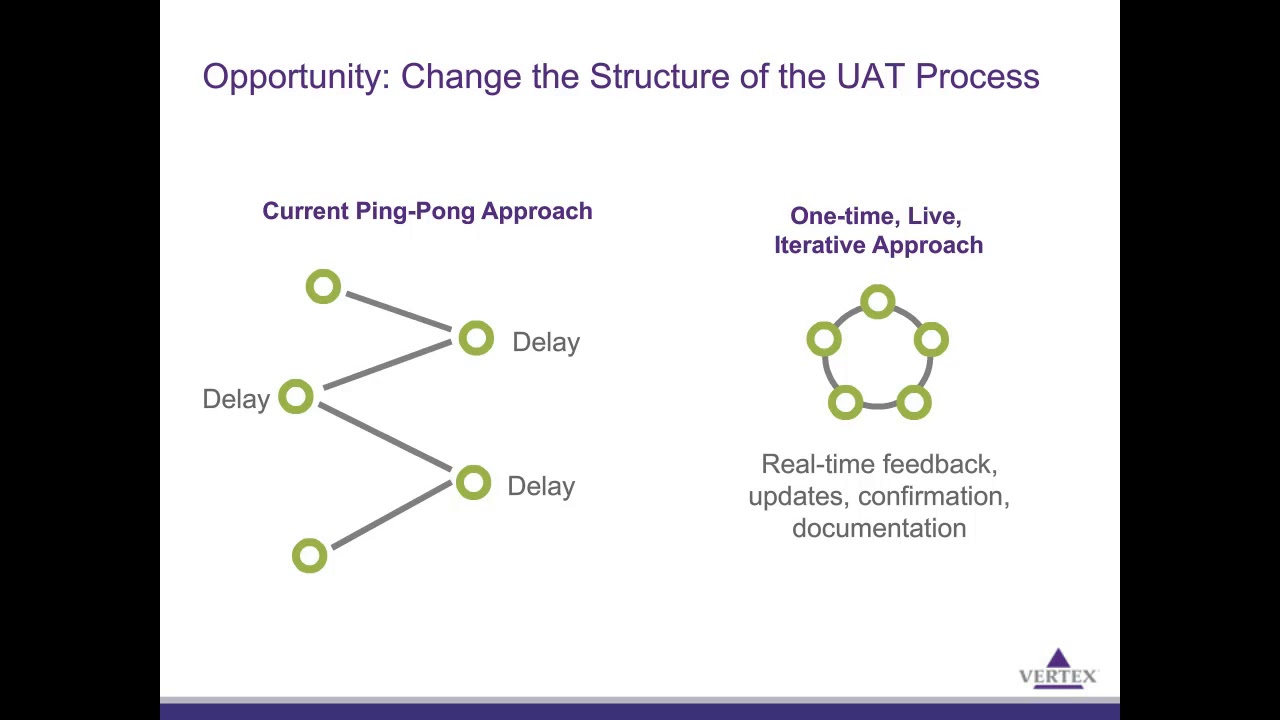
Vertex Takes a Risk-based Approach to UAT
Veeva Systems Inc
/@VeevaSystems
May 16, 2019
This video provides an in-depth exploration of how Vertex Pharmaceuticals successfully implemented a risk-based approach to User Acceptance Testing (UAT) for Electronic Data Capture (EDC) study builds, significantly reducing operational timelines and improving efficiency. The core premise challenges the traditional industry standard of performing 100% UAT on every study build, arguing that this practice often duplicates validation efforts already completed by developers and QA teams. The speakers advocate for a strategic shift where testing resources are concentrated only on high-risk, non-standard elements of a study. The methodology centers on standardization and leveraging vendor capabilities. Vertex focuses on building standard configuration settings and pages, testing them rigorously once, and then placing them into a reusable library. For subsequent studies that utilize these pre-validated, standardized components, re-testing is deemed unnecessary. Instead, UAT efforts are hyper-focused on the study’s primary and secondary endpoints, which carry the highest risk to data integrity and regulatory submission. A critical enabler of this approach is a "diff report" provided by Veeva, which generates a simple report detailing exactly what configuration changes have occurred between a current study and a previous, fully validated study. If the report indicates no changes, the team can justify avoiding 100% UAT. Beyond configuration testing, the discussion highlights major process improvements in how UAT is executed. The speakers critique the common "ping-pong" UAT approach—a sequential cycle where the vendor sends the database, the sponsor tests and provides comments, the vendor updates, and the process repeats—which often consumes four to five weeks. Vertex moved toward a "live UAT" roundtable model. In this accelerated approach, the vendor team (Veeva) sits concurrently with the sponsor’s UAT team. As the sponsor reviews and provides feedback or suggests edits, the software is updated and tested in real-time. This game-changing method allowed Vertex to compress what was typically three rounds of UAT into a timeframe as short as two days, drastically shortening the overall study build timeline by three to four weeks. The analysis also extends to optimizing the programming of error checks within the EDC system. While many clinical teams program 300 to 500 error checks per study, the speakers suggest that this volume often leads to excessive definition, programming, and UAT time, particularly for checks that rarely "fire." The strategic recommendation is to focus upfront on the 90% of checks that are most critical for data quality and regulatory adherence. The remaining 10%, especially those that are complex or low-firing, can be handled later by running data listings or utilizing other business intelligence tools for data review, saving significant cross-functional team time spent on initial definition and UAT. Finally, the speakers propose reframing change orders not as failures to be avoided, but as strategic opportunities. By holding off on implementing complicated checks until the first inevitable change order, teams can accelerate the initial go-live and strategically update the system as the study progresses. Key Takeaways: * **Adopt Risk-Based UAT:** Blindly performing 100% UAT on every study build is inefficient and redundant, especially when configuration settings have already been tested and validated in previous studies. * **Standardize and Reuse Configurations:** Build a library of standard configuration settings, pages, and components. Once these are tested and validated, they should be copied into subsequent studies without requiring re-testing, focusing UAT efforts only on novel or high-risk elements. * **Focus UAT on Endpoints:** Concentrate User Acceptance Testing on primary and secondary endpoints, as these represent the highest risk areas for data integrity and regulatory submission. * **Leverage Vendor Diff Reporting:** Utilize tools like Veeva’s diff report, which automatically identifies configuration changes between studies. If the report shows no change, it provides the justification needed to bypass full UAT. * **Eliminate "Ping-Pong" UAT:** Move away from the sequential, time-consuming UAT process (which can take 4-5 weeks) where feedback is exchanged asynchronously between sponsor and vendor. * **Implement "Live UAT" Sessions:** Conduct UAT as a real-time roundtable with both the sponsor's team and the vendor's development team present. This allows for immediate feedback incorporation and real-time testing, drastically shortening the UAT cycle (e.g., three rounds compressed into two days). * **Optimize Error Check Volume:** Clinical teams should critically review the necessity of having 300–500 error checks per study. Focus on programming the 90% of checks that are most essential for quality data capture. * **Shift Low-Risk Checks Post-EDC:** Complex or low-firing error checks (the remaining 10%) should be managed by running data listings or utilizing external data review and Business Intelligence tools post-data capture, rather than spending extensive upfront time programming and UAT-ing them within the EDC. * **Strategic Use of Change Orders:** View change orders as an opportunity rather than a hurdle. Strategically hold off on implementing complicated, non-critical checks until the first expected change order to accelerate the initial go-live timeline. * **Prioritize Quality over Quantity of Checks:** The goal is building a quality database, which can often be achieved with a focused set of critical checks, rather than maximizing the total number of programmed checks, which increases complexity and validation burden. Tools/Resources Mentioned: * **Veeva Systems:** The underlying platform vendor for the EDC system discussed. * **Veeva Diff Report:** A specific reporting tool that shows configuration changes between study builds, enabling risk-based testing decisions. * **EDC (Electronic Data Capture):** The system used for clinical trial data collection. Key Concepts: * **UAT (User Acceptance Testing):** The final stage of testing where end-users verify that the system meets business requirements before deployment. * **Risk-Based Approach:** A testing methodology that prioritizes validation efforts based on the potential impact or risk associated with specific system components or configurations. * **Ping-Pong UAT:** The traditional, sequential, back-and-forth process of UAT between a vendor and a sponsor, characterized by long cycle times. * **Live UAT:** A concurrent testing methodology where vendor and sponsor teams collaborate in real-time to review, update, and test the system immediately. * **Error Checks:** Automated rules programmed into the EDC system to ensure data quality and consistency during data entry.