Videos
Browse videos by topic
All Videos
Showing 1345-1368 of 1435 videos

The Evolution of Medical Affairs: A Changing Landscape
Veeva Systems Inc
@VeevaSystems
Jul 13, 2017
This podcast, presented by Robert Groebel, VP of Medical Strategy at Veeva Systems, initiates a series focused on the evolving role of Medical Affairs (MA) within the life sciences industry. The core purpose is to analyze the external and internal shifts impacting MA and to outline how organizations can leverage these changes to create a competitive advantage. Groebel establishes that the healthcare landscape is fundamentally changing, driven by shifts in quality care, patient outcomes, cost reduction, and enhanced patient experience. These external pressures are fueled by the emergence of new stakeholders, novel data sources, and an increased demand for deep, specific scientific information. Internally, the pharmaceutical pipeline is undergoing a massive transformation, moving away from chronic diseases toward highly targeted indications, particularly rare diseases. The video highlights that nearly 500 compounds currently under review are specific to the rare disease space, a significant shift from 10-15 years ago. This pipeline evolution places immense strategic demands on Medical Affairs, whose traditional function—disseminating data, building scientific relationships, and providing education—must now adapt to address complex information requests linked to highly targeted indications, all while considering patient access issues. The analysis underscores the growing strategic importance of MA, evidenced by substantial organizational growth and budget increases. MSL organizations, for example, saw a 300% increase in size by 2020. This growth contrasts sharply with the challenges faced by commercial teams, where nearly 50% of physicians place restrictions on commercial access. The video segments the drivers of change within MA into three key buckets: stakeholders, data, and scientific information. MA functions must now use quantifiable data to identify and engage different stakeholders in account-based models, becoming almost solely responsible for building long-term scientific relationships. Furthermore, MA must provide a single, consistent source of truth to the medical community, demonstrate performance impact through metrics, and ensure accurate reporting for compliance, especially in the context of Corporate Integrity Agreements. Ultimately, the goal is for MA to evolve from a required operational function to a truly differentiated strategic asset throughout the product lifecycle, linking people, process, strategy, technology, and metrics effectively. Key Takeaways: • **Fundamental Pipeline Shift:** The pharmaceutical industry is experiencing a fundamental shift in pipelines, moving heavily toward rare diseases and highly targeted indications, necessitating complex and specific scientific data dissemination by Medical Affairs. • **MA as a Strategic Differentiator:** Medical Affairs must evolve from being a required operational function to a strategic, differentiated asset that drives value throughout the product lifecycle, especially given the increasing restrictions placed on commercial access. • **Growth of MSL Organizations:** The size of MSL organizations saw a 300% increase by 2020, reflecting the growing reliance on scientific engagement channels, particularly as approximately 50% of physicians restrict commercial access. • **Data-Driven Stakeholder Identification:** MA teams must utilize quantifiable data sources to accurately identify and engage diverse stakeholders, moving toward account-based models and key account management partnerships. • **Single Source of Truth Requirement:** A critical responsibility for evolving MA functions is providing the medical community with a consistent, single source of scientific truth, requiring robust data integration and management systems. • **Compliance and Reporting Mandates:** Due to external pressures like Corporate Integrity Agreements (CIAs), MA functions require systems that enable accurate reporting on every external touchpoint, detailing who was engaged, why, and what information was shared. • **Managing Information Complexity:** The shift to rare diseases necessitates managing vast libraries of complex scientific information and delivering it accurately and aligned to the specific channel requested by the stakeholder (e.g., email, MSL direct contact, medical information call centers). • **Performance Measurement Necessity:** As MA budgets and responsibilities increase, organizations must implement performance measures and metrics to demonstrate the function's impact and value contribution to the larger business. • **Holistic MA Evolution:** Successful MA evolution requires integrating five core elements: people, process, strategy, technology, and metrics, ensuring they link together to provide accurate and strategic value. • **Evolving Stakeholder Landscape:** External changes are driven by an evolution of stakeholders, the emergence of new data sources, and an increased demand for better scientific information, all of which MA must address. Tools/Resources Mentioned: * Veeva Systems (Contextual platform of the speaker) * Medical Information Call Centers (Channel for information delivery) Key Concepts: * **Medical Affairs (MA):** The function responsible for disseminating scientific data, building scientific relationships, and educating healthcare professionals and stakeholders. * **Corporate Integrity Agreements (CIAs):** Agreements often mandated by government agencies (like the OIG) that require strict reporting and compliance measures, emphasizing the need for accurate tracking of external engagements. * **MSL (Medical Science Liaison):** Field-based professionals within MA responsible for building scientific relationships with key opinion leaders and disseminating complex scientific information. * **Account-Based Models:** Strategies where MA engages with entire healthcare accounts or systems rather than just individual physicians, requiring partnerships around key account management.

The Evolution of Medical Affairs: Stakeholder Engagement
Veeva Systems Inc
@VeevaSystems
Jul 13, 2017
This presentation, led by Robert Groebel, Vice President for Global Medical Strategy at Veeva Systems, focuses on the critical evolution of stakeholder engagement within the Medical Affairs function. The central thesis is that understanding the external landscape and the shifting influence of various groups is essential for creating a competitive advantage. Groebel emphasizes that Medical Affairs must move beyond traditional identification methods to accurately align its engagement strategies with the specific needs dictated by a product's life cycle and the current market dynamics. The discussion highlights a dramatic historical shift in influence within the pharmaceutical ecosystem. In the 1990s, the stakeholder landscape was relatively simple, centered on a triangle of influence: Healthcare Professionals (HCPs), Key Opinion Leaders (KOLs), and Regulators. Resources were primarily deployed to these three groups to ensure they were informed about drug development and that their viewpoints were understood. However, by the year 2000, the landscape expanded significantly with the advent of policy makers, payers, and patients. This shift was driven by the proliferation of direct-to-consumer advertising, the rise of the internet informing patients, and the growing influence of payer organizations demanding data on cost of care and health economics. Looking at the current and future landscape, the presentation stresses that these "new" stakeholders—payers, patient advocacy groups, and government bodies—have become even more influential and must be central to Medical Affairs strategy. As the primary delivery mechanism for scientific data and information, Medical Affairs teams must be prepared to address this highly evolved and diverse group of influencers. The core challenge is accurately identifying and building out this expanded stakeholder pool in a way that ensures a thorough understanding of the data and the disease state requirements. To meet this challenge, the methodology for stakeholder identification must fundamentally change. Historically, organizations relied on traditional methods such as clinical data, publications, academic affiliation, and internal word-of-mouth, which produced a homogeneous group of stakeholders relevant primarily to the 1990s model. Today, Medical Affairs must couple these traditional sources with advanced data streams. Groebel specifically calls for incorporating insights derived from social media, network connection analysis, and claims and referral data. This comprehensive approach is critical for building a complete understanding of all voices within the healthcare landscape, ensuring that Medical Affairs can address varying needs at different stages of the product life cycle. Key Takeaways: • **Stakeholder Alignment is Life Cycle Dependent:** Medical Affairs must align its engagement strategies with the specific stage of drug development. The types of advice needed and the corresponding stakeholders required for engagement change drastically as a product moves through its life cycle. • **The 1990s Influence Model is Obsolete:** The traditional focus on HCPs, KOLs, and Regulators as the primary influencers is no longer sufficient. This model resulted in a homogeneous stakeholder group that fails to capture the complexity of modern healthcare decision-making. • **The Rise of the Payer and Patient:** Since 2000, payers and patients have become critical influencers. Payers require data addressing cost of care and health economics, while informed patients, driven by consumer advertising and the internet, actively seek specific therapies. • **Government and Policy Influence is Growing:** Government bodies are increasingly demanding greater oversight and accountability regarding how pharmaceutical organizations bring drugs to market, necessitating proactive engagement from Medical Affairs. • **Medical Affairs Must Evolve as Data Deliverers:** Medical Affairs teams must be prepared to address a highly evolved group of stakeholders by acting as the primary, authoritative delivery mechanism for scientific and clinical data. • **Shift from Traditional to Data-Driven Identification:** Relying solely on publications, academic affiliations, and internal knowledge is insufficient. Modern stakeholder identification requires supplementing these sources with quantifiable, external data. • **Leverage Advanced Data Sources for Competitive Advantage:** To accurately build out the necessary stakeholder pool, organizations must integrate data from social media analysis, network connection mapping, and claims and referral data, moving beyond simple academic metrics. • **The Need for Comprehensive Landscape Understanding:** Utilizing advanced data integration allows Medical Affairs to gain a holistic understanding of all influential voices within the healthcare ecosystem, enabling targeted and timely engagement throughout the product life cycle. • **Optimizing Resource Deployment:** By accurately identifying the most influential stakeholders at any given time, Medical Affairs can strategically deploy resources to maximize impact and ensure that compounds and development plans are understood by those who matter most. Key Concepts: * **Stakeholder Evolution:** The shift in influential groups from a narrow focus (HCPs, KOLs, Regulators) to a broad ecosystem including policy makers, payers, and patients. * **Life Cycle Alignment:** The strategic necessity of tailoring stakeholder engagement based on the current stage of the drug's development (e.g., early development requires different advice than post-launch commercialization). * **Advanced Identification Methods:** The integration of non-traditional data sources (social media, network data, claims/referral data) with traditional sources (publications, clinical data) to create a comprehensive stakeholder map.

The Evolution of Medical Affairs: Considerations for the MSL
Veeva Systems Inc
@VeevaSystems
Jul 13, 2017
This video, presented by Robert Groebel, Vice President for Global Medical Strategy at Veeva Systems, provides an in-depth analysis of the evolving landscape of Medical Affairs and the critical considerations for the Medical Science Liaison (MSL) organization. The central theme is the drastic increase in the demand for complex medical information, driven primarily by the rapid evolution of pharmaceutical pipelines, particularly in specialized areas like rare diseases and Specialty Care. Groebel establishes that the need for deep, scientifically rigorous information is far greater today than even a few years ago, necessitating a shift in how MSLs operate and demonstrate their value. The presentation highlights that healthcare professionals (HCPs) are explicitly looking to Medical Affairs and the MSL organization to fulfill this growing information need. To meet this expectation, the MSL must provide a broad therapeutic knowledge base and deliver differentiated, comprehensive insights. Groebel references a 2013 survey by the Boston Consulting Group involving oncologists and hematologists, which indicated that their need for medical information from pharmaceutical companies was increasing due to the complexity of new interventions. Crucially, physicians view the MSL as a peer and seek true peer-to-peer interaction, demanding comprehensive responses that are not narrowly focused on a single intervention but cover a broad therapeutic area. A significant portion of the discussion focuses on the imperative for Medical Affairs to demonstrate quantifiable value, both to the external medical community and internally to the broader organization. This value is generated through developing a deep understanding of the disease state, engaging in external advice and consultation, and effectively translating that external intelligence into actionable opportunities for the larger pharmaceutical enterprise. Furthermore, MSLs are responsible for creating awareness of specific interventions through scientific support, education, CME, publications, and direct peer-to-peer engagement. The ultimate measure of success, Groebel argues, lies in the ability of Medical Affairs to communicate the impact of these efforts—specifically, whether they are successfully "closing the information need" and making it easier for HCPs to make informed choices about treatments. This shift requires MSLs to focus not just on activity, but on the measurable impact of every engagement. Key Takeaways: • The demand for complex medical information has grown drastically, primarily driven by the evolution of pharmaceutical pipelines focusing on highly specialized areas such as rare diseases and Specialty Care. • Healthcare professionals (HCPs) are increasingly turning to the Medical Science Liaison (MSL) organization as the preferred source for delivering complex, high-value scientific information. • The expectation for MSLs is to provide a broad therapeutic base of knowledge and deliver differentiated, comprehensive insights that span across the therapeutic area, moving beyond a narrow focus on a single intervention. • Physicians recognize the MSL as a peer and require authentic, open, peer-to-peer dialogue, underscoring the necessity for MSLs to maintain high scientific credibility and communication skills. • Medical Affairs must prioritize demonstrating quantifiable value, both externally to the medical community (by closing information gaps) and internally to the pharmaceutical organization (by providing actionable insights). • A critical function of Medical Affairs is translating external advice and consultation—gathered through MSL engagement—into strategic opportunities for the larger organization, influencing R&D, commercial, and clinical strategies. • Creating awareness of new interventions requires structured scientific support, including formalized education, Continuing Medical Education (CME), publications, and targeted peer-to-peer engagement. • The effectiveness of MSL efforts must be measured by their impact on closing the information gap and facilitating informed treatment choices for healthcare professionals, moving the focus from activity metrics to outcome metrics. • The role of Medical Affairs is evolving to be a strategic partner that helps create a competitive advantage by ensuring timely, accurate, and comprehensive scientific information reaches the necessary stakeholders. • The visibility and strategic importance of Medical Affairs continue to increase, requiring organizations to continuously evaluate and enhance the effectiveness and knowledge base of their MSL teams. Tools/Resources Mentioned: * **Veeva Systems:** The context of the presentation is set by the speaker's role at Veeva Systems, a key platform provider for pharmaceutical commercial and medical operations. * **Boston Consulting Group (BCG):** Reference is made to a 2013 BCG survey of oncologists and hematologists regarding their growing need for medical information from Pharma. Key Concepts: * **Medical Affairs:** The department responsible for communicating scientific and medical information to external stakeholders, ensuring appropriate use of products, and gathering external insights. * **MSL (Medical Science Liaison):** Field-based scientific experts who engage in peer-to-peer dialogue with key opinion leaders (KOLs) and HCPs. * **Differentiated Insights:** Information gathered or delivered by MSLs that provides unique, high-value perspectives not readily available through standard commercial channels or publications. * **Closing the Information Need:** A metric or goal for Medical Affairs, signifying the successful provision of necessary scientific data to HCPs, enabling them to make informed decisions and reducing knowledge gaps related to complex treatments.

Veeva Vault MedComms Demo
Veeva Systems Inc
/@VeevaSystems
Jul 13, 2017
This demonstration provides a focused overview of Veeva Vault MedComms, showcasing its capabilities for medical communication specialists within the pharmaceutical and life sciences industries. The application is designed to streamline the global coordination, management, and localization of critical medical content, such as FAQs, standard response documents, and medical letters. The presentation highlights features that enhance content discoverability, ensure version control, facilitate global-to-local content adaptation, and provide robust reporting for compliance and operational insights. The core functionality demonstrated centers on efficient content management and localization. Users can leverage a powerful, Google-like type-ahead search capability that scans both document properties and underlying content, significantly improving the speed of finding necessary information. This search is further refined using faceted filters, similar to those found on e-commerce or professional networking sites, allowing specialists to quickly narrow down results based on criteria like market (e.g., US market) or specific terms (e.g., diabetic). For content creation, the system promotes efficiency and compliance by allowing users to start new local documents directly from a globally approved "core" file. This process ensures that local market materials maintain traceability to the approved global source. A key feature is the seamless process for creating localized content while maintaining regulatory integrity. The demonstration illustrates how a globally approved core FAQ can be duplicated for a specific local market, such as Canada, using a simple "save as" function. Crucially, the system automatically carries along all necessary supporting documents (like associated Product Information or PIs) with the new local copy. This automatic linkage is vital for maintaining audit trails and ensuring that all market-specific materials are supported by the correct, approved regulatory documentation. Once the local copy is created, it follows the necessary market-specific review and approval workflows before being deployed for field use. The presentation concludes by highlighting the comprehensive reporting engine, which allows users to build simple yet powerful business reports based on document content and process data, crucial for operational oversight and compliance checks. Key Takeaways: • **Enhanced Content Discoverability:** Veeva Vault MedComms utilizes advanced search functionality, including Google-like type-ahead search and faceted filtering based on document properties and content, enabling medical communication specialists to rapidly locate specific documents needed for inquiries or content creation. • **Zero-Footprint Document Viewing:** The platform features an inline, zero-footprint browser for viewing documents, which improves user experience and accessibility, allowing specialists to review globally approved content (like core FAQs) without needing to download files or use external software. • **Globally Controlled Localization:** The system enforces compliance by facilitating the creation of local market copies directly from globally approved "core" documents, ensuring that all regional materials are derived from and traceable to the official source material. • **Automated Supporting Document Linkage:** When a local copy is created (e.g., a Canadian FAQ from a US core document), the system automatically carries along all associated supporting documents (such as PIs), which is critical for maintaining regulatory compliance and simplifying audit processes. • **Streamlined Review and Approval Workflows:** After localization, the new document is automatically routed through the necessary market-specific review and approval processes, ensuring that it meets local regulatory requirements before being deployed for use in the field. • **Comprehensive Reporting Engine:** Vault MedComms includes a robust, point-and-click query building interface that allows users to generate powerful business reports without requiring IT assistance, focusing on both content status and usage metrics. • **Expiration Tracking for Compliance:** The reporting engine supports the creation of critical expiration reports, which indicate when medical communication documents are approaching their expiration date, categorized by brand, ensuring proactive content lifecycle management and reducing compliance risk. • **Usage Metrics for Operational Insights:** Reports can track document usage, such as how many times a particular medical communication document has been utilized in response to a call center request, providing valuable data for assessing the effectiveness and necessity of specific content assets. Tools/Resources Mentioned: * **Veeva Vault MedComms:** The core application demonstrated, designed for managing medical communications content. * **Vault Library:** The central repository within Veeva Vault where documents are stored and managed. * **Inline Zero Footprint Browser:** The internal viewing tool used to display documents within the Vault interface. Key Concepts: * **Core FAQ:** A globally approved, foundational document that serves as the source material for localized versions across different markets. * **Medical Communication Documents:** Regulated content used by medical affairs teams, including standard response documents, medical letters, and frequently asked questions (FAQs), often used in interactions with healthcare professionals (HCPs). * **Faceted Filters:** A search refinement technique that allows users to narrow down results based on specific attributes (e.g., market, brand, document type), similar to filtering options on e-commerce websites. * **Supporting Documents (PIs):** Regulatory or clinical documents (like Product Information) that must be linked to and accompany medical communication materials to ensure accuracy and compliance.

The Evolution of Medical Affairs: Creating a Competitive Advantage
Veeva Systems Inc
@VeevaSystems
Jul 13, 2017
This video, presented by Robert Groebel, Vice President for Global Medical Strategies at Veeva Systems, explores the critical evolution of the Medical Affairs (MA) function and how it can transition from a supportive role to a source of competitive advantage within life sciences organizations. The central challenge facing modern MA teams is navigating complex stakeholder networks and delivering specialized scientific data throughout a drug's lifecycle, often hampered by technological fragmentation. Groebel posits that MA, due to its scientific expertise and peer-to-peer credibility, is uniquely positioned to solve these industry problems, provided it addresses its underlying technology debt. The core technological hurdle identified is the prevalence of multiple disconnected data sources across MA, involving various vendors and fragmented points of view. These systems are often not harmonized, limiting their long-term strategic value and incurring high maintenance costs. The speaker emphasizes that the path to competitive advantage lies in harmonizing these systems and data points to provide true strategic insights to the broader organization. This requires MA to shift its operating model from an "inside-out" approach (pushing information) to an "outside-in" approach (validating community needs and responding appropriately). Achieving strategic differentiation requires MA to focus on three key areas: metrics, partnering, and organizational mission. Metrics must evolve beyond simple activity tracking to include both qualitative and quantitative measures that align directly with broader organizational objectives. Furthermore, MA must improve internal partnering across the organization to drive collective effort, ensuring stakeholder engagement is tailored to the product lifecycle and existing data. Ultimately, the mission of MA should center on driving scientific credibility and coordinating efforts to maximize customer value. This transformation is enabled by bringing all information together, often in the cloud, and utilizing CRM systems, engagement tracking, and content management to place the healthcare professional (HCP) at the center of the conversation. By evolving strategically, MA can improve decision-making through better insights, track better engagements, and significantly increase productivity, moving the function toward strategic differentiation. Key Takeaways: • **Technology Fragmentation is the Primary Barrier:** Medical Affairs is currently challenged by multiple disconnected data sources, fragmented vendor ecosystems, and limited points of view, which prevents the generation of long-term strategic value and increases maintenance costs. • **Harmonization is Essential for Strategic Insight:** The critical technological step for MA is harmonizing disparate systems and data points to provide the larger organization with true strategic insights, moving beyond simple operational reporting. • **Shift from Inside-Out to Outside-In:** MA must adapt its strategy by shifting from driving information based on internal organizational needs (inside-out) to validating the information needs of the external community and providing responses aligned with individual channel preferences (outside-in). • **Metrics Must Be Strategic and Comprehensive:** Effective MA requires metrics that are both qualitative (measuring impact and credibility) and quantitative (measuring activity and reach), ensuring they ultimately align with the broader organizational objectives, not just departmental goals. • **Physician Centricity through Data:** The evolution involves placing the physician at the center of the conversation and effort, which is achieved by leveraging data captured through CRM systems, engagement tracking, event management, and content sharing. • **Continuous Evaluation of Needs:** Engagement strategies and informational needs must be constantly evaluated over time, as both the data and the stakeholder requirements will inevitably shift throughout the product lifecycle. • **Organizational Alignment Drives Value:** MA must actively partner with other organizational functions to drive a collective effort forward, ensuring that the mission—driving scientific credibility—is coordinated across the enterprise to maximize customer value. • **Competitive Advantage through Differentiation:** The ultimate goal of MA evolution is to create a competitive advantage by improving decisions through better insights, tracking better engagements, developing scientific credibility, and increasing functional productivity. • **Leveraging CRM Systems:** CRM systems are explicitly mentioned as a core technology for capturing engagement data and tracking the development of events and interactions with physicians, forming the backbone of the data strategy. Tools/Resources Mentioned: * **CRM Systems:** Used for capturing engagement data, tracking interactions, and developing events with physicians. * **Cloud Technology:** Recommended as the environment for bringing all disparate MA data and information together for harmonization. Key Concepts: * **Outside-In Strategy:** An approach where the organization prioritizes understanding and responding to the validated needs and preferences of external stakeholders (e.g., healthcare professionals) rather than simply pushing internal information outward. * **Scientific Credibility:** The core mission and value proposition of Medical Affairs, which must be maintained and coordinated across the entire organization to drive customer value. * **Strategic Differentiation:** The outcome of the MA evolution, where the function moves beyond operational support to become a source of unique competitive advantage and strategic insight for the overall life sciences company.

Collaborating with Partners in Vault QualityDocs at Karyopharm Therapeutics
Veeva Systems Inc
/@VeevaSystems
Jul 13, 2017
This video provides an in-depth exploration of how Karyopharm Therapeutics, through its associate director of QC, Maria Conklin, leverages Veeva Vault QualityDocs to manage compliant collaboration with external partners, a critical component of their externalized business model. The primary objective is to streamline the secure exchange of GxP (Good Practices) documents, ensuring efficiency and maintaining regulatory integrity throughout the manufacturing and development lifecycle. The speaker emphasizes that externalization significantly impacts quality, necessitating a robust, controlled platform for document management that moves beyond traditional, insecure methods like email and shared drives. The core functionality discussed centers on enabling vendors to upload documents directly into the Veeva Vault platform. This approach addresses several pain points inherent in traditional external collaboration. Firstly, it dramatically improves security, as documents reside securely within the Veeva environment, and vendor access is strictly limited to the necessary scope. Secondly, it enhances efficiency by creating a single source of truth, eliminating the need to search across disparate locations (emails, shared drives). This centralized system ensures that all parties are working with the most current, controlled version of any document. The types of content being managed are strictly GMP documents essential for pharmaceutical manufacturing and development. These include executed batch records, master batch records, data protocols, stability reports, method specifications, and various other reports. A significant benefit highlighted is the time savings associated with document retrieval; what previously took 20 minutes of searching across various internal and external sources now takes approximately two minutes, with the added assurance that the retrieved document is the correct, official version. Furthermore, the platform facilitates smoother internal communication and document flow. The final key benefit discussed is the strategic advantage of having a unified platform between QualityDocs and Regulatory Information Management (RIM). This integration eliminates content duplication and allows regulatory submissions to point directly to the controlled quality documents within the Vault, simplifying the submission process significantly. Key Takeaways: • **Strategic Externalization Requires Controlled Platforms:** For pharmaceutical companies relying on external partners (CROs, contract labs) for manufacturing and development, using a regulated platform like Vault QualityDocs is essential to maintain quality and compliance, as externalization directly impacts GxP processes. • **Security and Access Control are Paramount:** Direct vendor upload capabilities within a secure platform like Veeva ensure that sensitive GxP documents are protected, limiting vendor access only to the content they are authorized to see, thereby mitigating risks associated with email or unsecured file sharing. • **Significant Efficiency Gains in Document Retrieval:** The transition from decentralized storage (shared drives, emails) to a centralized Vault system reduces the time required to locate the correct, most recent version of a document from approximately 20 minutes to just two minutes, freeing up valuable QC and operational staff time. • **Single Source of Truth for GxP Content:** Centralizing documents like executed batch records, master batch records, stability reports, and specifications ensures that both internal teams and external partners are always referencing the official, controlled version, which is critical for audit readiness and compliance. • **Elimination of Content Duplication via RIM Integration:** A major operational advantage is the unification of QualityDocs with the company’s RIM system; this allows regulatory submissions to directly reference the controlled quality documents, avoiding the costly and risky process of duplicating content for submission packages. • **Improved Internal and External Collaboration Flow:** Utilizing the built-in communication and workflow features within the Veeva platform facilitates smoother document review and approval processes, reducing friction and delays typically associated with external communication methods. • **Focus on Manufacturing and Development Documentation:** The platform is specifically used to manage high-stakes, regulated content necessary for product lifecycle management, confirming its role as a mission-critical system for operational quality control. • **Compliance Assurance Through Version Control:** Knowing that the retrieved document is definitively the "correct version" provides essential compliance assurance, especially when dealing with audit trails and regulatory inspections where version history is scrutinized. Tools/Resources Mentioned: * Veeva Vault QualityDocs * Veeva Vault RIM (Regulatory Information Management) Key Concepts: * **Externalization:** The business model of relying on third-party vendors (e.g., contract labs, CMOs) for core functions like manufacturing and development, necessitating robust systems for quality oversight. * **GMP Documents:** Good Manufacturing Practice documents, which include critical records like executed batch records, master batch records, and standard operating procedures, all requiring strict version control and security. * **Unified Platform:** The strategic benefit of integrating systems (like QualityDocs and RIM) within the same ecosystem (Veeva Vault) to ensure data integrity, eliminate redundancy, and streamline cross-functional processes, particularly regulatory submissions. Examples/Case Studies: * **Karyopharm Therapeutics:** The company serves as the case study, demonstrating the successful implementation of Vault QualityDocs to manage collaboration with external partners involved in manufacturing and development, highlighting the operational necessity of secure, compliant document exchange.

Vault QualityOne Animated Explainer Video
Veeva Systems Inc
/@VeevaSystems
Jul 13, 2017
This video provides an animated explanation of Vault QualityOne, a unified Quality Management System (QMS) developed by Veeva Systems, designed to address the fragmentation and inefficiency common in legacy quality control processes within the pharmaceutical and life sciences industries. The presentation establishes the critical need for a modern QMS by illustrating a common failure scenario: a supplier deviation that goes undetected until the product reaches quality control, leading to line stoppage, extensive communication requirements, and significant operational disruption. The core message is that Vault QualityOne offers a single, complete, and easy-to-use system to manage quality processes across all stakeholders, including external suppliers. Vault QualityOne is positioned as a solution that eliminates the time wasted toggling between disparate, unconnected systems. It provides a unified quality management and document control application accessible securely from anywhere in the world. A key emphasis is placed on user experience, noting that the application is as intuitive to use as consumer platforms like Amazon or Google, thereby mitigating the confusion and resistance often associated with complex enterprise software. This ease of use facilitates quick document retrieval, real-time revisions, and seamless collaboration among internal teams and external partners. The system is built upon industry best practices, standardizing and managing critical GxP quality processes across the enterprise. These processes include CAPA (Corrective and Preventive Actions) management, internal and external audits, comprehensive supplier quality management, and complaint handling. The platform utilizes real-time dashboards to display the current status of all quality processes, with integrated hyperlinks connecting users directly to the latest approved versions of associated quality documents, ensuring immediate data integrity and visibility. Crucially, Vault QualityOne is designed to be highly adaptable, contrasting sharply with outdated legacy software that struggles to keep pace with evolving regulatory demands. The platform features robust security controls that allow organizations to specify granular capabilities and visibility for every individual, whether they are internal employees or external partners, ensuring that users only see and engage with authorized content. The video addresses the challenge of migrating to a new system by highlighting Veeva’s implementation experts, who partner with clients to understand their current document control and quality management processes, tailoring the new system to the company’s unique needs. The ultimate promise is a reduction in the total cost of quality while simultaneously saving time and maintaining stringent regulatory compliance. Key Takeaways: • **Unified Quality Management:** Vault QualityOne integrates quality process management (e.g., CAPA, audits) and document control into a single application, eliminating the inefficiencies and risks associated with fragmented, unconnected legacy systems. • **Supply Chain Integration:** The system extends quality management capabilities to external stakeholders, specifically suppliers, allowing for comprehensive management of supplier quality and ensuring that deviations are detected and addressed earlier in the production lifecycle. • **Focus on User Experience (UX):** By designing the application to be as easy to use as consumer platforms (like Amazon or Google), the system aims to increase user adoption, reduce training overhead, and minimize errors caused by complex, painful-to-use enterprise software. • **Real-Time Visibility:** Dashboards provide immediate, real-time status updates on all active quality processes, offering quality managers and executives actionable insights and preventing quality issues from escalating undetected. • **Standardized GxP Processes:** The platform standardizes and manages core regulatory processes, including CAPA management, audit management, complaint handling, and supplier quality management, ensuring consistency across the organization. • **Regulatory Adaptability:** Unlike rigid legacy systems, Vault QualityOne is designed to quickly adapt to meet evolving regulatory demands (e.g., FDA, EMA, 21 CFR Part 11 requirements), which is critical for maintaining continuous compliance in the life sciences sector. • **Granular Security and Control:** Robust security controls allow companies to precisely define the visibility and capabilities for every user, including internal staff and external partners, maintaining strict control over sensitive quality content and audit trails. • **Implementation Partnership:** Veeva provides dedicated implementation experts who work closely with clients to understand existing document control and quality management workflows, ensuring the new system is tailored to the company’s specific departmental needs for a smoother migration. • **Business Value Proposition:** The primary measurable benefits of adopting QualityOne are lowering the total cost of quality, saving operational time, and ensuring robust, demonstrable regulatory compliance. Tools/Resources Mentioned: * Vault QualityOne (Veeva Systems) * Veeva Systems Inc (Channel/Developer) Key Concepts: * **Vault QualityOne:** A specific, unified Quality Management System (QMS) application developed by Veeva Systems for the life sciences industry, integrating document control and quality process management. * **CAPA Management:** Corrective and Preventive Actions management, a critical GxP process for investigating and resolving quality issues to prevent recurrence. * **Supplier Quality Management:** The process of ensuring that materials and services provided by external vendors meet the required specifications and quality standards. * **Document Control:** The management of quality-related documents (SOPs, specifications, batch records) to ensure they are current, approved, and accessible only to authorized personnel. * **Regulatory Compliance:** The adherence to industry regulations (e.g., FDA, EMA), which Vault QualityOne supports by providing robust audit trails and adaptable features.

Gaining Transparency with Remote Audits at ICON plc
Veeva Systems Inc
@VeevaSystems
Jul 13, 2017
This video provides an in-depth look at how ICON plc, a major contract research organization (CRO), leveraged Veeva Vault QualityDocs to revolutionize its document control procedures, enhance audit transparency, and improve operational efficiency. The speaker, a document control associate at ICON, details the implementation process for controlling procedures, templates, and forms, emphasizing the immediate extension of system access to external stakeholders, including clients (sponsors) and subcontractors. This strategic move was designed to facilitate remote audits, eliminating the need for clients to travel to ICON offices, thereby generating significant cost savings for sponsors while maintaining high standards of quality and compliance. The central theme revolves around achieving a higher level of quality through radical transparency and accessibility. By granting clients 24/7 remote access to their procedures, ICON provides continuous visibility into their operational standards—a level of service that clients now expect. This accessibility is crucial for audit readiness, as the system allows sponsors and clients to review essential documentation, such as Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs), templates, and forms, well in advance of scheduled study audits. This proactive approach ensures that all parties are aligned and prepared, significantly streamlining the audit process and reducing friction. Furthermore, the implementation of QualityDocs directly addressed critical pain points experienced with ICON’s previous document management system. The primary challenges in the legacy system were poor search functionality and cumbersome reporting capabilities. With the new Veeva platform, the document control department has seen a marked decrease in complaints because employees can now locate documents much more easily. The reporting functionality has also been dramatically improved, allowing employees to generate and pull necessary reports independently, without requiring constant assistance from the document control department. The transition to Veeva Vault QualityDocs represents a strategic shift toward self-service and decentralized information access within a regulated environment. This not only optimizes the internal workflow for the document control team but also empowers internal users and external clients alike. The ability for non-document control personnel to run their own reports enhances business intelligence and operational agility, demonstrating the platform’s value beyond simple document storage to become a true tool for quality management and audit facilitation. Key Takeaways: * **Facilitating Remote Audits for Cost Savings:** ICON successfully implemented Veeva Vault QualityDocs to enable clients and subcontractors to perform audits off-site, eliminating travel requirements and resulting in substantial cost savings for the sponsoring organizations. * **Achieving 24/7 Transparency:** Providing clients with continuous, round-the-clock remote access to procedures, templates, and forms establishes a high level of operational transparency, which is now considered a key expectation from major CROs like ICON. * **Enhancing Audit Readiness:** The system improves audit readiness by allowing sponsors and clients direct access to critical SOPs and documentation *prior* to study audits, ensuring familiarity and preparation, which is a significant operational advantage. * **Overcoming Legacy System Limitations:** The new system directly resolved major challenges associated with the previous document control platform, specifically addressing poor search functionality and inadequate reporting capabilities. * **Improving Internal Efficiency via Search:** The enhanced search functionality within QualityDocs has led to fewer complaints and allows employees to find necessary documents more quickly and efficiently, streamlining internal workflows. * **Empowering Self-Service Reporting:** The improved reporting functionality allows employees to generate and pull customized reports independently, reducing reliance on the document control department and freeing up specialized staff for higher-value tasks. * **Strategic Value of QualityDocs:** The platform is positioned not just as a document repository but as a tool that provides a higher level of quality assurance and service delivery to clients in the highly regulated life sciences sector. * **Broad Access for Stakeholders:** The system was strategically rolled out to grant access not only to internal employees but also to clients and subcontractors who are off-site, highlighting the necessity of integrated access across the regulated ecosystem. Tools/Resources Mentioned: * **Veeva Vault QualityDocs:** The specific platform used by ICON plc for managing controlled documents, procedures, templates, and forms, central to audit readiness and quality management. Key Concepts: * **Remote Audits:** The practice of conducting regulatory or quality audits without the auditors needing to be physically present at the audited organization’s site, enabled by secure, remote access to controlled documentation. * **Document Control:** The systematic management of documents within a regulated environment, ensuring that all procedures, forms, and templates are current, accurate, approved, and readily accessible to authorized personnel. * **Audit Readiness:** The state of preparedness an organization maintains to successfully undergo regulatory or quality audits, often achieved through proactive organization and accessible documentation. Examples/Case Studies: * **ICON plc Implementation:** The video serves as a case study detailing how ICON plc, a major CRO, implemented Veeva Vault QualityDocs to manage its controlled documentation (procedures, templates, forms) and extend access to external clients and subcontractors to facilitate remote auditing.
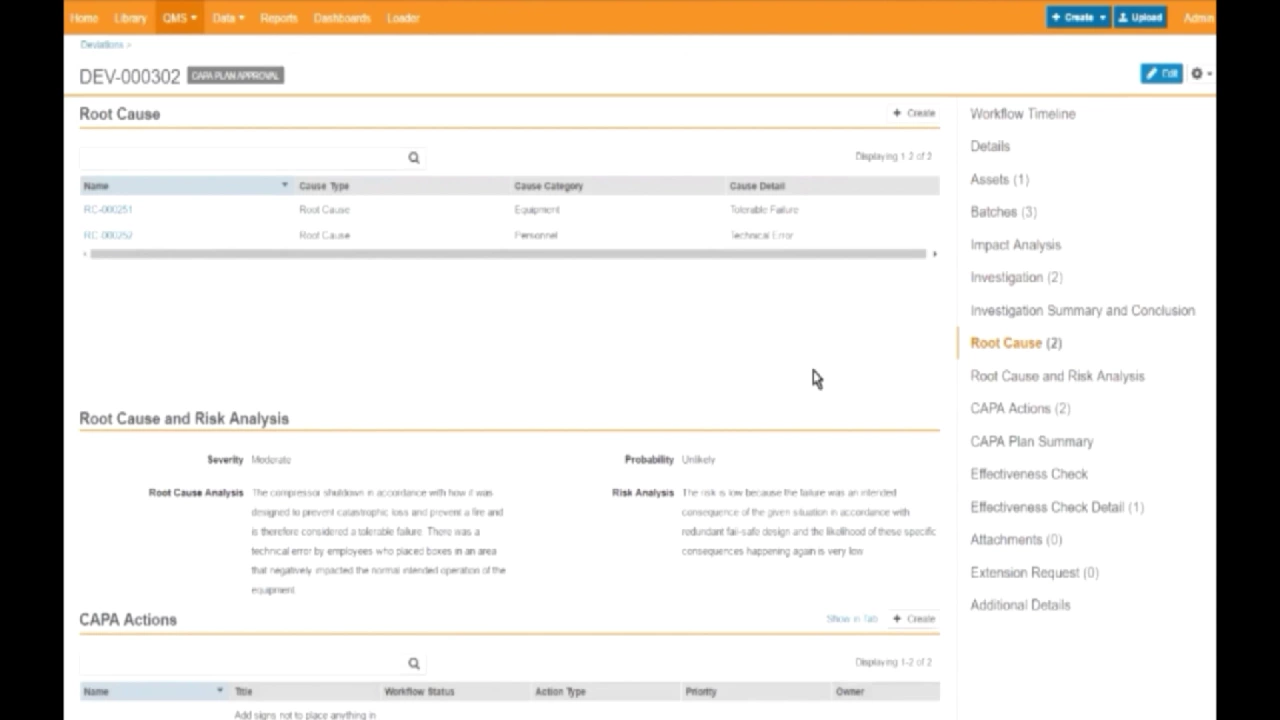
Veeva Vault QMS
Veeva Systems Inc
/@VeevaSystems
Jul 12, 2017
This video provides an in-depth demonstration of Veeva Vault QMS, showcasing its capabilities for managing quality processes within a regulated environment. The presentation begins by illustrating the system's dashboard functionalities, which offer immediate visibility into critical quality metrics such as deviations by department and CAPAs by category, quickly highlighting overdue items. The core of the demonstration revolves around a specific deviation event, guiding the viewer through the entire lifecycle from initial identification to final approval of corrective actions, emphasizing the system's integrated approach to quality management. The demonstration meticulously details the process of investigating a deviation, using the example of a refrigeration unit failure at a warehouse. It highlights how Vault QMS integrates document management by linking directly to relevant Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) for temperature monitoring and equipment information. The system facilitates comprehensive investigations, allowing for the attachment of evidence like internal temperature charts and stability testing data, and the identification of root causes, such as equipment failure and personnel error. This structured approach ensures thorough analysis and documentation, crucial for regulatory compliance. Furthermore, the video illustrates the seamless transition from root cause analysis to the development and implementation of Corrective and Preventive Actions (CAPAs). It shows how CAPAs, such as adding signs to prevent vent blockages and replacing equipment, are documented and linked to change control processes. This integration ensures that any necessary physical changes to equipment or updates to critical documents, like the equipment validation master plan, are systematically managed through their respective life cycles within the Vault platform. The demonstration concludes with the final approval of the CAPA plan, utilizing electronic signatures, underscoring the system's ability to maintain a complete and compliant audit trail for all quality events. Key Takeaways: * **Integrated Quality Management System:** Veeva Vault QMS provides a centralized platform for managing a wide array of quality processes, including deviations, CAPAs, change control, audits, and complaints, offering a holistic view of an organization's quality posture. * **Dashboard-Driven Insights:** The system features intuitive dashboards that offer real-time visibility into key quality metrics, enabling users to quickly identify trends, monitor performance, and prioritize overdue tasks, enhancing proactive quality management. * **Efficient Drill-Down Capabilities:** Users can easily navigate from high-level dashboard visualizations to detailed reports and individual records with just a few clicks, facilitating rapid investigation and resolution of quality events. * **Comprehensive Deviation Management:** The platform supports a structured workflow for managing deviations, from initial reporting and investigation to root cause analysis, CAPA planning, and final approval, ensuring all steps are documented and traceable. * **Seamless Document Integration:** Vault QMS integrates directly with document management functionalities, allowing for easy linking of quality events to relevant SOPs, equipment specifications, and validation master plans, ensuring all supporting documentation is readily accessible. * **Robust Investigation Tools:** The system supports detailed investigations by allowing the attachment of various forms of evidence, such as charts, data logs, and images, which are critical for thorough root cause analysis and informed decision-making. * **Structured Root Cause Analysis:** It facilitates the identification and documentation of multiple root causes, categorizing them (e.g., equipment-related, personnel error), and linking them directly to specific CAPAs for targeted remediation. * **Automated CAPA and Change Control Workflows:** CAPAs are systematically defined, assigned owners, and linked to automated workflows. The system also integrates with change control processes, ensuring that equipment modifications or document updates stemming from CAPAs are managed compliantly through their full lifecycle. * **Ensuring Regulatory Compliance:** The platform supports critical compliance requirements through features like electronic signatures for approvals, comprehensive audit trails, and the systematic management of quality processes, aligning with GxP and 21 CFR Part 11 standards. * **Asset Management and Trending:** By linking deviations to specific equipment assets, Vault QMS enables organizations to trend which pieces of equipment are prone to issues, supporting predictive maintenance and continuous improvement initiatives. * **Product Impact Assessment:** The system facilitates the assessment of product impact during quality events, such as placing affected batches on hold and conducting additional stability testing, to verify product quality and safety before release. * **Full Event History and Traceability:** From the initial event to the final actions and approvals, the system maintains a complete and traceable history, providing an end-to-end audit trail essential for regulatory scrutiny and internal quality assurance. Tools/Resources Mentioned: * **Veeva Vault QMS:** A quality management system designed for life sciences companies. Key Concepts: * **Deviation:** A departure from a standard or specification. * **CAPA (Corrective and Preventive Action):** Actions taken to eliminate the cause of a detected nonconformity or other undesirable situation (corrective action) and to prevent recurrence (preventive action). * **Change Control:** A formal process used to ensure that changes to products, processes, or systems are introduced in a controlled and coordinated manner. * **Root Cause Analysis:** A systematic process for identifying the underlying causes of problems or incidents. * **Electronic Signature:** A method of signing a document or record digitally, often used in regulated industries to ensure authenticity and integrity, compliant with regulations like 21 CFR Part 11. * **SOP (Standard Operating Procedure):** A set of step-by-step instructions compiled by an organization to help workers carry out routine operations. * **Validation Master Plan:** A high-level document outlining the validation strategy for a system, process, or equipment, ensuring it consistently produces a product or result meeting predetermined specifications. Examples/Case Studies: * **Refrigeration Unit Failure:** A detailed example of a deviation caused by a refrigeration unit failure at a Philadelphia warehouse, leading to a possible temperature excursion. This scenario triggers investigations into the cause of failure (boxes blocking air intake) and the condition of the product (internal temperature monitoring, stability testing). It culminates in CAPAs such as adding signs, creating exclusion zones, and replacing the compressor, along with an associated change control to update the equipment validation master plan.

What Makes Veeva Vault Unique in Life Sciences?
Veeva Systems Inc
/@VeevaSystems
Jul 12, 2017
This video provides an in-depth exploration of Veeva Vault, highlighting its unique attributes as a cloud-based regulated content management system specifically engineered for the life sciences industry. The speaker emphasizes that Veeva Vault's ground-up design for this sector is its core differentiator, allowing it to embed life sciences-specific requirements from the outset. This includes critical regulatory compliance considerations such as 21 CFR Part 11, Annex 11, and GxP-related requirements, which are fundamental to pharmaceutical and biotech operations. The presentation details Veeva Vault's robust platform, which is built for scalability and incorporates all expected core document management capabilities. These include sophisticated features like document types, attributes, life cycles, workflow management, and comprehensive security protocols. A key innovation highlighted is that Veeva is the first single software company to develop both the foundational platform for life sciences content management and a suite of best-of-breed applications that seamlessly integrate on top of it. This integrated approach ensures consistency and efficiency across various business functions. The applications built on the Veeva Vault platform address content-intensive areas across the entire life sciences value chain. In the clinical space, this includes electronic Trial Master File (eTMF) and investigator portals. For R&D, it supports regulatory submissions. Quality and manufacturing operations benefit from management of SOPs, batch records, and specifications. Even the commercial side of the business is covered, with applications for promotional materials management and medical affairs-related documentation, including standard written and verbal responses. Furthermore, the video underscores two significant differentiators that set Veeva Vault apart: its pre-validated status and its true cloud-based, multi-tenant Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) model. Veeva conducts the Installation Qualification (IQ) and Operational Qualification (OQ) for each software release, engaging a third party for the overall validation, delivering the software to customers in a Production Qualification (PQ) ready state. This dramatically reduces the validation burden for clients. The multi-tenant SaaS architecture offers distinct benefits, such as seamless and rapid upgrades, with significant new functionalities introduced across applications three times a year, eliminating the traditional 18 to 24-month upgrade cycles associated with legacy systems. Key Takeaways: * **Industry-Specific Design:** Veeva Vault is uniquely built from the ground up for the life sciences industry, embedding specific requirements like 21 CFR Part 11, Annex 11, and GxP compliance directly into its architecture. This ensures inherent regulatory adherence rather than bolted-on features. * **Robust and Scalable Platform:** The system offers a highly scalable and robust core platform with comprehensive document management capabilities, including custom document types, attributes, life cycles, workflow automation, and advanced security, essential for managing sensitive regulated content. * **Integrated Platform and Applications:** Veeva's unique value proposition lies in being the first single vendor to develop both the foundational content management platform and a full suite of best-of-breed applications that sit on top, ensuring seamless integration and a unified user experience across diverse functions. * **Comprehensive Functional Coverage:** Veeva Vault applications span critical content-intensive areas across the life sciences business, including clinical operations (eTMF, investigator portal), R&D (regulatory submissions), quality and manufacturing (SOPs, batch records), and commercial operations (promotional materials, medical affairs documentation). * **Reduced Validation Burden:** A significant benefit is Veeva's pre-validation process, where they conduct IQ, OQ, and third-party validation for each release, delivering the software in a Production Qualification (PQ) ready state. This substantially reduces the time, cost, and effort clients typically expend on system validation. * **Seamless and Frequent Upgrades:** As a true cloud-based, multi-tenant SaaS solution, Veeva Vault provides seamless and rapid upgrades. New functionalities are introduced across applications three times a year without requiring lengthy, disruptive upgrade cycles, ensuring users always have access to the latest features. * **Elimination of Legacy Upgrade Challenges:** The multi-tenant SaaS model eradicates the traditional 18 to 24-month upgrade sequences common with on-premise or older software versions, allowing organizations to stay current with minimal operational disruption. * **Enhanced Inspection Readiness:** For clinical operations, Veeva Vault eTMF enables active TMF management, which is crucial for real-time inspection readiness, providing continuous visibility and control over trial documentation. * **Optimized Commercial Operations:** The platform supports efficient management of promotional materials and medical affairs documentation, streamlining content review, approval, and distribution processes while maintaining compliance. * **Strategic Advantage for Compliance:** By providing a regulated content management system that is inherently compliant and pre-validated, Veeva Vault offers a strategic advantage for life sciences companies aiming to optimize operations while rigorously adhering to regulatory standards. Tools/Resources Mentioned: * Veeva Vault * Veeva Vault eTMF Key Concepts: * **Regulated Content Management System (RCMS):** A system designed to manage electronic documents and content in industries subject to strict regulatory oversight, ensuring compliance with regulations like 21 CFR Part 11. * **21 CFR Part 11:** A regulation from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) that sets forth criteria under which electronic records and electronic signatures are considered trustworthy, reliable, and equivalent to paper records and handwritten signatures. * **Annex 11:** An EU guideline on computerized systems in the context of Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP), similar in scope to 21 CFR Part 11, focusing on the validation and management of computerized systems used in regulated environments. * **GxP:** A general term for "Good Practice" quality guidelines and regulations, including Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP), Good Clinical Practice (GCP), Good Laboratory Practice (GLP), etc., which are designed to ensure the quality, safety, and efficacy of products in the life sciences. * **eTMF (electronic Trial Master File):** An electronic system used to manage and store essential clinical trial documents, ensuring they are readily available for inspection and audit. * **IQ (Installation Qualification):** Documented verification that the equipment or system has been installed according to the manufacturer's specifications. * **OQ (Operational Qualification):** Documented verification that the equipment or system operates according to its operational specifications within the established limits. * **PQ (Production Qualification):** Documented verification that the equipment or system performs consistently and reliably under actual production conditions. * **Multi-tenant SaaS (Software-as-a-Service):** A cloud computing model where a single instance of software runs on a server and serves multiple tenants (customers). This allows for shared infrastructure and resources, enabling seamless updates and lower costs.

How Veeva Vault Facilitates Information Sharing Across the Value Chain
Veeva Systems Inc
/@VeevaSystems
Jul 12, 2017
The video provides an in-depth exploration of how the Veeva Vault suite of products is architected to solve the pervasive problem of information silos within the life sciences value chain. The core vision articulated is to move away from disparate, siloed systems—often separated by functional areas like clinical, regulatory, and manufacturing—toward a unified platform that facilitates seamless content management and sharing. The speaker emphasizes that while business processes inherently dictate that information must be shared across departments, traditional systems have made this difficult, leading to significant pain points from both a process and data integrity perspective. Vault is specifically designed to manage the flow of regulated content from early development through commercialization. A primary example is the integration between clinical documentation and regulatory submissions. Information managed within applications like Vault eTMF (Electronic Trial Master File) and the Investigator Portal, which focus on clinical documentation, is automatically prepared to be "submission ready." This ensures that the data required for compiling critical documents, such as the Clinical Study Report (CSR), can flow directly into the eCTD (Electronic Common Technical Document) for submission to global health authorities. This application-to-application sharing within the Vault environment streamlines the complex process of compiling regulatory dossiers. The integration extends critically into quality, manufacturing, and commercial operations. Quality and manufacturing data, particularly the Chemical Manufacturing Control (CMC) information, must be easily accessible to populate Module 3 of the eCTD. Furthermore, the platform links foundational R&D data to commercial activities. Promotional materials and the claims they contain must be supported by robust clinical study results. By allowing organizations to leverage the original clinical studies as the supporting documents for promotional claims, Vault ensures a direct, auditable link between commercial content and the underlying scientific evidence. This unified architecture establishes a crucial "single source of the truth." This principle means there is one document, eliminating version confusion and the creation of multiple copies, which can then be leveraged in multiple contexts and reported on consistently. This is particularly vital for managing foundational documents like Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs). An SOP might govern investigator execution in a clinical trial, manufacturing processes, and even how sales representatives execute tasks in the field. By centralizing the SOP within Vault, the system provides necessary visibility into how that document is being used across the entire value chain, preventing unintended consequences when updates are made. Key Takeaways: • **Addressing Siloed Systems:** The primary architectural goal of Veeva Vault is to dismantle the historical silos that separate content management in Clinical, Regulatory, and Manufacturing, which traditionally impede necessary cross-functional business processes. • **Seamless Data Flow for Submissions:** Vault ensures that clinical documentation, particularly data within the eTMF, is inherently "submission ready," facilitating its direct transfer and compilation into regulatory documents like the Clinical Study Report (CSR) and the final eCTD (Electronic Common Technical Document). • **Mandatory Quality Integration:** Regulatory submissions require information originating from quality and manufacturing systems, specifically for the Chemical Manufacturing Control (CMC) section (Module 3 of the eCTD), necessitating seamless data sharing between these operational areas. • **Commercial Compliance Linkage:** The platform provides a mechanism to directly link promotional materials and their associated claims back to the supporting clinical study results, establishing an auditable and compliant foundation for commercial content. • **The Single Source of Truth Principle:** Centralizing content management eliminates version confusion and the proliferation of unauthorized copies, ensuring that one authoritative document can be leveraged consistently across multiple functional areas for both operational use and reporting. • **Enhanced SOP Governance:** Central management of documents like SOPs provides critical visibility into their usage across the entire enterprise—from clinical trial execution to manufacturing and commercial sales tasks—mitigating risks associated with updates made in isolation. • **Consistent Reporting:** By utilizing a single source of truth, organizations can ensure that reporting and business intelligence derived from core documents are consistent, accurate, and defensible across all departments. • **Architectural Necessity:** The system is designed to meet the complex information sharing requirements dictated by the life sciences business process, rather than forcing the business process to conform to the limitations of siloed technology. Tools/Resources Mentioned: * Veeva Vault * Veeva Vault eTMF * Investigator Portal Key Concepts: * **eTMF (Electronic Trial Master File):** A collection of essential documents that individually and collectively permit the evaluation of the conduct of a clinical trial and the quality of the data produced. * **eCTD (Electronic Common Technical Document):** A standardized format for submitting applications, amendments, supplements, and reports to regulatory authorities (like the FDA and EMA). * **Submission Ready:** Content that has been prepared, organized, and formatted according to regulatory standards, ready for inclusion in a formal submission dossier. * **Single Source of the Truth:** A data management concept where all data elements are stored in one place, ensuring consistency, accuracy, and integrity across the organization. * **Value Chain:** The entire sequence of activities or parties that contribute to the development, manufacturing, and commercialization of a product (e.g., Clinical, Regulatory, Manufacturing, Commercial). Examples/Case Studies: * **Clinical to Regulatory Flow:** Information from clinical documentation (eTMF) flows into the Clinical Study Report (CSR), which is then incorporated into the eCTD for global health authority submission. * **Quality Data Integration:** Quality and manufacturing data (CMC information) is transferred into Module 3 of the eCTD submission. * **SOP Management:** A single SOP is used simultaneously to govern clinical investigator execution, manufacturing processes, and sales representative tasks on the commercial side.

Strengthening the Supply Chain at Atrium Innovations
Veeva Systems Inc
/@VeevaSystems
Jul 12, 2017
This video provides an in-depth look at Atrium Innovations' strategic initiative to strengthen its global supply chain and quality management processes, emphasizing the critical role of regulated enterprise software in achieving harmonization and control. The speaker, James Huang, focuses on the necessity of extending quality oversight beyond the company's internal operations ("four walls") to encompass third-party manufacturers and suppliers. This expansion is crucial because Atrium outsources significant product manufacturing, requiring robust systems to qualify these external partners, manage product quality, and ensure consistent compliance across the entire value chain. The core of Atrium's strategy revolves around implementing a centralized Quality Management System (QMS) and Change Management System (CMS) globally across 14 different sites. A key component of this implementation is the use of Veeva QualityDocs (referred to as "Quala Doc" in the transcript) to serve as the single source of truth for managing quality documents and GxP records. This system provides the necessary authority control over all documentation, ensuring that all internal and external parties are operating under the correct, approved procedures. The goal is not just document control, but creating a unified, integrated approach to quality that involves all parties—internal sites and external suppliers—in the quality lifecycle. A significant challenge highlighted by the speaker is the transition from managing static quality information to tracking events and actions at a granular level. While QualityDocs effectively manages documents, Atrium is moving toward a comprehensive CMS that can handle dynamic processes like change control, linking specific tasks to individual executors, and following the entire life cycle of an event (e.g., a product defect or a system change) through to its conclusion. This shift creates a more integrated and accountable framework where defects lead directly to the creation of corrective and preventive actions (CAPAs) and change controls, ensuring that issues are resolved systematically and documented thoroughly. Ultimately, the implementation of this integrated technology platform is designed to harmonize disparate business processes across the global organization and its supplier network. By bringing all parties into a single system for managing quality events and changes, Atrium can clearly solve problems collaboratively. The technology provides the opportunity to standardize workflows, ensuring that whether a change originates internally or with a third-party manufacturer, the process for qualification, defect resolution, and overall quality improvement follows a consistent, auditable path, thereby strengthening the quality of the supply chain as a whole. Key Takeaways: • **Extending Quality Oversight:** Companies relying on outsourced manufacturing must integrate third-party suppliers into their internal quality systems to maintain control and compliance, moving beyond their own "four walls" to improve quality across the entire supply chain. • **Centralized GxP Record Management:** Utilizing a system like Veeva QualityDocs is essential for managing quality documents and GxP records as a single source of truth, providing necessary authority control over all critical documentation globally. • **Global System Implementation:** Quality and compliance systems must be implemented globally—Atrium is deploying its QMS/CMS across 14 different sites—to ensure harmonization of processes and standardized operations worldwide. • **Shift to Event-Level Tracking:** Effective QMS requires moving beyond static information management to tracking dynamic events and actions, such as change controls, CAPAs, and defect resolution, throughout their entire lifecycle. • **Integrated Change Management:** A robust CMS must be able to tightly link tasks to specific individuals responsible for execution, allowing for clear status checks and ensuring accountability for resolving quality issues or implementing changes. • **Supplier Qualification and Defect Management:** The QMS must support the full supplier lifecycle, including initial qualification, receiving product, identifying defects, and systematically creating CAPAs and change controls to resolve those issues. • **Harmonizing Business Processes:** Technology serves as a crucial enabler for harmonizing different business processes (BPs) across various global sites and external partners, ensuring consistency in how quality events are handled and documented. • **Collaborative Problem Solving:** A unified CMS ensures that when changes are made or problems arise, all relevant parties—both internal sites and external suppliers—are involved in the project, leading to clearer and more effective resolution. • **Auditable Life Cycle Follow-Through:** The system must facilitate the ability to follow an event (e.g., a defect or change control) from its inception to its conclusion, creating a complete and auditable record of the resolution process. Tools/Resources Mentioned: * **Veeva QualityDocs (Quala Doc):** Used for managing quality documents and GxP records, serving as the single source of augmentation and authority control for documentation. * **CMS (Change Management System):** The system used to manage change control, link tasks, and track the life cycle of quality events. Key Concepts: * **GxP Records:** Good Practices records, referring to documentation required to demonstrate compliance with regulatory standards (e.g., Good Manufacturing Practices). * **CAPA (Corrective and Preventive Action):** A process used to investigate and resolve product or process defects, ensuring that the root cause is addressed and recurrence is prevented. * **Change Control:** A formal process used to manage changes to regulated systems, processes, or products, ensuring that all changes are documented, reviewed, and approved before implementation. * **Saponification Module:** A specific reference to a manufacturing or quality operation process (likely related to chemical or ingredient processing) that requires qualification and quality control.

Data extraction from SmPCs into structured data for ISO IDMP compliance
Asphalion
/@Asphalion.
Jul 10, 2017
This video provides an in-depth exploration of automated data extraction from Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPCs) into structured data, primarily to address the complex requirements of ISO IDMP (Identification of Medicinal Products) compliance. The presentation, featuring experts from Asphalion and Unterpharma, highlights the inefficiencies of manual data handling, particularly in light of past xEVMPD (Extended EudraVigilance Medicinal Product Dictionary) implementations, and introduces a technological solution to streamline this critical regulatory process. The core message emphasizes that while ISO IDMP implementation faces delays, its strategic importance for the pharmaceutical industry remains paramount, necessitating a shift towards structured data management. The discussion begins by setting the stage for the challenge of ISO IDMP, which demands extensive data collection from traditionally unstructured documents like SmPCs. Jan Voskuil from TechniQ/Unterpharma introduces their "extractor" tool, built on semantic technologies and linked data, designed to innovate information flow in the pharma domain. This tool is presented as a flagship product within a larger suite that includes vocabulary management and text verification, aiming to transform text fragments into structured, annotated data. Remco Romijn from Asphalion then provides a live demonstration of the extractor, showcasing its ability to process SmPCs in multiple languages (Dutch, Spanish, English), automatically identify and extract key data elements such as product names, strengths, dosage forms, ATC codes, registration numbers, indications, and adverse effects. The demo highlights the tool's intuitive web-based interface for user verification and editing, as well as its capability to export structured data in various formats like Excel, CSV, and XML. A significant portion of the webinar focuses on the integration of this extracted data into a Regulatory Information Management (RIM) solution, specifically Exchido's mpd manager. This integration aims to establish a central product database for managing regulatory activities, generating reports, and tracking acknowledgments in a GxP-compliant environment. The vision extends to the future generation of electronic SmPCs (eSmPCs) and Patient Information Leaflets (ePILs) from this structured data, promising faster updates and direct patient communication, thereby optimizing current slow, paper-based processes. The presentation concludes with an update on the EMA's ISO IDMP status, acknowledging delays due to Brexit and organizational challenges but reaffirming the project's budget allocation and strategic necessity. It urges the industry to view IDMP as an opportunity for optimization and to prepare for this "marathon" by adopting advanced data extraction technologies. Key Takeaways: * **ISO IDMP is a Strategic Imperative:** Despite implementation delays, ISO IDMP remains a critical regulatory standard for the pharmaceutical industry, requiring a fundamental shift towards structured data management for medicinal products. It is a long-term "marathon" that demands proactive preparation. * **Manual Data Extraction is Inefficient:** Past experiences with xEVMPD demonstrated that manual data extraction from SmPCs is highly time-consuming, prone to errors, and leads to data inconsistencies across various internal systems, with many companies still relying on Excel as a primary "RIM solution." * **Automated Extraction Drastically Improves Efficiency:** Tools like Unterpharma's "extractor" can automate the process of converting unstructured SmPC text into structured data, reducing extraction time from hours to minutes or even seconds, significantly enhancing efficiency and accuracy. * **Multi-Language and Intelligent Processing:** The demonstrated tool supports data extraction from documents in multiple languages (e.g., Dutch, Spanish, English) and uses semantic technologies to intelligently identify and categorize data elements like invented names, strengths, dosage forms, and ATC codes. * **User-Friendly Verification and Editing:** The web-based interface allows users to easily verify, edit, and confirm extracted data, providing a semi-automated verification process that reduces manual effort while maintaining data quality. * **Integration with RIM Solutions is Key:** The structured data extracted can be seamlessly exported (e.g., to Excel, CSV, XML) and imported into Regulatory Information Management (RIM) systems like Exchido's mpd manager, creating a central product database for comprehensive regulatory activities and GxP-compliant tracking. * **Vision for Electronic Labeling:** The ultimate goal is to leverage structured data to generate electronic SmPCs and Patient Information Leaflets (ePILs/eSmPCs), enabling rapid updates of critical product information and direct, real-time notification to patients, thereby optimizing current slow processes. * **xEVMPD Remains Relevant:** Due to IDMP delays, xEVMPD will remain mandatory for at least another 3-5 years, underscoring the ongoing need for robust data management solutions for existing regulatory requirements. * **Beyond SmPCs:** While the focus is on SmPCs, the underlying technology is adaptable for extracting data from other unstructured documents, such as Patient Information Leaflets and Model 3 documents, offering broader applications for data comparison and regulatory compliance. * **Opportunity for Industry Optimization:** IDMP should be viewed as an opportunity to achieve a "single source of truth" for product information, streamline regulatory processes, and enhance overall operational efficiency, rather than solely as a compliance burden. * **Preparedness is Crucial:** Companies need to assess their current data processes, IT infrastructure, and organizational readiness for IDMP, including establishing specific objectives, providing training, and staying updated on regulatory developments. * **Advanced Data Classification:** The tool can also extract and classify adverse effects from SmPCs, including their frequencies, demonstrating its capability to handle complex and nuanced data elements beyond basic product characteristics. **Tools/Resources Mentioned:** * **Unterpharma's "extractor":** A flagship tool for automated data extraction from SmPCs. * **TechniQ:** Consultancy and parent company of Unterpharma, specializing in linked data and semantic technologies. * **Asphalion:** International regulatory and scientific consultancy, partner in the webinar. * **Exchido:** German software provider, specifically their "mpd manager" product database for RIM solutions. * **Rockabiary Connect:** Unterpharma's platform for managing controlled vocabularies. * **Text Verification Tool:** Used for cross-checks in the larger data management picture. * **EMA (European Medicines Agency):** Regulatory authority mentioned in the context of IDMP and xEVMPD. * **FDA (US Food and Drug Administration):** US regulatory authority, mentioned in relation to SPL (Structured Product Labeling) and IDMP. * **SPL (Structured Product Labeling):** FDA's standard for product labeling, mentioned as a structured data source in the US. **Key Concepts:** * **ISO IDMP (Identification of Medicinal Products):** A set of international standards for the unique identification and structured data management of medicinal products, crucial for global regulatory harmonization. * **SmPC (Summary of Product Characteristics):** A comprehensive document providing essential information about a medicinal product, primarily for healthcare professionals. * **xEVMPD (Extended EudraVigilance Medicinal Product Dictionary):** The EMA's system for collecting and managing data on authorized medicinal products, a precursor to IDMP. * **Linked Data:** A method of publishing structured data on the web so that it can be interlinked with other data, making it more useful through semantic queries. * **Semantic Technologies:** Technologies that enable machines to understand the meaning (semantics) of data, facilitating more intelligent data processing and interpretation. * **RIM (Regulatory Information Management) Solution:** Software systems used by pharmaceutical companies to manage and track regulatory submissions, product registrations, and compliance data throughout the product lifecycle. * **eSmPC/ePIL (Electronic SmPC/Patient Information Leaflet):** The future vision for digital, structured versions of these documents, designed for faster updates, easier access, and direct patient communication. **Examples/Case Studies:** * **Live Demo of SmPC Extraction:** The webinar included a live demonstration of the "extractor" tool processing SmPCs in Dutch, Spanish, and English. * **Specific Data Elements:** Examples of extracted data included product names (e.g., "Asphalina 10 milligram"), strengths, dosage forms (e.g., "capsule heart"), ATC codes, registration numbers, indications, and adverse effects. * **xEVMPD Manual Pain Points:** The speakers referenced the challenges faced by companies during xEVMPD implementation, where significant manual effort was required to copy-paste data from SmPCs into Excel or other basic systems. * **Integration with Exchido's mpd manager:** The concept of exporting structured data from the extraction tool and importing it into Exchido's mpd manager was presented as a solution for centralized product data management and regulatory activities.

Meet Veeva
Veeva Systems Inc
/@VeevaSystems
Jun 28, 2017
This video provides an internal perspective on the corporate culture, strategic focus, and operational philosophy of Veeva Systems, the leading cloud software provider for the global life sciences industry. Through employee testimonials, the video establishes the company's identity as a highly passionate, customer-centric organization that is actively defining the marketplace it serves. The overarching message is that Veeva is a special place to work due to its people, its mission, and its unique organizational structure that prioritizes speed and autonomy. A core theme explored is Veeva’s strategic role in the life sciences ecosystem. Employees express pride in working for a company that is "building the industry cloud for life sciences," suggesting a long-term vision and market dominance that provides stability and purpose. This sense of mission is coupled with a strong ethical foundation, highlighted by mentions of approachable executives who maintain the highest integrity. Crucially, the company’s management is noted for understanding the direct correlation between the success of its people—both the product users and the internal development teams—and overall customer success. This focus reinforces a holistic approach to service delivery and product development. The most critical operational insight revealed is the emphasis on autonomy and speed. Employees describe a culture that actively avoids the bureaucracy often associated with large companies. Autonomy is cited as a core value, enabling individual product groups to operate like independent startups. This means teams are empowered to hire their own personnel, define their own processes, and select their own tools and software, completely independently of other product groups. This decentralized model is explicitly framed as the mechanism for achieving exceptional speed, which employees identify as the defining characteristic of the company’s culture. This operational structure allows teams to execute faster by utilizing methodologies and tools they are most comfortable with, minimizing friction and maximizing efficiency across the organization. The overall tone is one of intense dedication and collaboration. Testimonials repeatedly describe the internal environment as one of strong relationships, passion, and a sense of "family." The challenging nature of the work is acknowledged, but the inherent interest in the projects and the constant drive toward speed and innovation make the daily work invigorating. This insight into Veeva’s internal dynamics is essential for any partner or consulting firm seeking to integrate deeply within their ecosystem, emphasizing the need for high-integrity, agile, and relationship-focused engagement. Key Takeaways: * **Market Definition and Longevity:** Veeva views its mission as "building the industry cloud for life sciences," positioning itself as the foundational software layer for the sector. This confirms the stability and long-term strategic importance of the Veeva platform for consulting firms like IntuitionLabs.ai. * **Customer Success Mandate:** The company maintains a number one focus on customer success, driven by high-integrity leadership. Consulting services must align with this mandate, ensuring that all AI and software solutions demonstrably contribute to the client's success metrics within the Veeva environment. * **Decentralized Autonomy:** Veeva grants significant operational autonomy to its individual product groups, allowing them to independently define processes, tools, and software stacks. This necessitates that consulting firms be highly adaptable, capable of integrating custom AI and data solutions into diverse, non-standardized technical environments across different Veeva product implementations. * **Speed as a Core Value:** Speed is identified as the defining characteristic of Veeva’s culture, actively preserved through decentralized operations. Consulting partners must adopt agile methodologies and focus on rapid deployment cycles to match the pace of innovation expected by Veeva and its clients. * **People-Centric Success Model:** Veeva management understands that customer success is directly dependent on the success of the people—both the users of the product and the internal development teams. This validates the value of AI solutions aimed at enhancing user experience, such as Generative AI Sales Ops Assistants, by directly improving the success of pharmaceutical commercial teams. * **Low Bureaucracy Environment:** Despite being a large company, Veeva minimizes bureaucracy by leveraging autonomy, which reduces legacy constraints. This creates a favorable environment for introducing innovative, custom software and LLM solutions without being bogged down by rigid corporate approval structures. * **High Passion and Integrity:** The culture is characterized by high passion and integrity among employees and executives. Successful partnership requires aligning with these values, emphasizing ethical AI deployment and transparent consulting practices. * **Focus on Challenging Work:** Employees find the work itself challenging and interesting, suggesting that Veeva attracts and retains high-caliber talent. Consulting engagements should focus on solving complex, high-value problems that leverage advanced capabilities like LLMs and data engineering. Key Concepts: * **Industry Cloud for Life Sciences:** The strategic vision of Veeva Systems to provide a comprehensive, integrated suite of cloud software specifically tailored to the regulatory and operational needs of the pharmaceutical and biotech sectors. * **Autonomy as a Core Value:** A decentralized operational model where individual product teams function independently, selecting their own tools and processes to maximize speed and efficiency, contrasting with traditional large corporate structures.

Veeva Vault QualityOne
Romain Marcel
/@romainmarcel1185
Jun 6, 2017
This video provides an in-depth exploration of Veeva Vault QualityOne, a unified, cloud-based solution designed to integrate Quality Management Systems (QMS) and Document Control within a single application. The presentation positions QualityOne as a necessary replacement for fragmented, outdated legacy software, which often leads to costly quality issues and compliance risks due to disconnected processes and poor stakeholder communication. The central purpose is to demonstrate how a single system can manage quality processes across all stakeholders, including critical external partners like suppliers, securely and efficiently. The video begins by illustrating a common pain point in regulated manufacturing: a supplier deviation that goes undetected until the product reaches quality control, forcing a line stoppage and creating a chaotic cascade of communication across departments and external parties. This scenario establishes the high impact of quality issues and the failure of existing, siloed systems. QualityOne is then introduced as the solution, promising to stop the time wasted toggling between unconnected systems. The platform is highlighted for its consistent, consumer-grade user experience, described as being as easy to use as Amazon or Google, which is crucial for maximizing user adoption and minimizing confusion often associated with complex enterprise applications. Vault QualityOne builds in best practices for a comprehensive suite of quality processes. These functionalities include Nonconformance and Investigation, Complaint Management, CAPA Management, Change Control, Audit Management, Supplier Quality Management, and Document Training Management. The system ensures real-time visibility through dynamic dashboards that display the current status of all quality processes and provide immediate hyperlinks to the latest, controlled versions of quality documents. Furthermore, the platform is designed to adapt to meet diverse and evolving regulatory demands, a critical feature for the life sciences sector. It employs robust security controls, allowing organizations to precisely specify the capabilities and visibility granted to each user, whether internal staff or external partners, thereby maintaining strict control over sensitive quality content and compliance requirements. The video concludes by addressing the significant hurdle of migration, assuring potential clients that implementation experts partner with them to understand current processes and tailor the new system to their unique needs, ultimately promising a reduction in the total cost of quality while enhancing compliance and saving time. Key Takeaways: • **Unified QMS and Document Control:** Vault QualityOne integrates the Quality Management System and Document Control into a single application, eliminating the need for users to switch between disparate systems and ensuring that quality processes are consistently managed alongside their associated documentation. • **End-to-End Stakeholder Management:** The platform extends quality process management beyond internal teams to include external stakeholders, such as suppliers, which is essential for proactive detection and management of deviations and nonconformances across the entire supply chain. • **Enhanced User Adoption through UX:** A core value proposition is the platform’s simple, intuitive user experience, designed to mimic consumer applications, which helps overcome resistance to new enterprise software and reduces the likelihood of errors caused by complex interfaces. • **Real-Time Process Visibility:** The system provides dynamic dashboards that offer real-time status updates on all active quality processes (e.g., CAPA, audits), with direct hyperlinks to the most current, controlled versions of supporting quality documents for immediate access and action. • **Comprehensive Quality Modules:** QualityOne incorporates built-in best practices for managing the full lifecycle of quality events, including critical processes such as Nonconformance and Investigation, Complaint Management, Change Control, and Supplier Quality Management. • **Regulatory Flexibility and Security:** The system is engineered to adapt quickly to changing regulatory landscapes and features robust security controls that allow organizations to define granular access permissions, ensuring that compliance is maintained while collaborating securely with partners. • **Cloud-Native Architecture:** As a pure cloud solution, QualityOne facilitates easy and secure access for all global stakeholders, simplifying collaboration and ensuring data integrity and availability across diverse operating environments. • **Mitigating Migration Risk:** Veeva offers specialized implementation expertise to guide companies through the transition, taking time to understand existing document control and quality management processes to ensure the new system is properly tailored to the organization's specific operational and regulatory needs. • **Focus on Total Cost of Quality:** The implementation of a unified system is positioned as a strategic move to lower the overall cost of quality by saving time, reducing manual effort, streamlining audit trails, and ensuring continuous regulatory adherence. Tools/Resources Mentioned: * Veeva Vault QualityOne (QMS and Document Control platform) Key Concepts: * **QMS (Quality Management System):** A centralized system for documenting and managing quality processes, procedures, and responsibilities. * **Document Control:** The systematic management of quality-related documents, including their creation, review, approval, version control, and archival, ensuring only the latest, approved versions are in use. * **CAPA Management (Corrective and Preventive Action):** The process of identifying the root cause of quality issues (corrective) and implementing measures to prevent their recurrence or future occurrence (preventive). * **Nonconformance and Investigation:** The process initiated when a product or process deviates from specifications, requiring formal documentation and investigation to determine the impact and necessary resolution.

Veeva Systems CEO: Chasing the Cloud | Mad Money | CNBC
CNBC
/@CNBC
Jun 2, 2017
This video provides an in-depth exploration of Veeva Systems' strategic position and growth within the cloud computing landscape, specifically tailored for the pharmaceutical, biotech, and life sciences industries. Jim Cramer interviews Peter Gastner, co-founder and COO of Veeva Systems, to discuss the company's recent financial performance, its unique market approach, and future prospects. The conversation highlights how Veeva has successfully carved out a niche by bringing the benefits of cloud computing to highly specialized industry applications, a strategy that Gastner asserts is both innovative and highly effective. The discussion delves into Veeva's comprehensive suite of cloud-based software solutions, which address critical operational needs across the life sciences value chain. These applications range from enhancing the effectiveness of pharmaceutical sales representatives and streamlining data capture for clinical trials to ensuring robust compliance with government regulations. Gastner emphasizes that despite the competitive nature of the cloud market, Veeva's differentiated strategy of deep industry specificity allows it to be a strategic partner for its customers, including major players like Pfizer and Novartis, as well as smaller, emerging biotechs. A significant portion of the interview addresses the macro trend of cloud computing, with Gastner agreeing with other tech leaders that the industry is still in its "early days" and will continue to expand over the next two to three decades. He counters skepticism about Veeva's total addressable market (TAM), stating that the life sciences market alone represents a $7 billion opportunity, which Veeva continuously expands by introducing new products. Gastner also cites Gartner's analysis, which identifies industry-specific applications as the largest and fastest-growing segment of cloud computing, a $132 billion market that is twice the size of ERP and CRM combined. This reinforces Veeva's long-term growth potential and its resilience against broader economic or regulatory shifts. The video also touches upon Veeva's financial strength, noting its consistent delivery of "30/30 quarters," characterized by over 30% revenue growth and 30% profit. This robust performance is attributed to the company's extensive product portfolio and its ability to serve as a strategic, long-term partner to its diverse customer base. The interview concludes with a strong endorsement of Veeva's momentum and earnings growth, positioning it as a leading example of a successful cloud company in a specialized market. Key Takeaways: * Veeva Systems has successfully implemented a differentiated strategy by focusing exclusively on providing cloud-based software for the pharmaceutical, biotech, and life sciences industries, distinguishing itself from broader cloud competitors. * The company's product offerings are comprehensive, designed to optimize various critical functions within life sciences, including improving pharmaceutical sales force effectiveness, accelerating clinical trials through efficient data capture, and ensuring adherence to government regulations. * Veeva's "Vault regulatory information management" is highlighted as a key solution, assisting major pharmaceutical companies like Merck in automating regulatory processes required for product registration and compliance. * Cloud computing is presented as a long-term, macro-level trend still in its nascent stages, with significant growth expected over the next 20-30 years, underscoring the enduring market opportunity for specialized cloud solutions. * Veeva serves as a strategic partner to a wide range of clients, from large pharmaceutical enterprises such as Pfizer and Novartis to smaller, emerging biotechs, by offering a complete and integrated suite of products. * New biotechs commercializing their first products often opt for a full suite of Veeva products from inception, bypassing legacy client-server systems to leverage integrated solutions and achieve faster time-to-market. * Concerns regarding potential deregulation impacting Veeva's regulatory compliance software are dismissed, as the company operates globally and supports customer innovation and effectiveness irrespective of specific policy changes. * The total addressable market (TAM) for Veeva within the life sciences sector is substantial, estimated at $7 billion, and the company actively expands this market by continuously introducing new applications, with 8 of its 24 products launched in the past year. * According to Gartner, industry-specific applications constitute the largest and fastest-growing segment of cloud computing, representing a $132 billion market that grew 10% last year, making it twice the size of the combined ERP and CRM markets. * Veeva demonstrates strong financial performance, consistently achieving "30/30 quarters" (over 30% growth in both revenue and profit), a testament to its extensive product portfolio and strategic customer relationships. * The video underscores the market's appreciation for companies with strong momentum and consistent earnings growth, positioning Veeva as a prime example of a successful, specialized cloud provider. * Veeva's success validates the power of a targeted, industry-specific strategy combined with continuous innovation, proving that a focused approach can lead to significant market leadership and expansion within a niche. Tools/Resources Mentioned: * Veeva CRM * Veeva Vault regulatory information management * Gartner (for market analysis) Key Concepts: * **Cloud Computing:** The delivery of on-demand computing services—including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence—over the Internet ("the cloud"). * **Industry-Specific Applications:** Software solutions designed and tailored to meet the unique needs and regulatory requirements of a particular industry, such as pharmaceutical and life sciences. * **TAM Expanders:** Companies that not only capture existing market share but also expand the total addressable market by introducing new products or services that create new demand. * **30/30 Quarter:** A term used to describe a company's financial quarter where both revenue growth and profit growth exceed 30%, indicating strong performance and profitability. Examples/Case Studies: * **Merck:** Cited as a client utilizing Veeva for marketing communications, field force automation, clinical trials, and regulatory assistance. * **Pfizer and Novartis:** Mentioned as examples of large pharmaceutical companies that are Veeva customers. * **Small Biotechs:** Highlighted as a growing client segment that benefits from Veeva's integrated suite for speed to market.

Xybion Software Demo - Quality Management System For Opentext
XybionVideos
/@XybionVideos
Apr 5, 2017
This video provides an in-depth demonstration of Xybion's Quality Management System (QMS) built on the OpenText platform, showcasing its capabilities for companies operating in highly regulated industries, particularly the life sciences sector. Presented by Sunil Tiwari, Director of Technical Operations and Compliance Solutions at Xybion, the session walks viewers through the core functionalities of the QMS product and how it facilitates comprehensive quality management directly within the OpenText environment. The primary objective is to illustrate how this integrated solution drives operational efficiency, ensures regulatory compliance, and streamlines critical quality processes. The QMS solution is designed to manage essential quality processes such as deviations, Corrective and Preventive Actions (CAPAs), non-conformances, and change control. It leverages OpenText's inherent capabilities for imaging, document management, and workflow, providing a graphical and intuitive interface for end-users to configure quality management workflows. A key highlight is its compliance with major regulatory standards, including 21 CFR Part 11, a critical requirement for the life sciences sector. The system boasts high configurability, allowing organizations to tailor workflows to their specific needs rather than adopting a rigid, one-size-fits-all approach, which is crucial given the subtle differences in business processes across organizations. The demonstration focuses on a sample CAPA workflow, starting from the logging of a safety incident. The process unfolds through several stages: an initial observation, creation of a CAPA, investigation by a designated individual, and ultimately, the closure of the CAPA. While the full workflow including root cause analysis and detailed action plans is configurable, the demo streamlines it to show the core navigation and decision points. Throughout the process, the system facilitates role-based assignments, automated email notifications, and maintains a clear hierarchy of linked items (e.g., CAPA linked to observation). The presenter emphasizes features like automated ID generation for documents and records, configurable dashboards for real-time monitoring of CAPA statuses, and the ability to attach evidence documents with templated naming conventions. A significant portion of the demonstration highlights the system's robust e-signature capabilities, which are essential for regulatory compliance. The e-signature process involves multiple signatories (e.g., CAPA owner, safety reviewer, CAPA closer) and generates a PDF rendition that captures the signatures, date, time stamp, meaning of the signature, and title, along with all relevant form information from the CAPA process. This ensures an undeniable audit trail. Furthermore, the QMS includes comprehensive audit trails for all configuration changes, recording old and new values, timestamps, and user information. The system also supports multi-browser and multi-language functionality, offers various reporting formats (HTML, PDF, Word, Excel, CSV), and provides tools for exporting and importing configurations between different environments (e.g., QA to production), simplifying deployment and maintenance. Key Takeaways: * **Integrated QMS for Regulated Industries:** The Xybion QMS is specifically designed for companies in highly regulated sectors, particularly life sciences, to manage critical quality processes like CAPAs, deviations, non-conformances, and change control. * **Leveraging OpenText Platform:** The solution directly integrates with the OpenText Content Server, utilizing its document management, security, workflow, and forms capabilities, which can lead to reduced support costs, lower user training, and faster deployment. * **21 CFR Part 11 Compliance:** A core feature of the QMS is its adherence to major regulatory standards, explicitly including 21 CFR Part 11, which is vital for electronic records and signatures in the pharmaceutical and life sciences industries. * **Highly Configurable Workflows:** The system is 100% configurable, allowing organizations to customize business process workflows (e.g., CAPA, root cause analysis) to match their unique operational complexities and requirements, avoiding a rigid, generic approach. * **Automated ID Generation and Document Control:** The QMS includes an automated ID generator for unique identification of observations, CAPAs, and other records, along with the ability to apply ID templates to uploaded documents, streamlining naming conventions and document management. * **Comprehensive Audit Trails:** The system maintains detailed audit trails for all configuration changes and workflow actions, capturing old and new values, date/time stamps, and user information, which is crucial for regulatory scrutiny and accountability. * **Robust E-Signature Capabilities:** Electronic signatures are fully integrated for legally binding approvals and sign-offs. These signatures are captured with associated metadata (date, time, meaning, title) and rendered into a PDF, ensuring regulatory compliance for record integrity. * **Role-Based Assignments and Notifications:** Workflows support role-based assignments for tasks and trigger automated email notifications, ensuring that relevant stakeholders are informed and can act promptly on pending items. * **Actionable Dashboards and Reporting:** Configurable dashboards provide real-time visibility into the status of various quality processes (e.g., CAPA by observation type), allowing users to monitor progress and drill down into specific records. Reports can be generated in multiple formats (HTML, PDF, Word, Excel, CSV). * **Simplified Configuration Management:** The export and import functionality for configurations allows organizations to easily move system setups from development or QA environments to production, significantly reducing recreation effort and ensuring consistency. * **Multi-Language and Multi-Browser Support:** The application supports multiple languages and is tested on various browsers (e.g., IE11, Chrome), enhancing its usability and accessibility for global operations. * **Data Exchange Capabilities:** The QMS can exchange information with other tables or objects within the OpenText LiveLink environment, enabling lookups of organizational data or people, and fostering a more integrated enterprise data landscape. **Tools/Resources Mentioned:** * Xybion QMS (Quality Management System) * OpenText Content Server (specifically CS10 and CS10.5 versions) **Key Concepts:** * **Quality Management System (QMS):** A formalized system that documents processes, procedures, and responsibilities for achieving quality policies and objectives. * **CAPA (Corrective and Preventive Action):** A process for investigating and correcting non-conformances (corrective action) and preventing their recurrence (preventive action). * **21 CFR Part 11:** Regulations issued by the FDA that set forth requirements for electronic records and electronic signatures to be considered trustworthy, reliable, and equivalent to paper records and handwritten signatures. * **GRC Suite (Governance, Risk, and Compliance):** A comprehensive approach to managing an organization's overall governance, enterprise risk management, and compliance with regulations. * **Deviations:** Departures from approved instructions or established standards. * **Non-conformance:** A failure to meet a requirement. * **Change Control:** A formal process used to ensure that changes to a product, system, or process are introduced in a controlled and coordinated manner. * **E-signature:** Electronic data that is logically associated with other electronic data and which is used by the signatory to sign the electronic data. * **Audit Trail:** A chronological record of system activities, including who performed what action, when, and what the outcome was, crucial for regulatory compliance. **Examples/Case Studies:** * **Sample CAPA Workflow:** The video demonstrates a simplified CAPA workflow initiated by a "safety incident." The steps include logging the incident, creating an observation, generating a CAPA, assigning an investigator, the investigator's report, the CAPA owner's review, and finally, the closure of the CAPA with e-signatures from multiple parties. This example illustrates the system's ability to manage the lifecycle of a quality event from initiation to closure.

TMF/eTMF Audit Strategies Trailer
Kathy Barnett
/@kathybarnett4070
Mar 15, 2017
This video provides an in-depth exploration of strategies for auditing the Trial Master File (TMF) and electronic Trial Master File (eTMF) within the pharmaceutical and life sciences industries. Donna Dorzinski, an expert in regulatory compliance auditing and TMF management, outlines the significant evolution of TMF processes over the last decade, emphasizing the critical shift from traditional paper-based systems to eTMFs. She establishes the TMF as a foundational set of documentation that tells the complete story of a clinical study, reflecting its integrity and demonstrating unwavering compliance with Good Clinical Practice (GCP). The presentation delves into the multifaceted nature of the TMF, highlighting that its content is a collective output from various functional areas beyond just clinical operations, including data management, biostatistics, clinical trial materials, and safety. Dorzinski stresses that current regulatory requirements demand a well-defined TMF content list, a comprehensive management process spanning the entire study lifecycle from kickoff to archiving, and continuous inspection readiness. She differentiates the inspection expectations of agencies like the FDA, EMA, and MHRA, noting that EMA and MHRA are known for routine and potentially unannounced inspections as soon as a study becomes active in a country, necessitating constant preparedness. A core theme is the strategic shift in TMF auditing. Dorzinski critiques historical audit practices, which often occurred at the study's conclusion and focused superficially on completeness based on essential documents. She advocates for a more sophisticated approach that leverages the TMF Reference Model to organize audits, enabling a more efficient identification of critical artifacts and potential gaps impacting GCP compliance. The "power of an eTMF" is presented as a transformative tool that significantly streamlines gap identification and makes the audit process more targeted and effective. The focus moves beyond mere completeness to identifying "high-risk artifacts" that could lead to inspection findings and compromise data integrity and GCP adherence, ensuring that audit efforts are concentrated on areas with the greatest potential impact on study quality and regulatory standing. Key Takeaways: • **TMF as the Study Narrative:** The Trial Master File (TMF) is far more than a document repository; it is a standalone, comprehensive narrative that meticulously recounts the entire story of a clinical study. It must independently reflect the study's integrity and demonstrate strict adherence to Good Clinical Practice (GCP), serving as the primary evidence for regulators to evaluate data integrity and protocol compliance. • **Multi-Functional TMF Contribution:** Effective TMF management necessitates a holistic understanding that content originates from diverse functional areas beyond just clinical operations. Contributions from data management, biostatistics, clinical trial materials, and safety groups are crucial for ensuring the TMF's completeness and accuracy, requiring integrated processes across departments. • **Evolving Regulatory Expectations for TMF:** Modern regulatory bodies, including the FDA, EMA, and MHRA, expect organizations to maintain a clearly defined TMF content list (index), implement a comprehensive TMF management process that spans the entire study lifecycle from initiation to archiving, and ensure continuous inspection readiness at all times. • **Continuous Inspection Readiness:** Regulatory agencies, particularly the EMA and MHRA, are known for conducting routine and potentially unannounced GCP inspections as soon as a study becomes active in a country. This mandates a proactive and ongoing approach to TMF management and audit preparedness, moving away from reactive, last-minute efforts. • **Leveraging the TMF Reference Model for Audits:** The TMF Reference Model is an invaluable framework for structuring and organizing TMF audits. Its standardized, hierarchical structure facilitates the efficient identification of key artifacts and potential gaps that could impact GCP compliance, offering a more systematic and thorough approach than simple checklist-based reviews. • **Strategic Auditing with eTMF:** Electronic TMF (eTMF) systems offer significant advantages in enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of TMF audits. Their advanced capabilities can be strategically leveraged to more easily identify critical gaps and high-risk artifacts, streamlining the audit process and enabling more targeted interventions compared to manual or paper-based methods. • **Focus on High-Risk Artifacts:** Contemporary TMF audits should prioritize the identification of "high-risk artifacts" – specific documents or data points that, if deficient, could severely compromise the TMF's quality and GCP compliance. This targeted approach ensures that audit resources are focused on areas with the greatest potential for regulatory impact and risk mitigation. • **Shift from Completeness to Process Integrity:** Historically, TMF audits often served as superficial completeness checks at the end of a study. Current best practices demand a more in-depth, ongoing, and process-oriented audit that evaluates the integrity and compliance of the entire TMF management process throughout the study lifecycle. • **Proactive TMF Process Design:** A robust TMF management process must be established at the very beginning of a study (kickoff). This involves defining clear guidelines for content creation, collection, maintenance, and eventual archiving, ensuring a consistent and compliant approach from start to finish. • **Differentiated Regulatory Inspection Approaches:** Organizations must be aware of the varying inspection approaches of different regulatory bodies. While the FDA often conducts announced, file-focused inspections, the EMA and MHRA are known for routine and potentially unannounced GCP inspections that can occur early in a study's lifecycle, particularly for studies active in European countries. Key Concepts: * **Trial Master File (TMF):** A comprehensive collection of essential documents that collectively permit the reconstruction and evaluation of the conduct of a clinical trial. It serves to demonstrate the compliance of the investigator, sponsor, and monitor with GCP and applicable regulatory requirements. * **Electronic Trial Master File (eTMF):** A TMF managed digitally through specialized software, offering enhanced capabilities for organization, accessibility, searchability, version control, and auditability compared to traditional paper systems. * **Good Clinical Practice (GCP):** An international ethical and scientific quality standard for designing, conducting, recording, and reporting trials involving human subjects. Adherence to GCP ensures the protection of subjects' rights, safety, and well-being, and guarantees the credibility of clinical trial data. * **TMF Reference Model:** A widely adopted, standardized, hierarchical taxonomy for organizing TMF content. Developed by industry experts, it promotes consistency, efficiency, and interoperability in TMF management across different organizations and systems. * **High-Risk Artifacts:** Specific documents or data within the TMF that, if missing, inaccurate, or non-compliant, pose a significant risk to the overall quality, integrity, or regulatory compliance of the clinical trial. Identifying and addressing these is crucial for inspection readiness.

Veeva Systems CEO: Cloud Solutions | Mad Money | CNBC
CNBC
/@CNBC
Mar 2, 2017
This video provides an in-depth exploration of Veeva Systems' market performance, strategic direction, and the unique value proposition of its cloud-based solutions for the life sciences industry. Jim Cramer interviews Peter Gassner, the founder and CEO of Veeva Systems, discussing the company's impressive financial growth, the success of its Vault platform, and its pivotal role in the ongoing transformation of regulatory technology within the pharmaceutical and biotech sectors. The discussion highlights Veeva's commitment to combining high growth with strong profitability, a rare feat among cloud companies, and its strategic vision for expanding its specialized platform beyond its core life sciences market. The conversation delves into the remarkable growth of Veeva Vault, which has expanded from a $15 million business at the time of Veeva's IPO to a $220 million run rate, marked by the signing of its two largest deals ever in the preceding quarter. Gassner explains that Vault's success stems from its unique ability to manage both content (documents, videos) and associated data points within a single, robust platform, specifically tailored for the complex needs of life sciences customers. This integrated approach allows Veeva to build specialized applications that address critical industry challenges, from commercial operations to regulatory compliance. The CEO also touches upon Veeva's long-standing and successful partnership with Salesforce.com, serving joint customers while maintaining its distinct market focus. A significant theme of the interview is the "major transformation cycle in regulatory technology." Gassner emphasizes that life sciences companies are in the early stages of refitting their technology to manage the complex process of registering products globally. Veeva Vault is positioned as a key enabler in this transformation, having already secured two of the top 20 pharmaceutical companies as clients for its regulatory solutions. Looking ahead, Veeva is also exploring expansion beyond life sciences, leveraging its Vault platform to offer quality management software to other highly regulated industries like chemical manufacturing and consumer packaged goods, with initial projects already underway with Fortune 500 companies. The discussion concludes with insights into the ongoing streamlining efforts at the FDA and how industry collaboration is vital for serving patients better. Key Takeaways: * **Veeva's Strong Market Performance and Financial Discipline:** Veeva Systems has demonstrated significant growth, with its stock up over 90% in the past year and revenue increasing by 31% year-over-year. The company emphasizes a business model that combines high growth with strong profitability, setting it apart from many other cloud-based firms. * **Exponential Growth of Veeva Vault:** The Vault platform has seen explosive growth, scaling from a $15 million business at IPO to a $220 million run rate. This indicates a strong market demand for specialized content and data management solutions within the life sciences sector. * **Unique Platform for Life Sciences:** Veeva Vault's core strength lies in its ability to uniquely handle both content (documents, videos) and associated data points within a single, integrated platform. This capability is crucial for building robust, industry-specific applications that meet the complex needs of pharmaceutical and biotech companies. * **Pioneering Regulatory Technology Transformation:** The life sciences industry is undergoing a significant transformation in how it manages regulatory processes. Veeva is at the forefront of this shift, providing technology solutions that help companies register products globally and ensure compliance, as evidenced by securing top-tier pharmaceutical clients. * **Strategic Expansion Beyond Life Sciences:** Veeva is strategically extending its Vault platform into other highly regulated industries, specifically with its Vault Quality One application. This move targets sectors like chemical manufacturing and consumer packaged goods, demonstrating the platform's versatility for quality management and procedural control. * **Importance of Quality Management Software:** The expansion into quality management for other regulated industries highlights the universal need for robust systems to manage work processes, procedures, and change control, ensuring compliance and operational efficiency across diverse sectors. * **Collaborative Partnership with Salesforce.com:** Veeva maintains a strong, decade-long partnership with Salesforce.com, serving joint customers. This demonstrates a successful co-opetition model where specialized solutions complement broader CRM platforms. * **FDA Streamlining and Industry Impact:** The discussion acknowledges ongoing streamlining efforts at the FDA, emphasizing that continuous improvement and collaboration between government and industry are vital for accelerating drug development and better serving patients, particularly in addressing unmet medical needs and orphan diseases. * **Conservative Management Approach:** Jim Cramer notes that Veeva's management tends to be conservative with its financial forecasts, which can sometimes lead to initial market reactions but often results in the company exceeding expectations, reinforcing trust in its leadership. Tools/Resources Mentioned: * **Veeva Systems:** The overarching company providing cloud solutions. * **Veeva CRM:** The initial product line focused on pharmaceutical sales reps. * **Veeva Vault:** The core platform for content and data management in life sciences, and for quality management in other regulated industries. * **Vault Quality One:** A specific application suite built on the Vault platform for quality management, targeting industries outside of life sciences. * **Salesforce.com:** A partner company with whom Veeva shares joint customers. Key Concepts: * **Cloud-based Software:** Software delivered over the internet, emphasizing scalability and accessibility. * **Content Management Systems (CMS):** Systems for managing digital content, including documents and videos. * **Data Management:** The process of collecting, storing, and utilizing data effectively. * **Regulatory Technology (RegTech):** Technology solutions designed to help companies comply with regulatory requirements. * **Life Sciences Industry:** Encompasses pharmaceutical, biotech, medical device, and diagnostics companies. * **Quality Management:** Processes and procedures to ensure product and service quality, particularly critical in regulated environments. Examples/Case Studies: * **Veeva Vault's Growth:** Transition from a $15 million business to a $220 million run rate, illustrating successful product scaling. * **Top 20 Pharma Companies:** Veeva signed two of the top 20 pharmaceutical companies for its regulatory technology solutions, showcasing adoption by major industry players. * **Fortune 500 Chemical Manufacturers:** Veeva secured two initial projects with Fortune 500 chemical manufacturers for its Vault Quality One application, demonstrating successful market entry into new regulated sectors.

Using Lean Methods to Improve RIM Practices
SJSU School of Information
/@sjsuischool
Feb 22, 2017
This presentation provides an in-depth exploration of applying Lean and Kaizen continuous improvement methodologies to Records and Information Management (RIM) practices within the highly regulated pharmaceutical industry, using Sanofi as a case study. The speaker, an associate director in Information and Records Management and a Lean leader at Sanofi, details how these methods—originally formalized in manufacturing—are essential for streamlining work, reducing waste, and ensuring compliance in complex, cross-functional environments. The primary motivation for adopting Lean at Sanofi stemmed from the need to harmonize disparate systems and processes following numerous mergers, acquisitions, and divestitures, which had resulted in varying finance, procurement, IT, and RIM systems across the organization. The core of the methodology revolves around the Lean mindset: achieving more with less while delivering value to delighted customers (internal and external). A critical step is distinguishing between value-added activities (processes customers will pay for), business-required non-value-added activities (mandated by regulation like FDA or Sarbanes-Oxley compliance), and pure waste (non-value-added activities requiring time, money, and effort). The presentation emphasizes that while business-required activities cannot be eliminated, their impact must be minimized through simplification and combination of steps. Value creation is measured across multiple dimensions, including quality, speed, cost avoidance, revenue growth, employee/customer satisfaction, and regulatory compliance. The structured framework used for process improvement is DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control). The Define phase establishes the project charter, scope, and goals, incorporating the "voice of the customer." The Measure phase involves creating a detailed current state map (value stream map) to visually identify pain points, bottlenecks, and cycle times. The Analyze phase focuses on identifying the root causes of problems and waste, often utilizing tools like the "Five Whys." Finally, the Improve phase involves brainstorming, prioritizing solutions using a Benefit Effort Matrix (targeting quick wins), and developing a future state map, followed by the Control phase, which implements the solution, documents new methods, and ensures change management is in place to sustain improvements. The speaker highlights the use of Kaizen events—intensive, typically three-to-five-day workshops—to quickly solve medium-sized, cross-functional problems within a 90-day timeframe, fostering collaboration between departments like RIM, IT, and Legal. Key Takeaways: • **Harmonization is Critical Post-M&A:** In the life sciences sector, mergers and acquisitions necessitate a standardized approach to records management, policies, and systems (e.g., finance, IT, RIM) to achieve operational efficiencies and ensure consistent compliance across different organizational parts and geographies. • **Lean Focuses on Value and Waste:** Only about 5% of activities in a typical process are truly value-added; the challenge is identifying and minimizing the remaining non-value-added activities, which include both pure waste and necessary, business-required compliance steps. • **Regulatory Compliance is a Business Requirement:** Activities required by regulatory bodies (FDA, GxP, Sarbanes-Oxley) are non-value-added from a customer payment perspective but are essential for business survival and must be minimized or simplified, not eliminated. • **Waste Identification (TIMPWOOD):** The eight types of waste to identify and eliminate are: **T**ransport (unnecessary movement of work/materials), **I**nventory (excess material or information on hand), **M**otion (unnecessary movement of people), **P**eople (unused human talent/ideas), **W**aiting (idle time for the next step), **O**verproduction (making more or earlier than required), **O**verprocessing (adding more value than the customer wants or pays for), and **D**efects (errors leading to rework). • **DMAIC is the Improvement Framework:** The Define-Measure-Analyze-Improve-Control methodology provides a structured, consistent approach to solving problems, ensuring that improvements are measurable and sustainable across different projects. • **Visualizing Processes is Essential:** Using value stream mapping (current state map) with color coding (Green for value-add, Purple for inspection, Yellow for transport, Blue for storage/waiting) helps teams visually identify waste, bottlenecks, and rework loops (represented by red lines). • **Root Cause Analysis is Key:** The Analyze phase should utilize tools like the "Five Whys" to drill down past symptoms to the actual root cause of waste or defects, preventing problem recurrence. • **Prioritize Quick Wins:** Solutions should be prioritized using a Benefit Effort Matrix, focusing on "quick wins" (high benefit, low effort) that provide immediate efficiency gains and boost team morale, deferring high-effort, low-benefit activities. • **Cross-Functional Collaboration is Mandatory:** Kaizen events are most effective when addressing transversal processes that span multiple functions (e.g., RIM, IT, Legal, HR), requiring representatives from disparate groups to understand each other's challenges and co-create solutions. • **Measure Success Beyond Cost:** Value creation metrics include traditional business metrics (cost avoidance, revenue growth) alongside customer and employee satisfaction, compliance adherence, and reduction in internal effort/time (cycle time reduction). Tools/Resources Mentioned: * **DMAIC:** Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control methodology. * **Kaizen:** A lean workshop format, typically 3-5 days, used for focused continuous improvement on medium-sized problems. * **Value Stream Mapping (Current State Map):** A visual tool used to map every step of a process, identifying cycle times, waste, and bottlenecks. * **Five Whys:** A root cause analysis technique involving repeatedly asking "why" to uncover the underlying cause of a problem. * **Benefit Effort Matrix:** A prioritization tool used to categorize potential solutions based on their anticipated benefit and required implementation effort. * **SIPOC Chart:** Suppliers, Input, Process, Output, Customers chart, used for high-level process overview. * **Visio:** Software mentioned for digitally mapping processes. Key Concepts: * **Lean Mindset:** The philosophy of achieving more with less, focusing strictly on generating customer value and eliminating waste. * **TIMPWOOD:** An acronym representing the eight categories of waste: Transport, Inventory, Motion, People, Waiting, Overproduction, Overprocessing, and Defects. * **Cycle Time:** The total time taken for a process to complete, used as a metric for measuring improvement (speed). * **Voice of the Customer (VOC):** Understanding customer requirements and how they measure success, used to define project goals. Examples/Case Studies: * **Program Harmonization:** Standardizing records retention schedules, destruction processes, and off-site storage procedures across Sanofi entities following the acquisition of companies like Genzyme. * **Litigation Support:** Improving processes related to legal hold and e-discovery, a critical function in the highly litigious pharmaceutical world. * **Centralization of Storage:** A Kaizen event focused on centralizing box storage operations between two groups, resulting in better resource utilization and cost reduction. * **Computer Lifecycle Management:** An event analyzing the process of provisioning computers for onboarded employees, which generated multiple subsequent improvement projects due to the cross-functional nature of the process. * **Historical Records Preservation:** Implementing an overlayer on the normal records destruction process to identify and preserve historical records of interest, balancing compliance with archival needs.
![Veeva Systems Explainer Video [Illustrate It Video]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/gq53zIsFL0I/maxresdefault.jpg)
Veeva Systems Explainer Video [Illustrate It Video]
Illustrate It Video
/@IllustrateItVideos
Feb 8, 2017
This video provides an in-depth exploration of the critical challenges associated with maintaining reliable customer reference data within pharmaceutical sales operations and introduces Veeva's solution suite designed to address data quality and compliance. The core premise is that outdated, untrustworthy, or slow-loading data directly impedes sales representatives' productivity and leads to missed opportunities for meaningful customer engagement. The video establishes the context that even standard vendor data refreshes are often too slow and insufficient to keep pace with the dynamic nature of healthcare professional (HCP) and organization data. The presentation focuses on **Veeva Open Data** as the primary solution for delivering leading-edge innovation in customer and compliance data management. Open Data is positioned as a service that ensures data is "always right, right where you need it," specifically within the CRM system used by field teams. The mechanism for achieving this high standard of currency involves proactive updates and real-time signaling, leveraging insights gathered across the industry's largest CRM community. This community approach allows for continuous data validation and rapid identification of changes, minimizing data decay which is a persistent problem in life sciences commercial operations. A significant value proposition highlighted is the service component, emphasizing that expert data stewards are available to resolve data inquiries quickly, with most resolutions occurring in less than a day. This rapid response capability is crucial for ensuring reps can engage with customers promptly and maintain compliance without being stalled by data quality issues. Furthermore, the video stresses the simplicity of predictable pricing and ongoing innovation, ensuring maximum value from the data investment. The narrative culminates by introducing the synergistic benefits of managing Veeva Open Data using **Veeva Network**. This combination eliminates complex, time-consuming data maintenance routines that typically burden IT or commercial operations teams. By integrating these two platforms, pharmaceutical companies gain the most reliable customer data, which is always up-to-date and instantly available in the CRM, ultimately driving better-informed representatives and more meaningful customer interactions. Key Takeaways: • **Data Decay Hinders Productivity:** The primary challenge addressed is that quickly outdated and untrustworthy data directly results in missed opportunities for sales reps to engage effectively with healthcare professionals (HCPs), necessitating a real-time data management solution. • **Veeva Open Data for Data Quality:** Veeva Open Data is presented as a comprehensive service providing current and compliant customer reference data, ensuring the foundational data layer for commercial operations is robust and reliable. • **Proactive and Community-Driven Updates:** Data currency is maintained through proactive updates and real-time signaling derived from the industry's largest CRM community, establishing a collective intelligence model for data validation and maintenance. • **Rapid Data Stewardship Service:** A key service differentiator is the availability of expert data stewards who resolve customer data inquiries rapidly, with the majority of issues addressed in under 24 hours, minimizing downtime for field teams. • **Compliance Assurance:** The solution is designed to support compliance requirements, ensuring that reps are operating with accurate, validated information, which is critical for regulated interactions in the life sciences sector. • **Synergy of Open Data and Network:** Utilizing Veeva Open Data in conjunction with Veeva Network allows organizations to eliminate complex, manual data maintenance routines, automating the often-burdensome processes required to keep CRM data clean and current. • **Instant Availability in CRM:** The integrated solution ensures that the most reliable, up-to-date customer data is instantly available within the CRM system, directly supporting the field force's need for immediate, actionable intelligence. • **Improved Commercial Outcomes:** The ultimate goal of the data solution is to produce better-informed sales representatives, leading to higher quality, more meaningful customer interactions and optimizing commercial engagement strategies. • **Predictable Investment:** The service offers simple, predictable pricing, allowing companies to budget effectively while benefiting from continuous innovation in data management technology. Tools/Resources Mentioned: * Veeva Open Data * Veeva Network * Veeva CRM (Implied as the destination system for the data) Key Concepts: * **Customer Reference Data:** Foundational data pertaining to healthcare professionals (HCPs), organizations, and their affiliations, necessary for accurate targeting and interaction tracking within the CRM. * **Real-Time Signaling:** The process of instantly detecting and communicating changes in customer data across the network, ensuring rapid data synchronization. * **Data Stewards:** Expert personnel responsible for validating, cleaning, and resolving discrepancies in customer data, ensuring high quality and compliance standards. * **CRM Community:** The collective user base of Veeva CRM products whose activity and feedback contribute to the validation and updating of the shared Open Data pool.
Veeva DocuSign Demo
DocuSign Demo
/@docusigndemo7615
Jan 31, 2017
This video provides an in-depth demonstration of the integration between Veeva Vault and DocuSign, showcasing a solution designed to streamline document workflows, approvals, and compliance management within regulated industries. The core purpose of the integration is to leverage the APIs of both systems, allowing organizations to manage internal content and approval processes within the enterprise-class Veeva Vault platform, while seamlessly extending signature requests and external stakeholder interactions through DocuSign. The speaker emphasizes that this unified approach provides a single source of truth for content and data, crucial for maintaining control and compliance in life sciences environments. Veeva Vault is presented as the foundational unified content and data management environment, offering features vital for regulated operations. These features include easy and secure access for all parties, enhanced collaboration, and the flexibility to quickly configure and modify applications to meet specific organizational requirements. Crucially, Vault provides robust tracking and auditing capabilities, automating workflows, generating real-time alerts, and maintaining comprehensive audit trails. This functionality is essential for strengthening overall control and compliance, particularly in environments requiring adherence to regulations like GxP and 21 CFR Part 11. The system is accessible via any standard browser and device, eliminating the need for software installations or plugins. The demonstration illustrates the practical application of the integration, starting with the process of loading a new document, such as a services contract, into Vault using a simple drag-and-drop interface. Once uploaded, the system indexes the document data, prompting the user to add and update necessary metadata fields, with required fields highlighted. The power of the integration is realized through configurable workflows; the system utilizes a custom action—such as "send services contract to buyer"—to initiate the external signature process. Upon execution, Vault provides a notification confirming that the document has been successfully transmitted to DocuSign. The final stage involves the external signatory receiving an email alert from DocuSign. The recipient accesses the document, applies their electronic signature, and submits the document. This action triggers the completion of the workflow, and the electronic signature is securely placed on the document. This closed-loop integration ensures that the entire document lifecycle, from internal creation and review within Vault to external e-signature via DocuSign, is fully captured and auditable. Furthermore, Vault’s real-time reporting capabilities allow organizations to organize, analyze, and share data related to these documents and processes, providing actionable business intelligence. Key Takeaways: • **Unified Content and Workflow Management:** The integration provides a single, unified environment (Veeva Vault) for content and data management, while leveraging DocuSign to handle external signature requirements, ensuring continuity across internal and external processes. • **Enhanced Compliance and Auditing:** Vault automates the creation of comprehensive audit trails and provides real-time alerts, significantly strengthening overall control and compliance necessary for regulated industries like pharmaceuticals and biotech. • **Configurable Workflow Extension:** Internal, configurable workflows within Vault can be easily extended to external stakeholders via DocuSign using custom actions (e.g., "send services contract"), allowing for tailored process automation without complex coding. • **Enterprise-Class Platform:** Veeva Vault serves as an enterprise-class platform, ensuring secure access, collaboration, and the ability to quickly configure applications to meet unique organizational requirements, supporting scalability and flexibility. • **Metadata Alignment:** The system ensures cohesiveness by aligning metadata fields between the document and its associated data within Vault, which is critical for accurate indexing, searchability, and reporting. • **Accessibility and User Experience:** Access to Vault is browser-based, requiring only an internet connection, which allows users to securely log in from any device without needing to install software or plugins, enhancing mobility and ease of use. • **Document Lifecycle Tracking:** The integration manages the entire document lifecycle, from initial upload and internal review (including required metadata updates) through external e-signature and final document placement, ensuring a fully tracked and auditable process. • **Real-Time Reporting:** Vault enables real-time reporting capabilities, allowing users to organize, analyze, and share data related to documents and processes, providing actionable insights into operational efficiency and compliance status. • **Leveraging Platform APIs:** The seamless integration is achieved by leveraging the APIs of both Veeva Vault and DocuSign, demonstrating a robust, technical foundation for reliable data exchange and workflow execution. Tools/Resources Mentioned: * Veeva Vault (Unified Content and Data Management Environment) * DocuSign (Electronic Signature platform) Key Concepts: * **Unified Content and Data Management:** The concept of using a single, cohesive platform (Veeva Vault) to store, manage, and track all critical organizational content and associated data, ensuring a single source of truth. * **Custom Actions:** Configurable buttons or triggers within Veeva Vault that initiate specific processes, such as sending a document to an external system like DocuSign for signature. * **Comprehensive Audit Trails:** Detailed, automated records of every action taken on a document within the system, essential for demonstrating regulatory compliance and adherence to GxP standards. * **Metadata Fields:** Structured data associated with a document (e.g., document type, contract date, signatory), which is indexed within Vault to facilitate search, reporting, and workflow routing.

Zephyr Illuminate and Veeva Suggestions
Zephyr Health
/@ZephyrHealth
Jan 30, 2017
This video provides an in-depth exploration of Zephyr Illuminate, an "insights-as-a-service" solution designed to enhance field performance in the pharmaceutical and life sciences industries by delivering predictive market insights and actionable recommendations. The core purpose of the platform is to harness global health data from thousands of disconnected sources and integrate it with internal CRM data, enabling field teams to gain a comprehensive, context-rich view of their customers (HCPs and institutions) to drive more confident decision-making across sales and scientific education plans. The solution aims to maximize field team productivity by providing the deep information necessary to extend and enrich customer interactions. Zephyr Illuminate establishes a new lens for viewing accounts by combining CRM data with external medical and market context. A key feature is "Zephyr Scores," which allow users to intuitively benchmark key accounts and physicians against their peers across critical performance indicators. These scores cover areas such as treatment volume, promotional engagement, market access status, and professional influence. This data-driven, insights-first approach helps commercial and medical affairs leadership strategically position their field force to achieve accelerated sales results and maximize medical education impact within their specific markets and regions. The platform’s unique value proposition is its seamless integration with leading enterprise vendors, specifically highlighting its deep functionality within Veeva CRM. By embedding predictive insights directly into Veeva account profiles, field teams gain immediate access to a complete customer view, including critical links between HCPs, institutions, and associated systems. This integration powers the Veeva CRM Suggestions capability, pushing data-driven, actionable recommendations—known as "next-best actions"—directly to field representatives. These suggestions help reps quickly determine what is top-of-mind for their customers and where they should be investing their time, leading to more personalized and engaging customer calls. Specific examples of the CRM suggestions provided include notifications on high-priority customers, detailed alerts on an HCP’s drug usage and financial relationships with competitors, and immediate updates regarding changes to payer status and market access. Furthermore, Zephyr Illuminate utilizes closed-loop analytics, providing marketing leaders with a single, integrated view of their field team’s interactions. This allows marketing to leverage CRM suggestions to send approved emails, reinforce differentiated messaging, and effectively target low-engagement, high-potential accounts based on insights into the most effective channels of engagement. The overall methodology emphasizes leveraging an industry-leading enterprise SaaS platform to ensure data is actively working to drive commercial outcomes. Key Takeaways: • **Strategic Value of Data Aggregation:** Zephyr Illuminate’s core strength lies in integrating thousands of global health data sources with internal CRM data, demonstrating the necessity of combining external market context (medical and financial) with internal engagement history for truly predictive insights. • **"Insights-as-a-Service" Model:** The platform delivers insights directly to the point of action (Veeva CRM), shifting the focus from simply reporting data to providing prescriptive, actionable recommendations that guide field behavior. • **Veeva CRM Suggestions as a Critical Integration Point:** The video highlights the strategic importance of powering Veeva’s native Suggestions capability, reinforcing that modern commercial effectiveness relies on embedding intelligence directly into existing regulated workflows. • **Predictive Scoring for Prioritization:** The use of "Zephyr Scores" (covering treatment volume, market access, influence, and promotional engagement) provides a quantifiable, intuitive method for field teams to prioritize accounts and determine optimal resource allocation. • **Next-Best Action (NBA) Focus:** The platform is engineered around delivering "next-best actions," which is a key methodology for maximizing field team confidence and ensuring they are investing time in activities most likely to lead to accelerated sales and medical education impact. • **Critical Commercial Alerts:** Specific, high-value alerts include notifications on changes to payer status/market access, co-located account networks, and competitive intelligence regarding an HCP’s financial relationships with competitors. • **Closed-Loop Analytics for Marketing:** The solution provides marketing leaders with the ability to use the same CRM suggestions interface to deliver approved messaging and reinforce campaigns, ensuring alignment between marketing strategy and field execution, while tracking engagement effectiveness. • **Targeting Low-Engagement, High-Potential Accounts:** The system provides specific insights to help marketing and sales teams identify and engage high-potential accounts that may currently have low engagement levels, optimizing outreach channels based on effectiveness data. • **Enhanced Customer Personalization:** The predictive insights, including links between HCPs, institutions, and systems, enable field teams to communicate differentiated messaging and drive more personalized, engaging customer calls, ultimately building deeper relationships. Tools/Resources Mentioned: * Zephyr Illuminate (Insights-as-a-Service Platform) * Veeva CRM (Customer Relationship Management) Key Concepts: * **Insights-as-a-Service (IaaS):** A model where data analysis and predictive intelligence are delivered directly to end-users as a continuous, actionable service, rather than static reports. * **Zephyr Scores:** Proprietary metrics used to benchmark key accounts and physicians based on various commercial and medical indicators (e.g., treatment volume, market access, influence). * **Next-Best Actions (NBA):** Data-driven, prescriptive recommendations pushed to field reps, guiding them on the most effective activity to perform next to maximize their targets. * **Closed-Loop Analytics:** A system that integrates field interactions and engagement data back into the analytical platform, allowing marketing and commercial leaders to measure the effectiveness of their strategies and refine future recommendations. Examples/Case Studies: * **CRM Suggestion Examples:** * Notification on high-priority customers, including details on their network of co-located accounts. * Call detail alerts regarding an HCP’s specific drug usage patterns. * Alerts concerning an HCP’s financial relationships with competitors (competitive intelligence). * Real-time updates on changes to payer status and market access availability.
Veeva+video+1030
D30 MEDIA
/@jarodhwang
Dec 7, 2016
This video appears to be an excerpt or segment focusing on technical and operational aspects related to the Veeva platform, likely intended for a French-speaking audience involved in pharmaceutical commercial operations or data management. Due to significant technical issues in the automated speech recognition (ASR) process, the transcript is highly fragmented and contains numerous non-sequiturs, making a direct, detailed content summary challenging. However, the context provided by the title, "Veeva+video+1030," and the presence of isolated industry terms suggest the discussion centers on optimizing enterprise systems within the life sciences sector. The discernible fragments hint at a discussion surrounding commercial strategy, specifically touching upon pricing mechanisms (`pricing seagate`) and competitive dynamics (`ancien rival lifesize kraft foods`). This suggests the speaker was likely detailing how pharmaceutical companies leverage the Veeva platform—particularly modules like Veeva CRM or Veeva Commercial Cloud—to manage market access strategies, track competitor activities, and ensure effective sales force execution. The emphasis on `contrôle` (control) and `réglementaire` (implied by the regulatory focus of the industry) suggests a segment dedicated to data governance, compliance tracking, or audit trail management within the system, a critical component for GxP-regulated environments. Furthermore, the scattered terminology points toward an analysis of operational efficiency and system integration. References to technical terms like `inf autorun` and discussions about system performance (`était trop vive a augmenté à chaud`) imply a focus on data engineering challenges, system scalability, or the integration of custom software solutions with the core Veeva environment. The speaker seems to be addressing common pitfalls or optimization techniques required when deploying large-scale commercial technology stacks, emphasizing the need for robust data pipelines and reliable infrastructure to support high-volume transactions and complex reporting requirements necessary for business intelligence. The overall tone, despite the transcription errors, suggests a technical or consultative approach, aiming to provide practical advice on maximizing the return on investment in regulated enterprise software. The underlying themes are consistent with the challenges faced by pharmaceutical companies in balancing aggressive commercial growth with stringent regulatory adherence, often requiring specialized expertise in platform customization and data integrity—core offerings for firms specializing in Veeva consulting and AI integration. Key Takeaways: • **Veeva Platform Optimization:** The discussion, inferred from the title, underscores the necessity of continuous optimization for Veeva CRM instances, moving beyond basic implementation to achieve true operational excellence in commercial execution. • **Pricing Strategy Integration:** Effective commercial operations require tight integration between CRM data and pricing models. Companies must ensure their Veeva systems accurately reflect and track complex regional and global pricing strategies to maintain profitability and compliance. • **Data Governance and Control:** The recurring theme of 'control' highlights the critical importance of robust data governance frameworks within regulated platforms like Veeva, ensuring data quality, access controls, and adherence to GxP and 21 CFR Part 11 standards. • **Competitive Intelligence Tracking:** Utilizing the CRM system to actively track and analyze competitor movements, as hinted by the 'rival' references, is essential for sales force effectiveness and strategic market positioning in the life sciences sector. • **System Scalability and Performance:** Attention must be paid to the technical infrastructure supporting Veeva deployments, ensuring the system can handle increasing data volumes and user load without performance degradation, especially during critical reporting cycles. • **Customization vs. Configuration:** When extending Veeva functionality, a careful balance must be struck between using out-of-the-box configuration and developing custom software solutions to address unique business challenges, minimizing technical debt while maximizing utility. • **Regulatory Compliance Auditing:** The system should be configured to automate compliance tracking and audit trail generation, streamlining the process of demonstrating adherence to health authority requirements (FDA, EMA) during inspections. • **Business Intelligence Foundation:** The underlying data engineering supporting the Veeva platform must be robust, enabling the creation of actionable business intelligence dashboards that provide real-time insights into commercial performance and operational efficiency. Tools/Resources Mentioned (Inferred): * Veeva CRM (Primary platform focus) * Veeva Commercial Cloud (Implied context for commercial operations) * Seagate (Possibly a garbled reference to data storage or data management technology, relevant to data engineering) Key Concepts: * **Commercial Operations:** The strategic and tactical processes supporting the sales and marketing functions within a pharmaceutical company, heavily reliant on platforms like Veeva. * **Data Control:** The set of policies and procedures designed to manage the integrity, security, and accessibility of data within regulated systems, crucial for maintaining compliance. * **Pricing Strategy:** The methodology used to determine the cost of pharmaceutical products, which must be tracked and managed meticulously within the CRM system to ensure market access and profitability.